33766 ATPase-IIA2_CaThalassiosira pseudonana
| Chromosome | Product | Transcript Start | End | Strand | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33766 | chr_4 | ATPase-IIA2_Ca | 1920560 | 1924116 | - | ATPase-IIA2_Ca |
| NCBI ID | Ensembl Genomes exon ID |
|---|---|
| 7443779 | Thaps33766.5, Thaps33766.4, Thaps33766.1, Thaps33766.3, Thaps33766.2, Thaps33766.6 |
| Expression Profile | Conditional Changes | Cluster Dendrogram | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|
Thaps_hclust_0171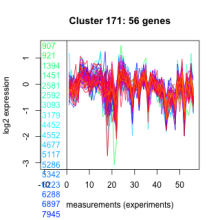 |
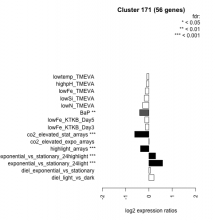 |
 |
 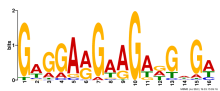 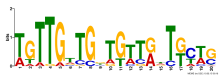 |
| T. pseudonana | P. tricornutum | P. tricornutum DiatomCyc | F. cylindrus | Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries | E. huxleyi | C. reinhardtii | A. thaliana | P. sojae |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not available | PHATRDRAFT_53964 | PHATRDRAFT_53964 | 177067 | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | 247933 |
| KEGG description | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| Not available | Not available |

Add comment