Details:
An intracellular organelle, about 200 A in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein. It is the site of protein biosynthesis resulting from translation of messenger RNA (mRNA). It consists of two subunits, one large and one small, each containing only protein and RNA. Both the ribosome and its subunits are characterized by their sedimentation coefficients, expressed in Svedberg units (symbol: S). Hence, the prokaryotic ribosome (70S) comprises a large (50S) subunit and a small (30S) subunit, while the eukaryotic ribosome (80S) comprises a large (60S) subunit and a small (40S) subunit. Two sites on the ribosomal large subunit are involved in translation, namely the aminoacyl site (A site) and peptidyl site (P site). Ribosomes from prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have characteristically distinct ribosomal proteins.
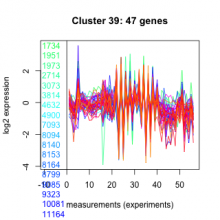
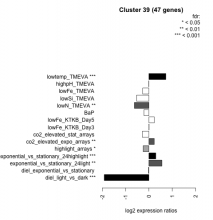
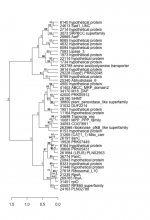


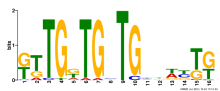


Add comment