Organism : Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 | Module List:

Motif information (de novo identified motifs for modules)
There are 2 motifs predicted.
| Motif Id | e-value | Consensus | Motif Logo |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7994 | 9.60e+00 | GaTcc.TtTC |
 |
| 7995 | 2.50e-01 | CCGGaatTCcT |
 |

Functional Enrichment
Regulon 137 is enriched for following functions.
COG Enrichment Table
| Function Name | Function Type | Unadjusted pvalue | Benjamini& Hochberg pvalue | Genes with function | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function unknown | cog subcategory | 2.74e-03 | 4.66e-03 | 6/26 | |
| Uncharacterized protein conserved in bacteria | cog | 0.00e+00 | 0.00e+00 | 3/26 |

Members for Module 137
There are 26 genes in Module 137
| Name | Common name | Type | Gene ID | Chromosome | Start | End | Strand | Description | TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSP_0413 | RSP_0413 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2148157 | 2149542 | + | two component diguanylate cyclase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0515 | RSP_0515 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2251882 | 2252958 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0516 | RSP_0516 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2252955 | 2254046 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0517 | RSP_0517 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2254046 | 2255155 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0518 | RSP_0518 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2255157 | 2256257 | - | putative glycosyltransferase protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0523 | RSP_0523 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2261634 | 2262422 | + | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_0919 | RSP_0919 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2668910 | 2669767 | + | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_1117 | RSP_1117 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2877118 | 2879298 | + | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_1120 | RSP_1120 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 2882283 | 2883584 | + | protein secretion protein, HlyD family, membrane fusion protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_1357 | RSP_1357 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 3133645 | 3136194 | + | cytoplasmic sensor hybrid histidine kinase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_1530 | RSP_1530 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 118266 | 119174 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_1821 | RSP_1821 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 410429 | 412729 | - | Molybdopterin-containing oxidoreductase, probable formate dehydrogenase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_2067 | RSP_2067 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 660237 | 661538 | - | putative prophage LambdaSo, major capsid protein, HK97 family (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_2069 | RSP_2069 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 662387 | 663637 | - | putative phage portal protein, HK97 family (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_2177 | RSP_2177 | CDS | None | chromosome 1 | 781012 | 782130 | + | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_2292 | RSP_2292 | DUMMY | None | chromosome 1 | 0 | 0 | + | None | False |
| RSP_3014 | RSP_3014 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 46296 | 47048 | - | putative aldolase protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3016 | RSP_3016 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 48026 | 48889 | - | Possible phenol degradation enzyme (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3019 | RSP_3019 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 50714 | 51388 | - | putative hydrolase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3021 | RSP_3021 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 51852 | 52766 | - | putative catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3063 | RSP_3063 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 103038 | 104378 | + | AMP-dependent synthetase and ligase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3100 | RSP_3100 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 143050 | 143562 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3427 | RSP_3427 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 495626 | 497350 | + | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3623 | RSP_3623 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 735111 | 736232 | - | putative integrase (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3763 | RSP_3763 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 893702 | 894592 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
| RSP_3791 | RSP_3791 | CDS | None | chromosome 2 | 894592 | 899766 | - | hypothetical protein (NCBI) | False |
Help
What is a module?
Regulatory units (modules) in the Network Portal are based on the network inference algorithm used. For the current version, modules are based on cMonkey modules and Inferelator regulatory influences on these modules. More specifically, module refers to set of genes that are conditionally co-regulated under subset of the conditions. Identification of modules integrates co-expression, de-novo motif identification, and other functional associations such as operon information and protein-protein interactions.
Module Overview
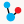
The landing module page shows quick summary info including co-expression profiles, de-novo identified motifs, and transcription factors and/or environmental factors as regulatory influences. It also includes module residual, motif e-values, conditions and links to other resources such as NCBI and Microbesonline. . If a transcription factor is included in the manually curated RegPrecise database, further information from RegPrecise is shown, allowing users to perform comparative analysis.
Expression Profiles
Expression profiles is a plot of the expression ratios (log10) of the module's genes, over all subset of the conditions included in the module. The X-axis represent conditions and the Y-axis represents log10 expression ratios. Each gene is plotted as line plot with different colors. Colored legend for the lines are presented under the plot. This plot is dynamic. Clicking on the gene names in the legend will show/hide the plot for that particular gene. A tooltip will show expression ratio information if you mouseover the lines in the plot.
Motif Locations
Location of the Identified motifs for the module in the upstream regions of the member genes are shown under the expression profiles plot. This plot shows the diagram of the upstream positions of the motifs, colored red and green for motifs #1, and 2, respectively. Intensity of the color is proportional to the significance of the occurence of that motif at a given location. Motifs on the forward and reverse strand are represented over and under the line respectively.
Network
A network view of the module is created using cytoscapeWeb and enables dynamic, interactive exploration of the module properties. In this view, module member genes, motifs, and regulatory influences are represented as peripheral nodes connected to core module node via edges. Module members are green circles, regulators are red triangles and motifs are blue diamonds. Selection of a node gives access to detailed information in a pop-up window, which allows dragging and pinning to compare multiple selections. Selecting module members will show information about the selected gene such as name, species and fucntions. Motif selection will show motif logo image and e-values. Bicluster selction will show expression profile and summary statistics for the module.
 Module member
Module member 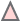 Regulator
Regulator  Motif
Motif
Regulators
For each module, single or AND logic connected regulatory influences are listed under the regulators tab. These regulatory influences are identified by Inferelator. Table shows name of the regulator and its type. tf: Transcription factor, ef: Environmental factor and combiner:Combinatorial influence of a tf or an ef through logic gate. Tabel is sortable by clicking on the arrows next to column headers.
Motifs
Transcription factor binding motifs help to elucidate regulatory mechanism. cMonkey integrates powerful de novo motif detection to identify conditionally co-regulated sets of genes. De novo predicted motifs for each module are listed in the module page as motif logo images along with associated prediction statistics (e-values). The main module page also shows the location of these motifs within the upstream sequences of the module member genes.
Motifs of interest can be broadcasted to RegPredict (currently only available for Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough) in order to compare conservation in similar species. This integrated motif prediction and comparative analysis provides an additional checkpoint for regulatory motif prediction confidence.
Functions
Biological networks contain sets of regulatory units called functional modules that together play a role in regulation of specific functional processes. Connections between different modules in the network can help identify regulatory relationships such as hierarchy and epistasis. In addition, associating functions with modules enables putative assignment of functions to hypothetical genes. It is therefore essential to identify functional enrichment of modules within the regulatory network.
Functional annotations from single sources are often either not available or not complete. Therefore, we integrated KEGG pathway, Gene Ontology, TIGRFam and COG information as references for functional enrichment analysis.
We use hypergeometric p-values to identify significant overlaps between co-regulated module members and genes assigned to a particular functional annotation category. P-values are corrected for multiple comparisons by using Benjamini-Hochberg correction and filtered for p-values ≤ 0.05.
Network Portal presents functional ontologies from KEGG, GO, TIGRFAM, and COG as separate tables that include function name, type, corrected and uncorrected hypergeometric p-values, and the number of genes assigned to this category out of total number of genes in the module.
Genes
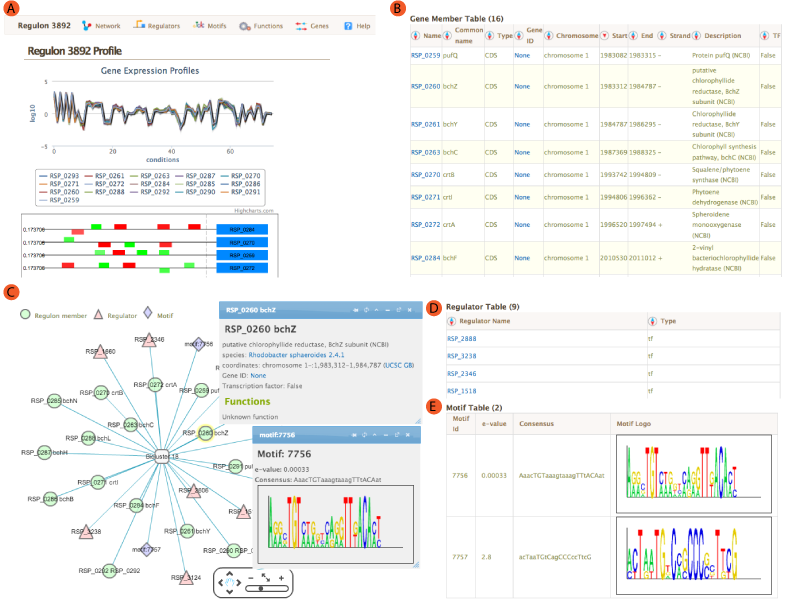
Gene member table shows all the genes included in the module. Listed attributes are;
- Name: Gene name or Locus tag
- Common Name: Gene short name
- Type: Type of the feature, usually CDS.
- Gene ID: Link to NCBI Gene ID
- Chromosome: Chromosome name from annotation file
- Start/End:Feature start and end coordinates
- Strand: strand of the gene
- Description: Description of the gene from annotation file
- TF: If the gene is a Transcription Factor or not.
If you are browsing the Network Portal by using Gaggle/Firegoose, firegoose plugin will capture the NameList of the gene members. Captured names can be saved into your Workspace by clicking on "Capture" in the firegoose toolbar or can be directly sent other desktop and web resources by using "Broadcast" option.
Definitions
Residual: is a measure of bicluster quality. Mean bicluster residual is smaller when the expression profile of the genes in the module is "tighter". So smaller residuals are usually indicative of better bicluster quality.
Expression Profile: is a preview of the expression profiles of all the genes under subset of conditions included in the module. Tighter expression profiles are usually indicative of better bicluster quality.
Motif e-value: cMonkey tries to identify two motifs per modules in the upstream sequences of the module member genes. Motif e-value is an indicative of the motif co-occurences between the members of the module.Smaller e-values are indicative of significant sequence motifs. Our experience showed that e-values smaller than 10 are generally indicative of significant motifs.
Genes: Number of genes included in the module.
Functions: We identify functional enrichment of each module by camparing to different functional categories such as KEGG, COG, GO etc. by using hypergeometric function. If the module is significantly enriched for any of the functions, this column will list few of the these functions as an overview. Full list of functions is available upon visiting the module page under the Functions tab.



Social
You can start a conversation about this module or join the existing discussion by adding your comments. In order to be able to add your comments you need to sign in by using any of the following services;Disqus, Google, Facebook or Twitter. For full compatibility with other network portal features, we recommend using your Google ID.