8253 Lipase superfamilyThalassiosira pseudonana
| Chromosome | Product | Transcript Start | End | Strand | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8253 | chr_10 | Lipase superfamily | 101874 | 104313 | + | Lipase superfamily |
| NCBI ID | Ensembl Genomes exon ID |
|---|---|
| 7451032 | Thaps8253.3, Thaps8253.2, Thaps8253.1 |
| Expression Profile | Conditional Changes | Cluster Dendrogram | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|
Thaps_hclust_0261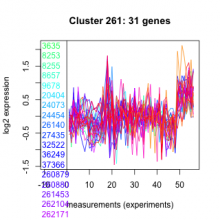 |
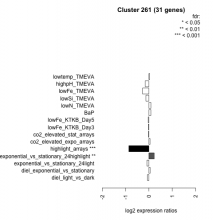 |
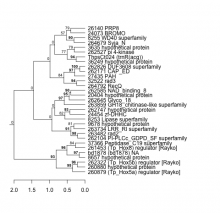 |
   |
| KEGG description | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| Not available | Not available |

Add comment