Details:
A ribonucleoprotein particle of 325 kDa composed of a 7S (300 nucleotide) RNA molecule and a complex of six different polypeptides. This binds both to the N-terminal signal peptide for proteins destined for the endoplasmic reticulum as they emerge from the large ribosomal subunit and also to the ribosome. This binding arrests further translation thereby preventing the proteins from being released into the cytosol. The SRP-ribosome complex then diffuses to the endoplasmic reticulum where it is bound to the signal recognition particle receptor, which allows resumption of protein synthesis and facilitates the passage of the growing polypeptide chain through the translocon. Through a process involving GTP hydrolysis, the SRP-SRP receptor complex dissociates and SRP returns to the cytosol. Of the six polypeptides of SRP the 54 kDa subunit (SRP54) is the central player. It contains an N-terminal GTPase domain and a C-terminal domain that binds directly to the signal peptide and the SRP RNA. Examples of this component are found in Mus musculus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Arabidopsis thaliana.



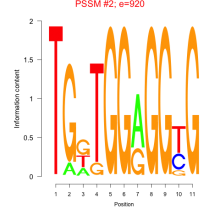

Add comment