Details:
A nearly universal metabolic pathway in which the acetyl group of acetyl coenzyme A is effectively oxidized to two CO2 and four pairs of electrons are transferred to coenzymes. The acetyl group combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, which undergoes successive transformations to isocitrate, 2-oxoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, succinate, fumarate, malate, and oxaloacetate again, thus completing the cycle. In eukaryotes the tricarboxylic acid is confined to the mitochondria. See also glyoxylate cycle.
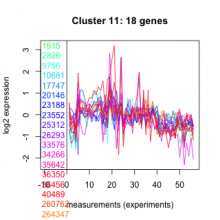
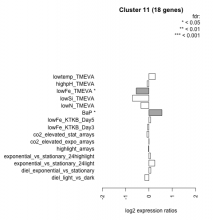
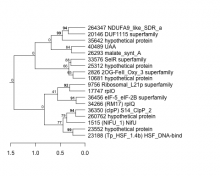

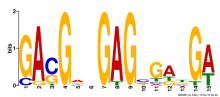
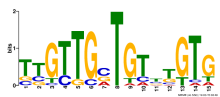
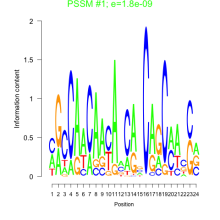
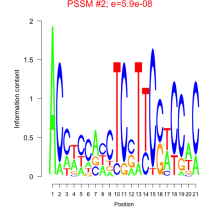

Add comment