1083 MATE_eukaryoticThalassiosira pseudonana
| Chromosome | Product | Transcript Start | End | Strand | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1083 | chr_1 | MATE_eukaryotic | 618788 | 620578 | - | MATE_eukaryotic |
| NCBI ID | Ensembl Genomes exon ID |
|---|---|
| 7449757 | Thaps1083.2, Thaps1083.3, Thaps1083.1 |
| Expression Profile | Conditional Changes | Cluster Dendrogram | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|
Thaps_hclust_0266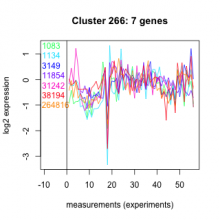 |
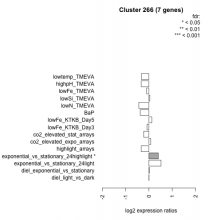 |
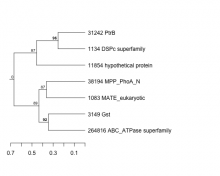 |
   |
| Normalized Mean Residue | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs | |
|---|---|---|
|
Thaps_bicluster_0024 |
0.39 |
| T. pseudonana | P. tricornutum | P. tricornutum DiatomCyc | F. cylindrus | Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries | E. huxleyi | C. reinhardtii | A. thaliana | P. sojae |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not available | PHATRDRAFT_48159 | PHATRDRAFT_48159 | Not available | Not available | 213895 | Cre14.g610750.t1.1 | AT1G71140.1 | Not available |
| KEGG description | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| Not available | Not available |

Add comment