264285 crotonase-likeThalassiosira pseudonana
| Chromosome | Product | Transcript Start | End | Strand | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 264285 | chr_15 | crotonase-like | 291824 | 292879 | - | crotonase-like |
| Expression Profile | Conditional Changes | Cluster Dendrogram | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|
Thaps_hclust_0007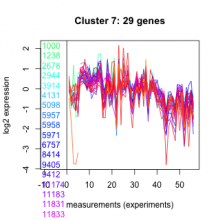 |
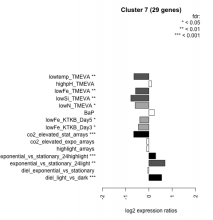 |
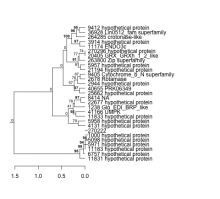 |
   |
| Normalized Mean Residue | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs | |
|---|---|---|
|
Thaps_bicluster_0104 |
0.31 |
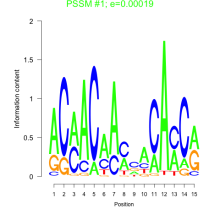 0.00019 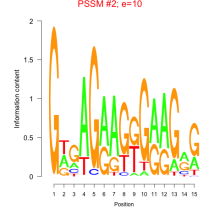 10 |
| KEGG description | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| Not available | Not available |

Add comment