Module Detail Page
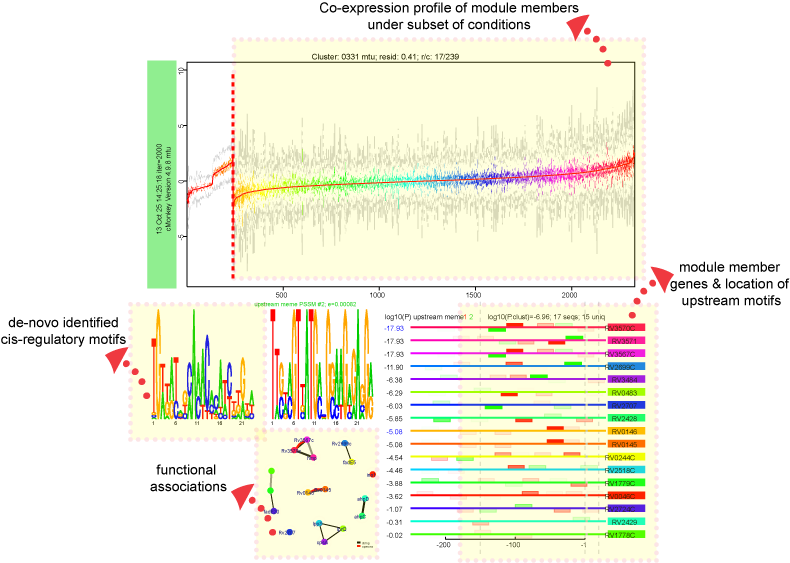
Regulatory module (bicluster) refers to set of genes that are conditionally co-regulated under subset of the conditions. Identification of modules integrates co-expression, de-novo motif identification, and other functional associations such as operon information and protein-protein interactions. Modules are based on cMonkey algorithm and Inferelator regulatory influences on these modules.
The landing module page shows quick summary info including co-expression profiles, de-novo identified motifs, and transcription factors as regulatory influences.
Expression Profiles :
Expression profiles is a plot of the expression ratios (log10) of the module's genes, over all subset of the conditions included in the module. The X-axis represent conditions and the Y-axis represents log10 expression ratios. Each gene is plotted as line plot with different colors. Colored legend for the lines are presented under the plot.
Motifs:
De novo predicted motifs for each module are listed in the module page as motif logo images along with associated prediction statistics (e-values). The main module page also shows the location of these motifs within the upstream sequences of the module member genes.
Motif Locations:
Location of the Identified motifs for the module in the upstream regions of the member genes are shown under the expression profiles plot. This plot shows the diagram of the upstream positions of the motifs, colored red and green for motifs #1, and 2, respectively. Intensity of the color is proportional to the significance of the occurence of that motif at a given location. Motifs on the forward and reverse strand are represented over and under the line respectively.
Functions:
Biological networks contain sets of regulatory units called functional modules that together play a role in regulation of specific functional processes. Connections between different modules in the network can help identify regulatory relationships such as hierarchy and epistasis. In addition, associating functions with modules enables putative assignment of functions to hypothetical genes. It is therefore essential to identify functional enrichment of modules within the regulatory network.
We use hypergeometric p-values to identify significant overlaps between co-regulated module members and genes assigned to a particular Gene Ontology category. P-values are corrected for multiple comparisons by using Benjamini-Hochberg correction and filtered for p-values ≤ 0.05.















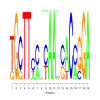
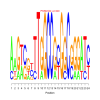
Discussion