Details:
Any process involved in the assembly of the RNA polymerase preinitiation complex (PIC) at the core promoter region of a DNA template, resulting in the subsequent synthesis of RNA from that promoter. The initiation phase includes PIC assembly and the formation of the first few bonds in the RNA chain, including abortive initiation, which occurs when the first few nucleotides are repeatedly synthesized and then released. The initiation phase ends just before and does not include promoter clearance, or release, which is the transition between the initiation and elongation phases of transcription.

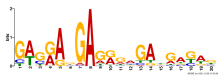
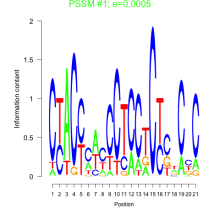


Add comment