37376 (MYO6) MYScThalassiosira pseudonana
| Chromosome | Product | Transcript Start | End | Strand | Short Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37376 | chr_14 | (MYO6) MYSc | 584339 | 589861 | + | MYSc |
| NCBI ID | Ensembl Genomes exon ID |
|---|---|
| 7451254 | Thaps37376.3, Thaps37376.1, Thaps37376.2 |
| Expression Profile | Conditional Changes | Cluster Dendrogram | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs |
|---|---|---|---|
Thaps_hclust_0377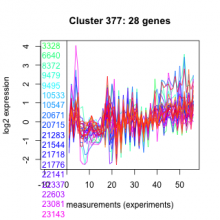 |
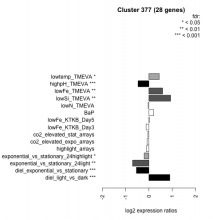 |
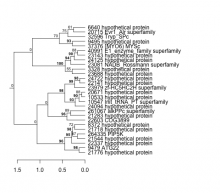 |
 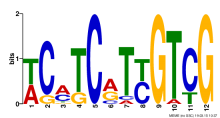 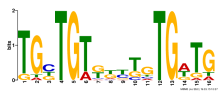 |
| Normalized Mean Residue | Discovered Potential cis-Regulatory Motifs | |
|---|---|---|
|
Thaps_bicluster_0010 |
0.38 |
 14000000  370 |
| KEGG description | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| Not available | Not available |

Add comment