Module 127
Summary
| Residual | Gene Count | Condition Count | 1st Q Condition Block * | 5th Q Condition Block * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.43 | 27 | 61 | In vivo vs. In vitro | NA |
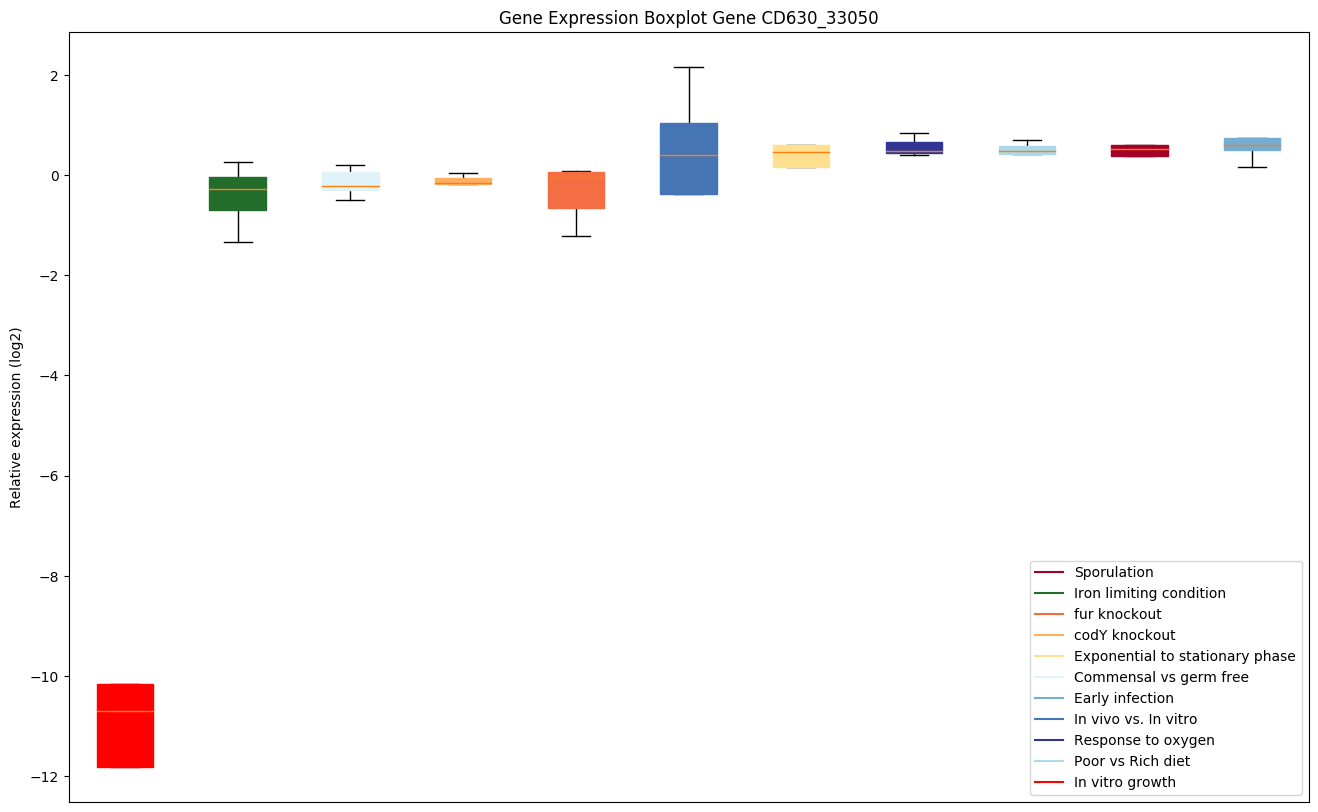
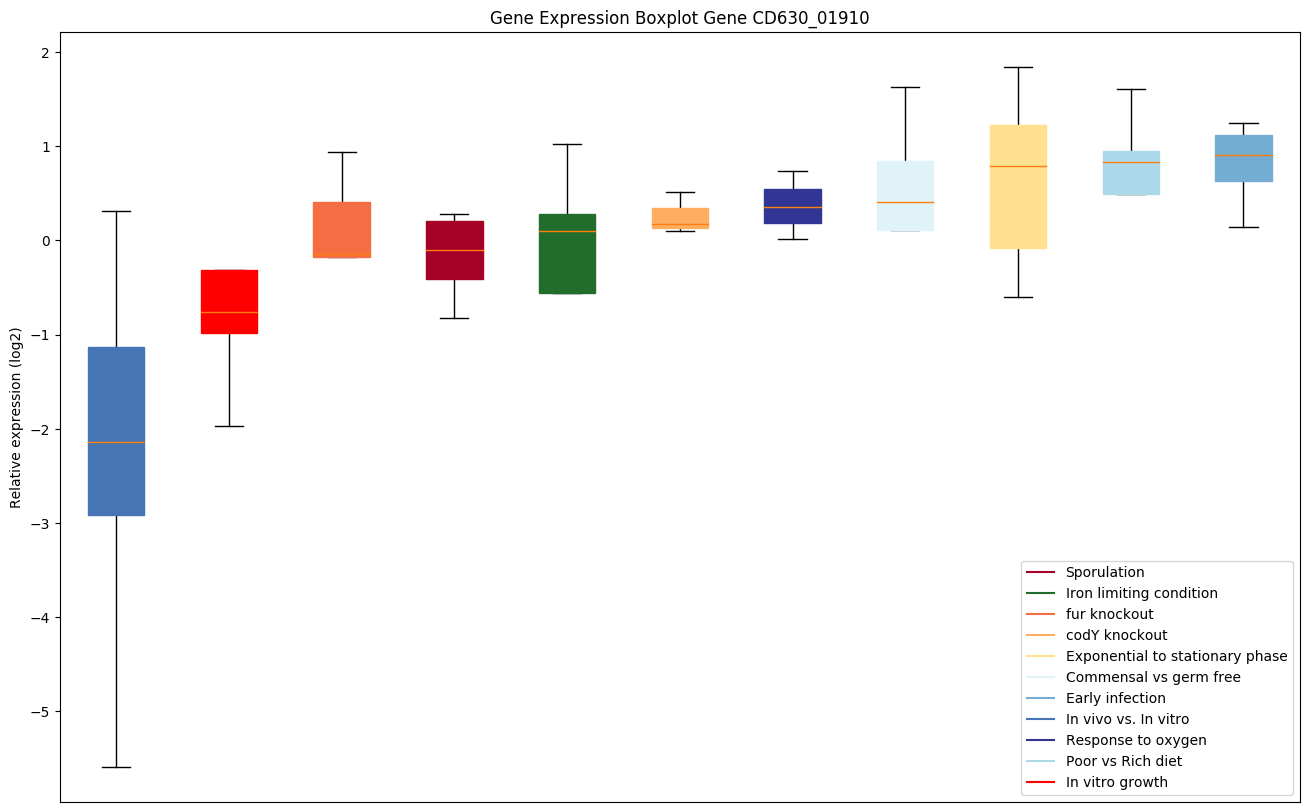
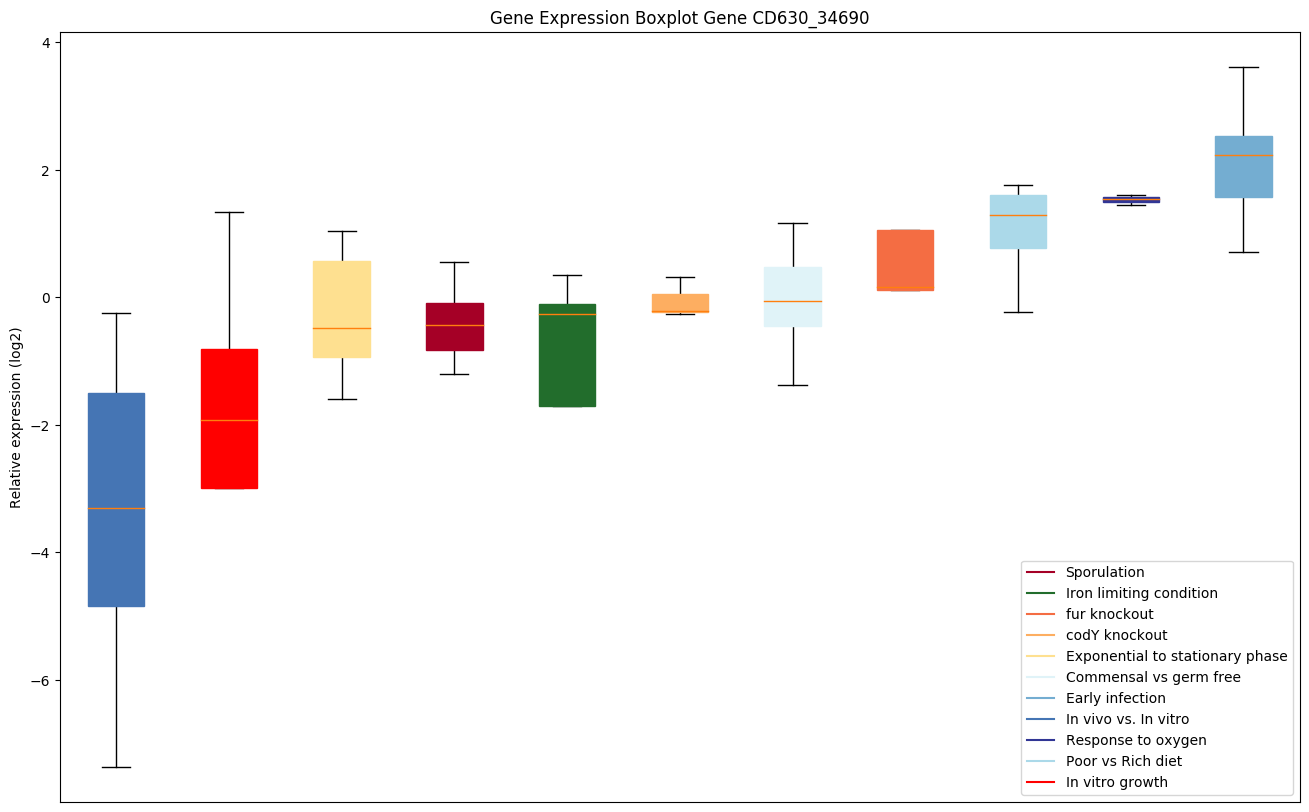
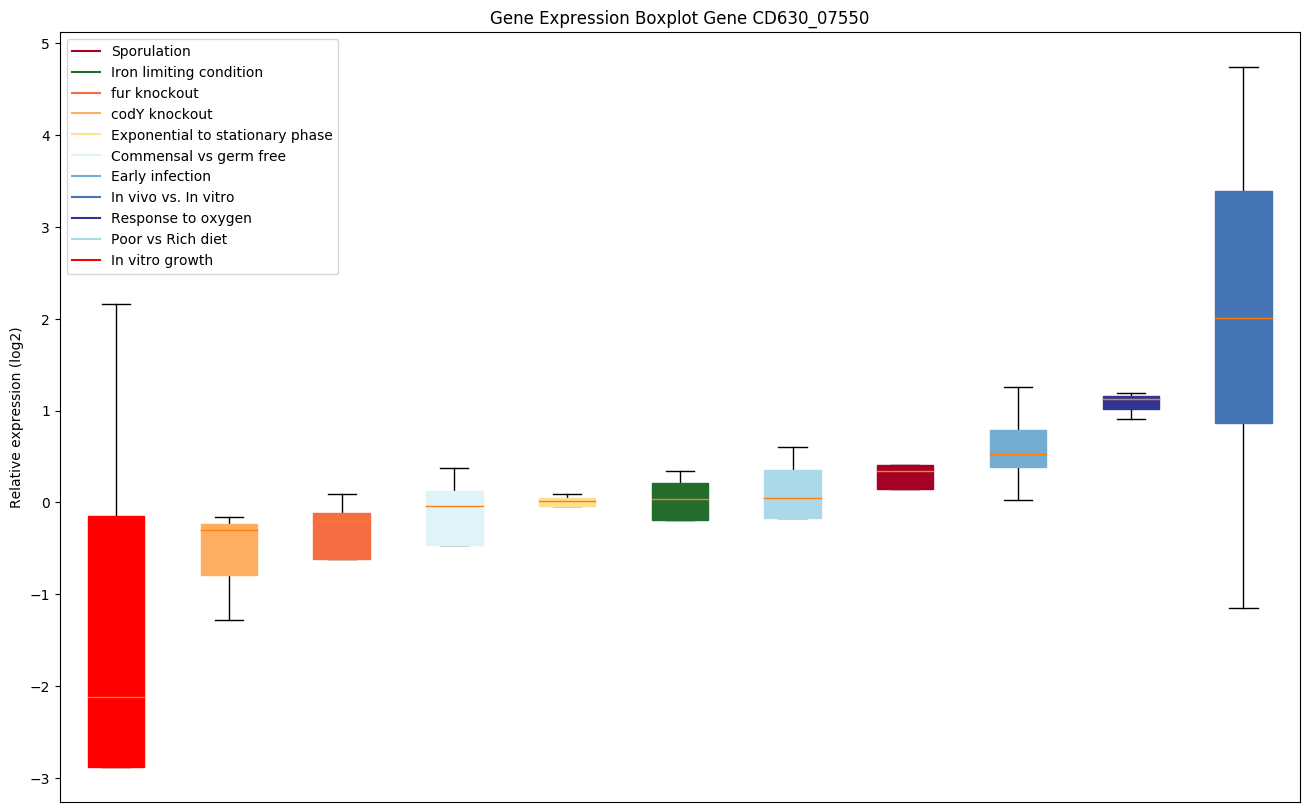
Bicluster expression profile
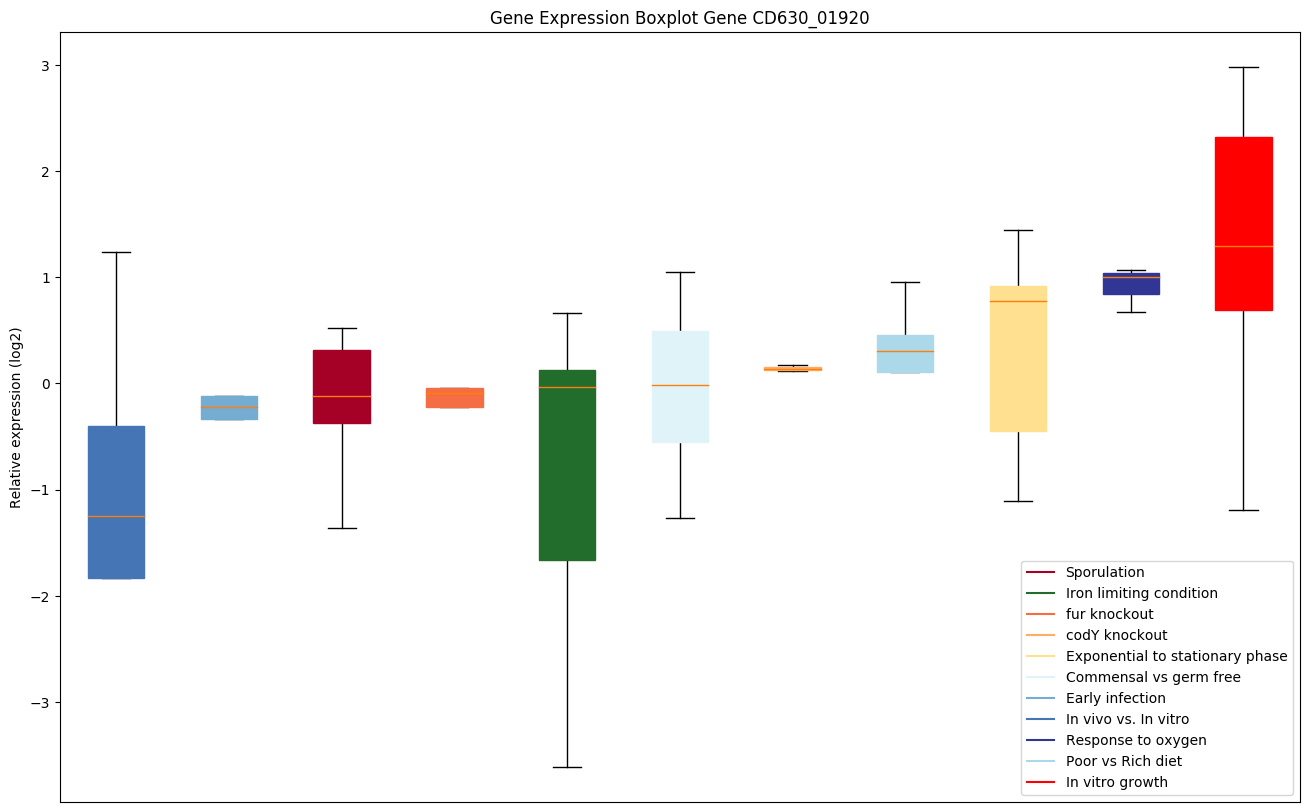
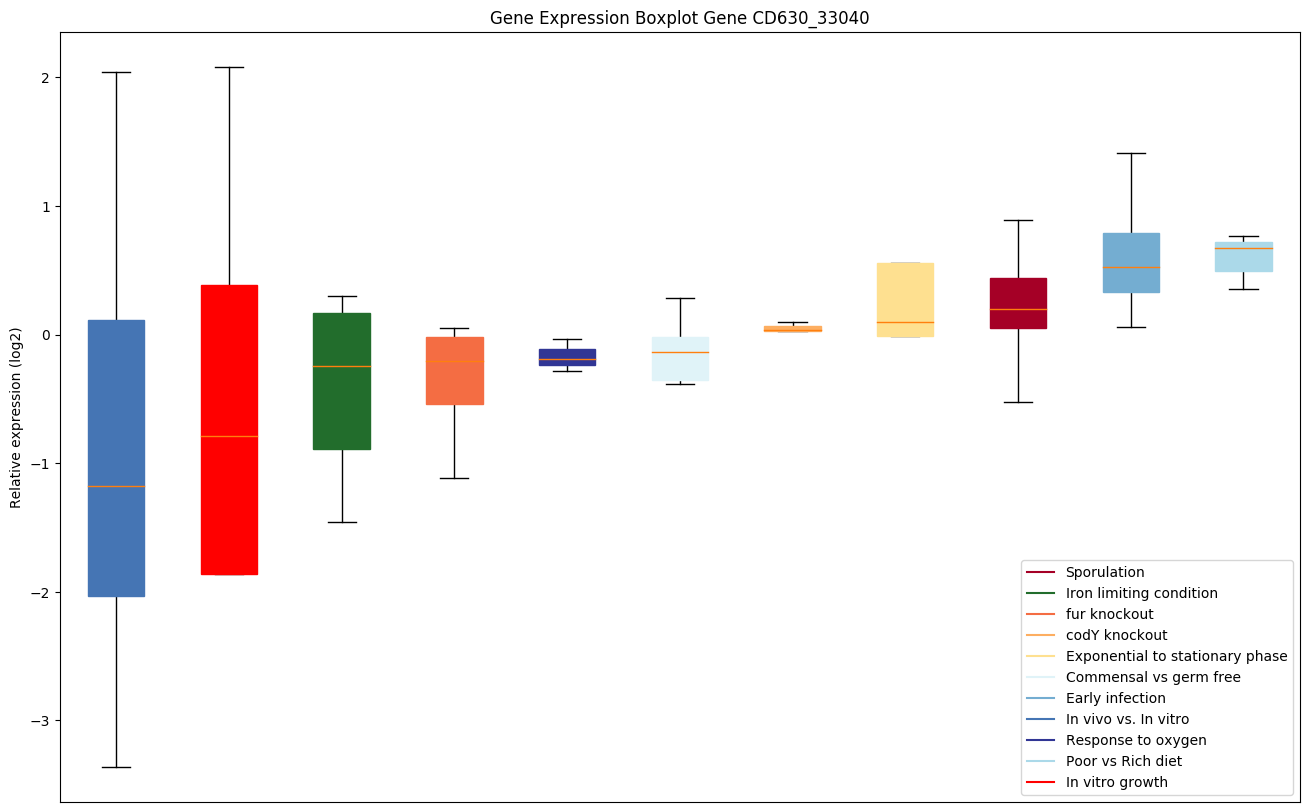
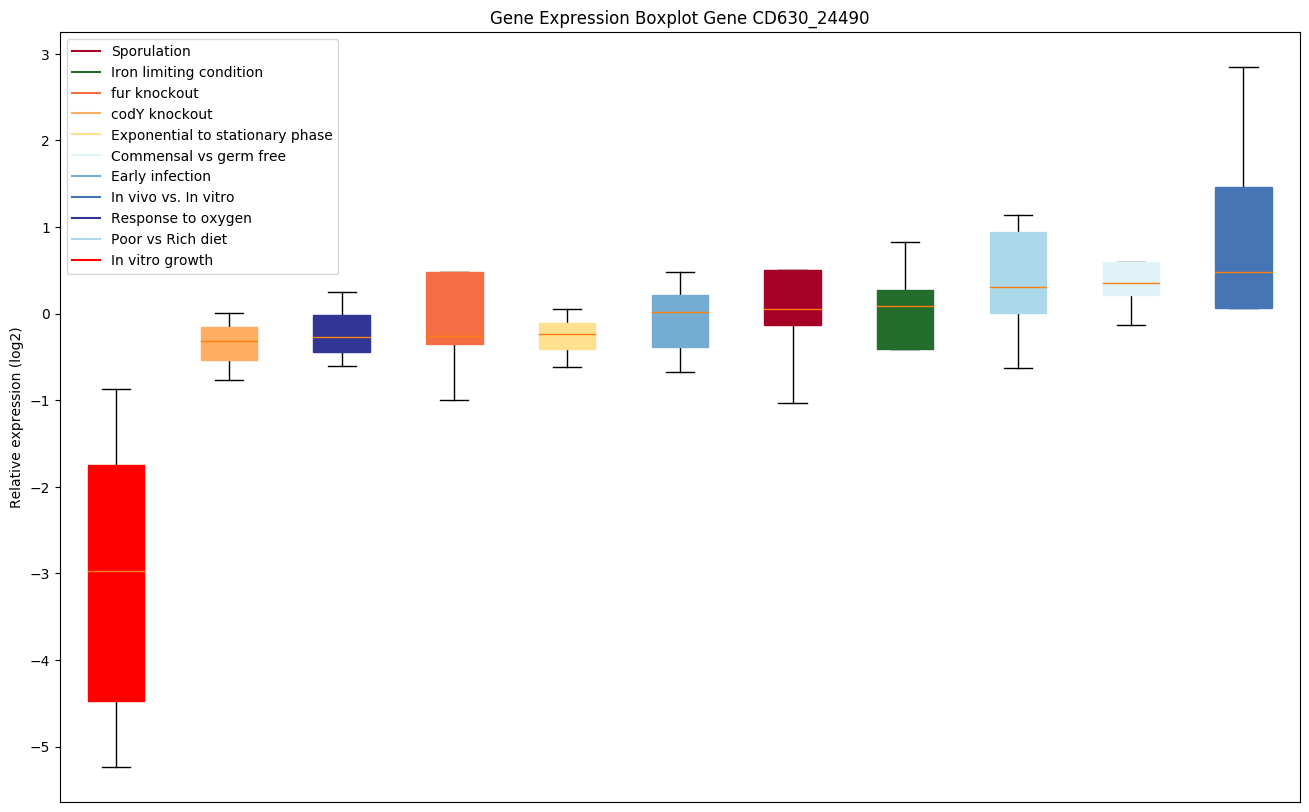
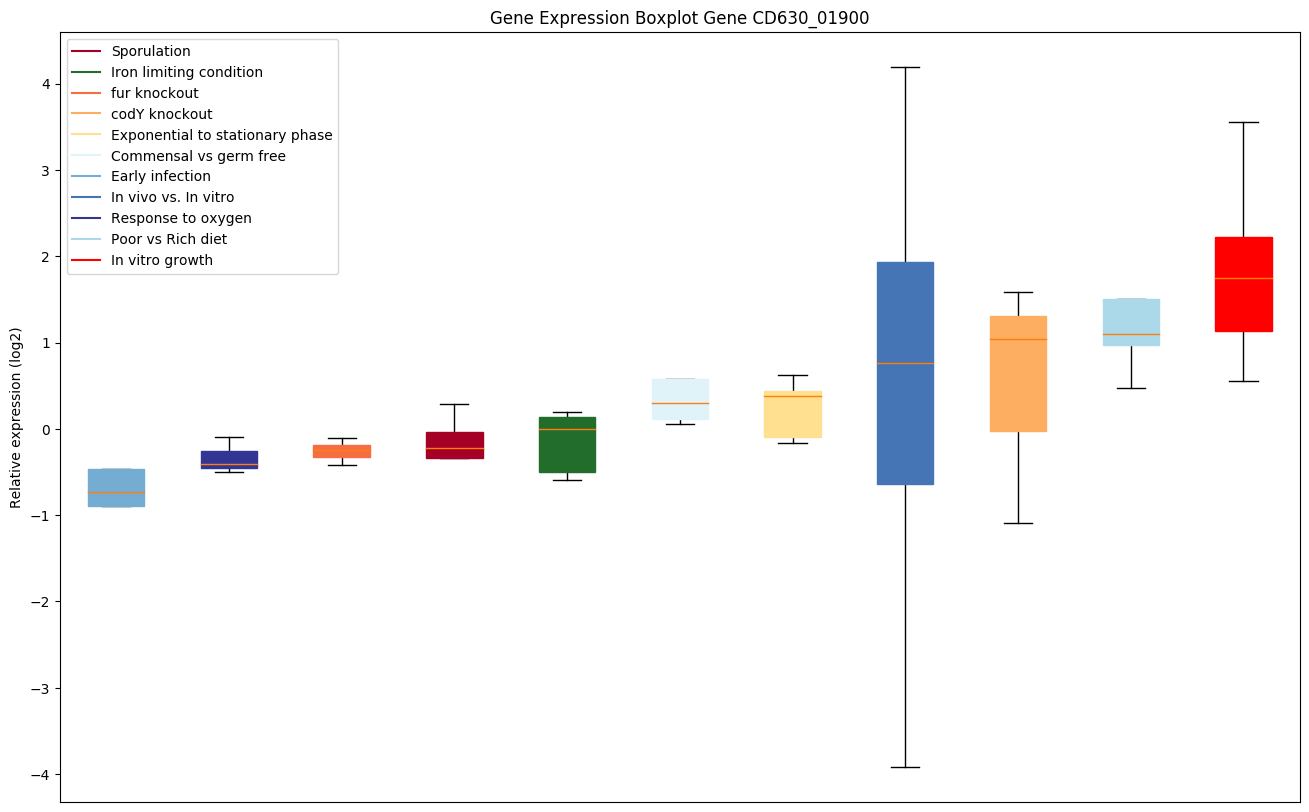
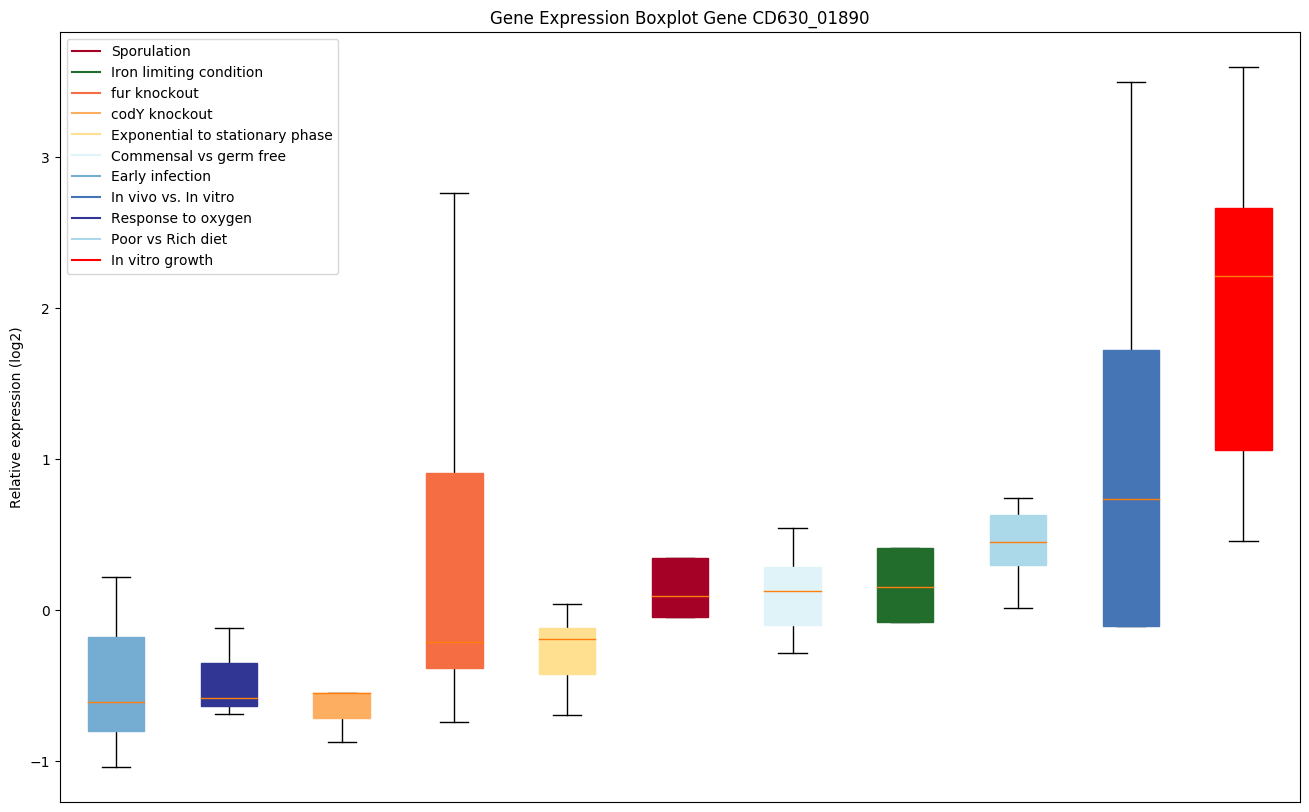
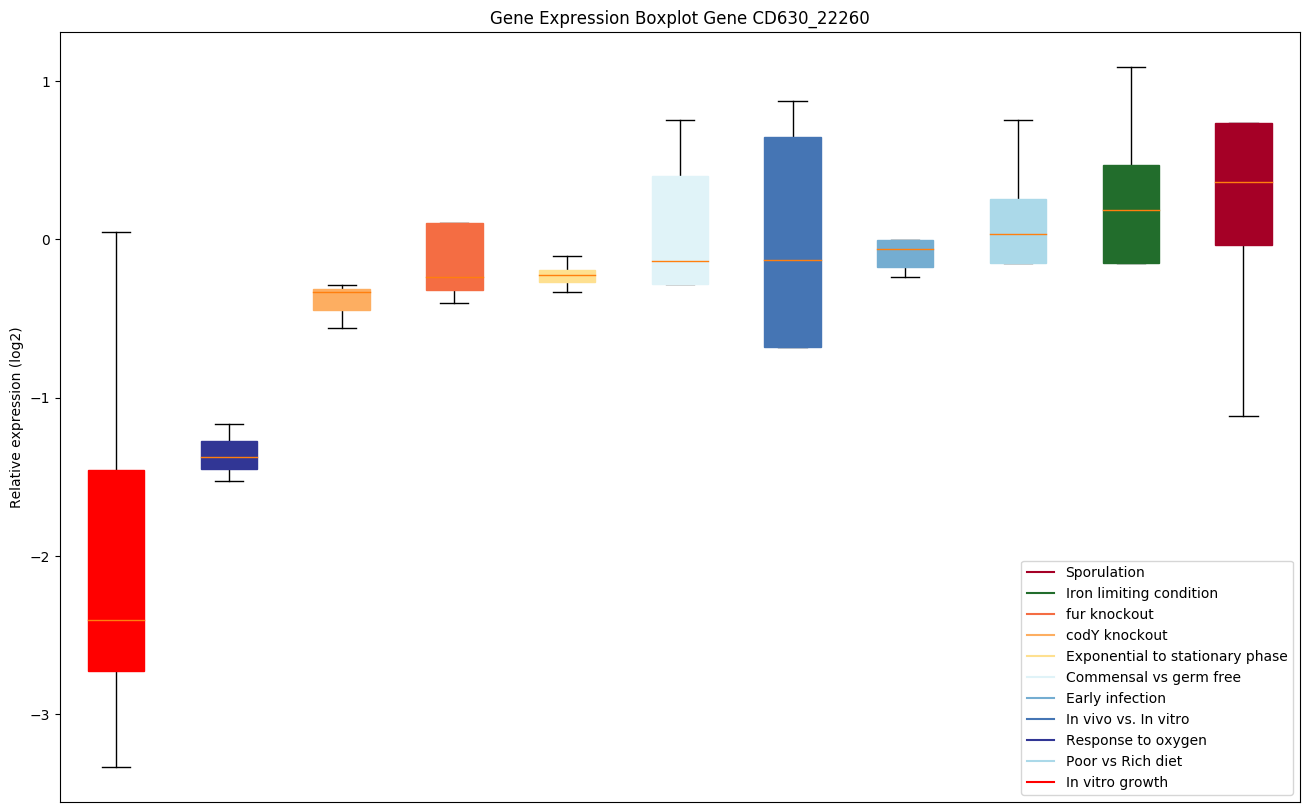
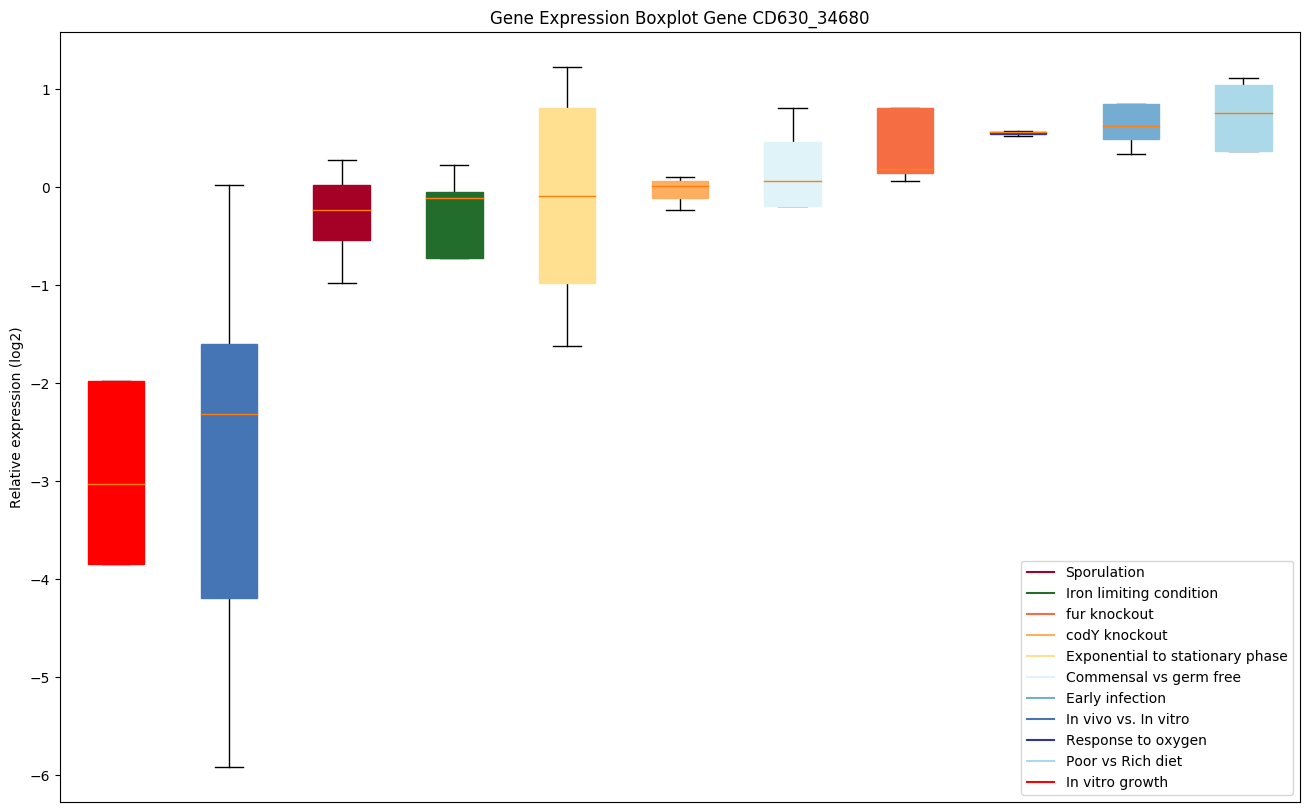
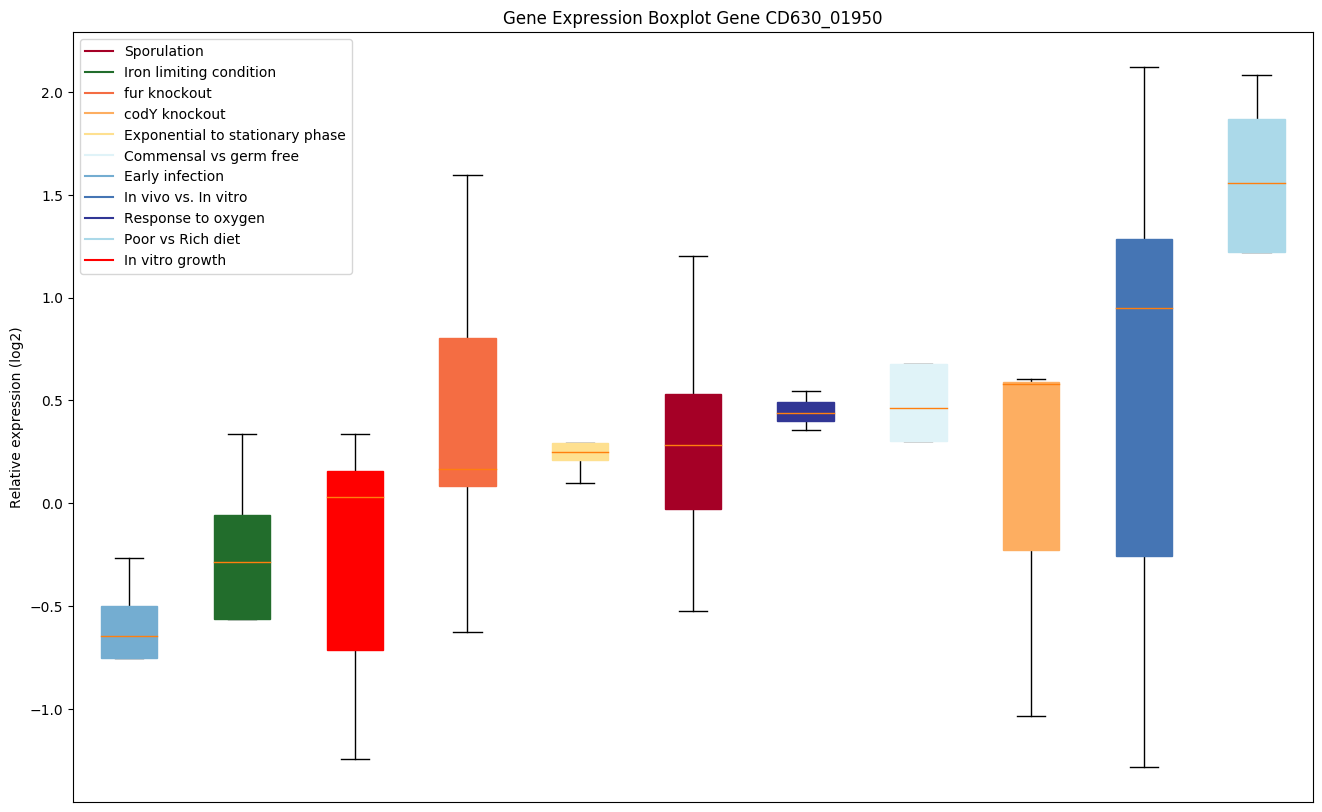
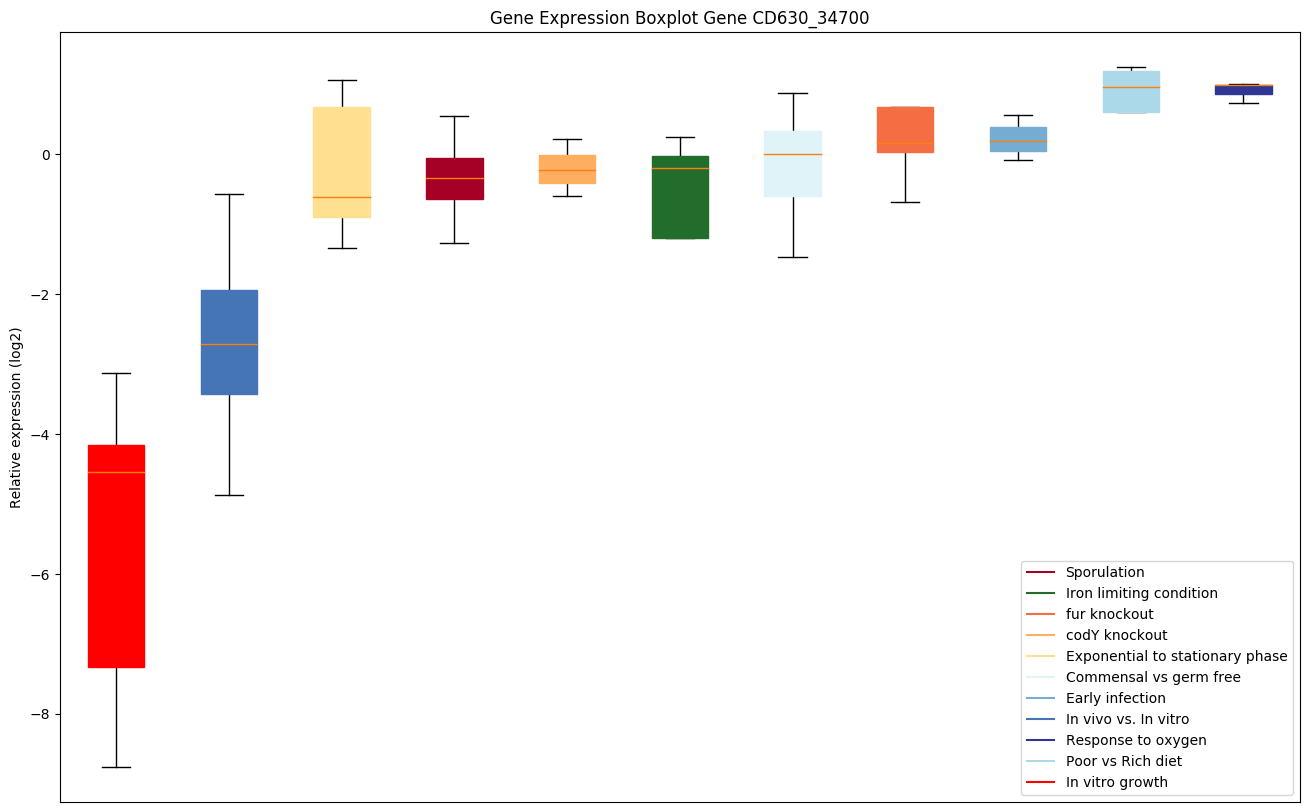
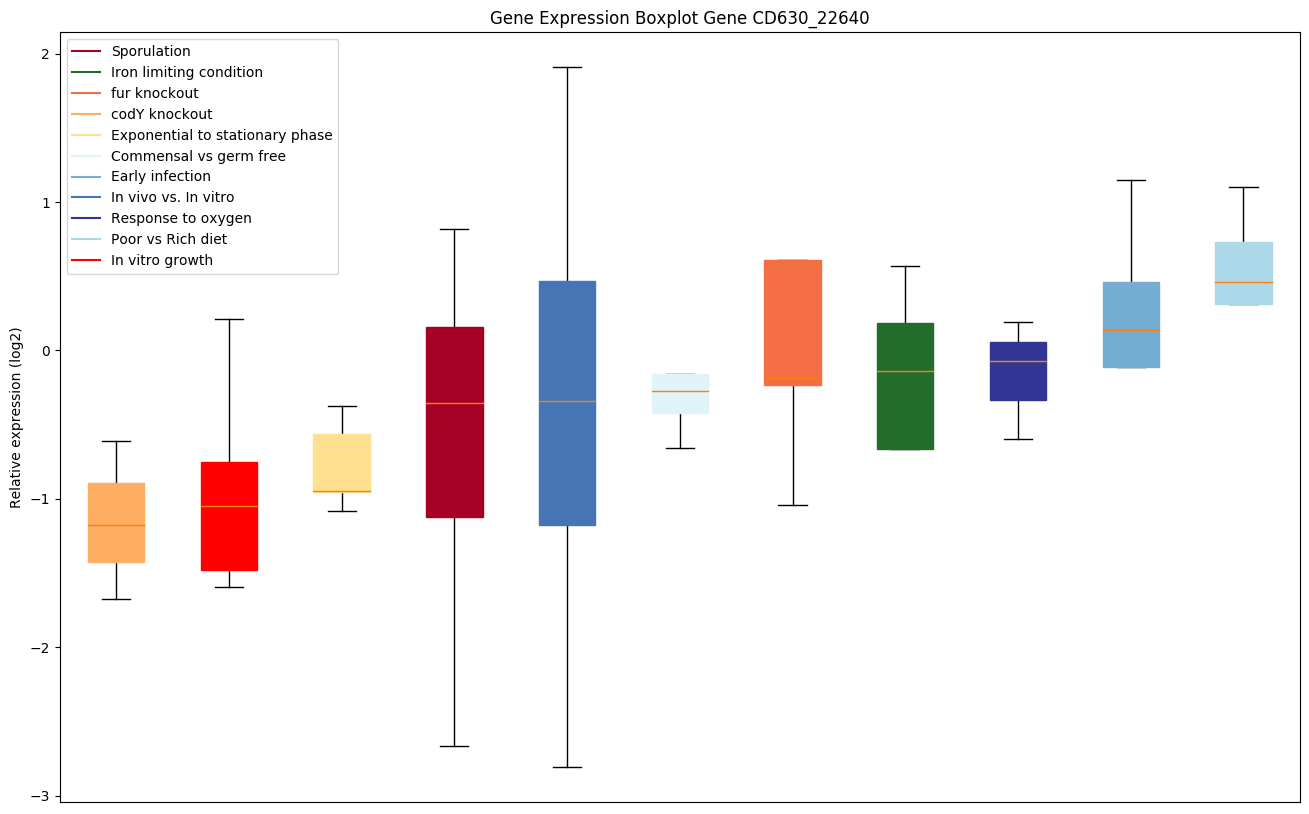
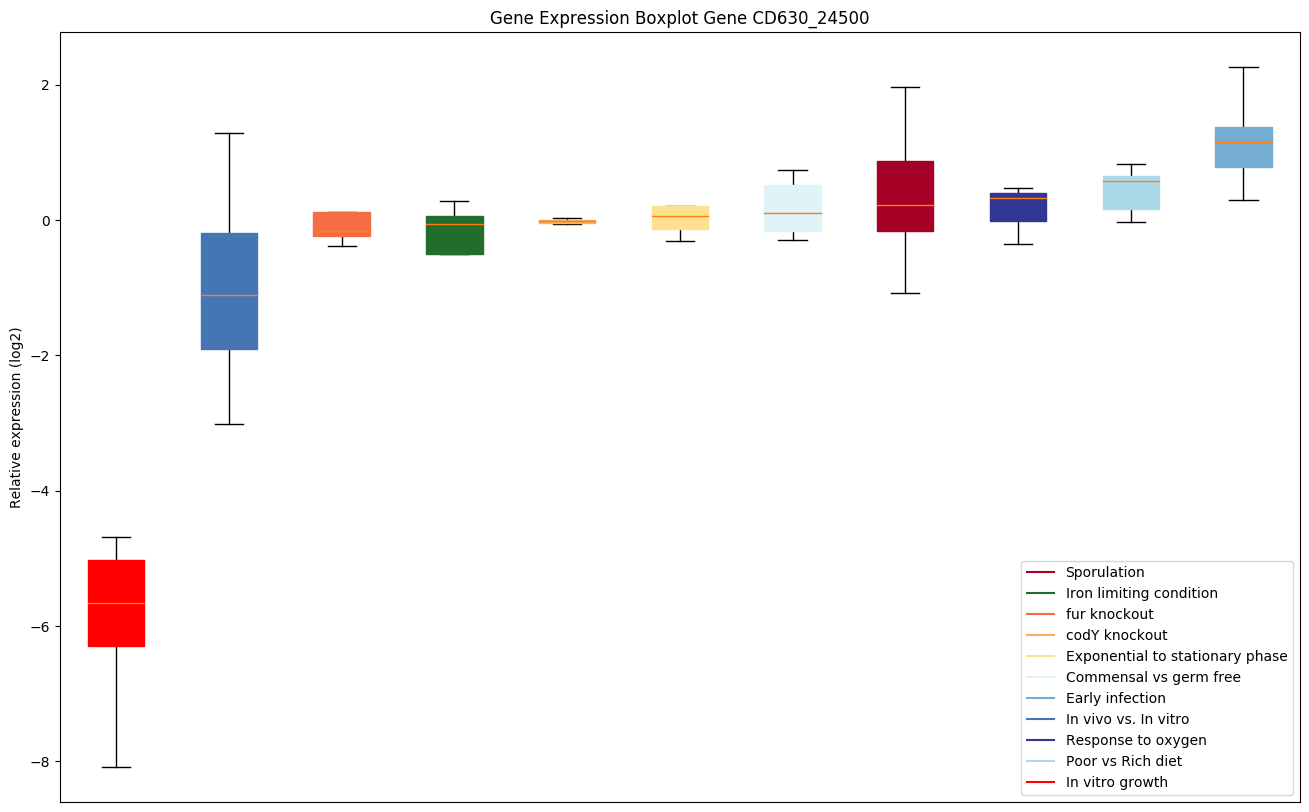
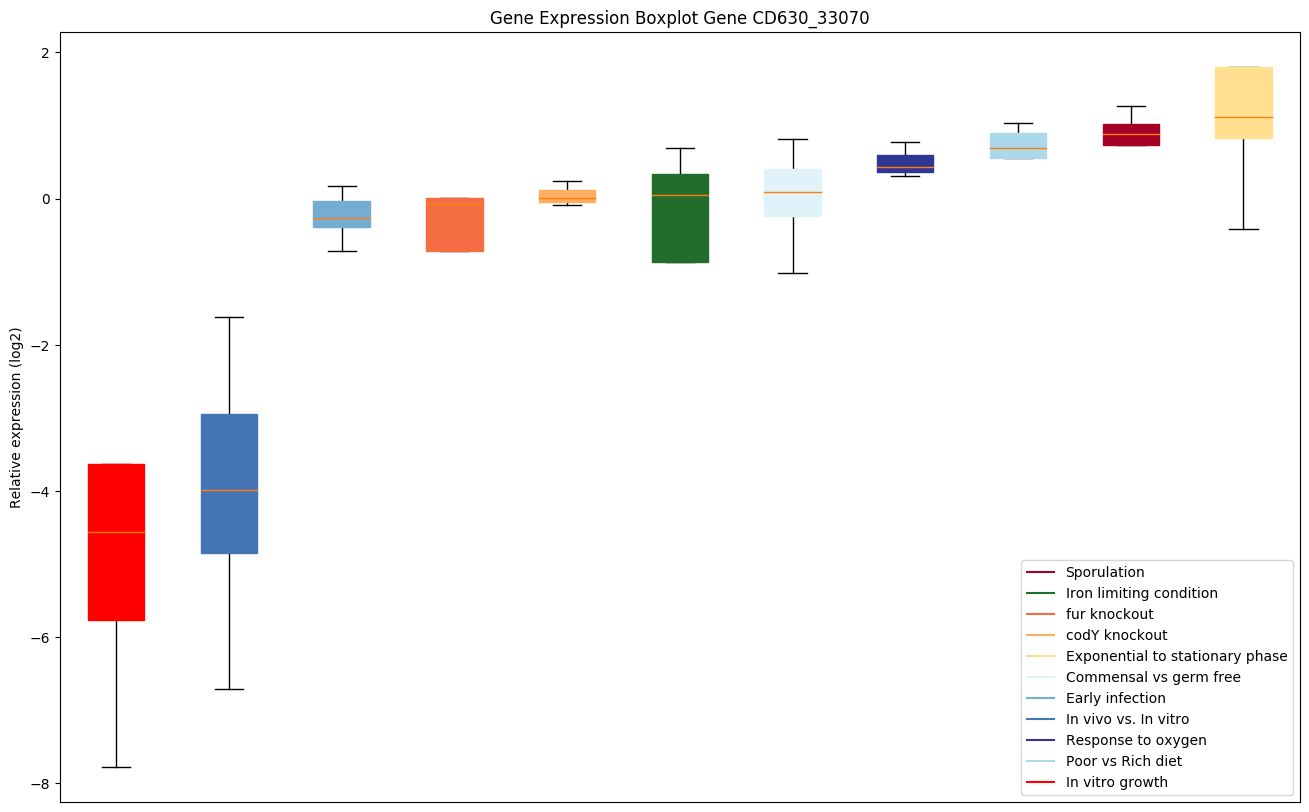
Expression of genes in subset of conditions included in bicluster on left side of red dashed line and out of bicluster on right of red dashed line. Each condition is represented as a boxplot, ordered by their median expression for the bicluster genes (smallest to largest) and colored according to condition blocks.
|
|
de novo identified motifs are listed below
| Motif 1 | Motif 1 e-value | Motif 2 | Motif 2 e-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | NA | NA | NA |
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
1. Betas: correspond to the average coefficients of the Bayesian regressions between module expression and TF expression profiles. The values indicate the magnitude and direction (activation or repression for positive or negative values, respectively) of each TF-module interaction.
2. Confidence scores: indicate the likelihood of the TF-module interactions.
The module is significantly enriched with genes associated to the indicated functional terms
The enrichment was determined with hypergeometric test using the genome functional annotation compiled by Girinathan et al (2020).
| Module | Pathway | Overlap | pvalue | Adjusted pvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127 | ATP Synthesis | 5 | 0.000000 | 0.000008 |
Genes that are included in this module
* "Gene essentiality is based on TnSeq Data from: Dembek M, Barquist L, Boinett CJ, et al. High-throughput analysis of gene essentiality and sporulation in Clostridium difficile. mBio. 2015;6(2):e02383. Published 2015 Feb 24.doi:10.1128/mBio.02383-14".
| Title | Short Name | Product | Function | Essentiality * | in vivo Essentiality | Rich broth Essentiality | Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD630_01920 | cls | Cardiolipin synthetase 1 | Catalyzes the reversible phosphatidyl group transfer from one phosphatidylglycerol molecule to another to form cardiolipin (CL) (diphosphatidylglycerol) and glycerol. |
 |
|||
| CD630_33040 | clpX | ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunitclpX | ATP-dependent specificity component of the Clp protease. It directs the protease to specific substrates. Can perform chaperone functions in the absence of ClpP. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_24490 | Putative methyltransferase | Specifically methylates the N3 position of the uracil ring of uridine 1498 (m3U1498) in 16S rRNA. Acts on the fully assembled 30S ribosomal subunit. |
 |
||||
| CD630_01900 | Putative membrane protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_01890 | Transcriptional regulator, LysR family |
 |
|||||
| CD630_22260 | sat | Streptogramin A acetyltransferase (Virginiamycinacetyltransferase D) (Vat(D)) |
 |
||||
| CD630_34680 | atpD | ATP synthase subunit beta | Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_01950 | Putative NCAIR-mutase (PurE)-related protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_34700 | atpA | ATPase subunit alpha | Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_22640 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_24500 | prmA | Ribosomal protein L11 methyltransferase (L11Mtase) | Methylates ribosomal protein L11. |
 |
|||
| CD630_33070 | Putative phosphoesterase |
 |
|||||
| CD630_22520 | Glutamate 2,3-aminomutase | Catalyzes the interconversion of L-glutamate and L-beta-glutamate. Does not have L-lysine 2,3-aminomutase activity. |
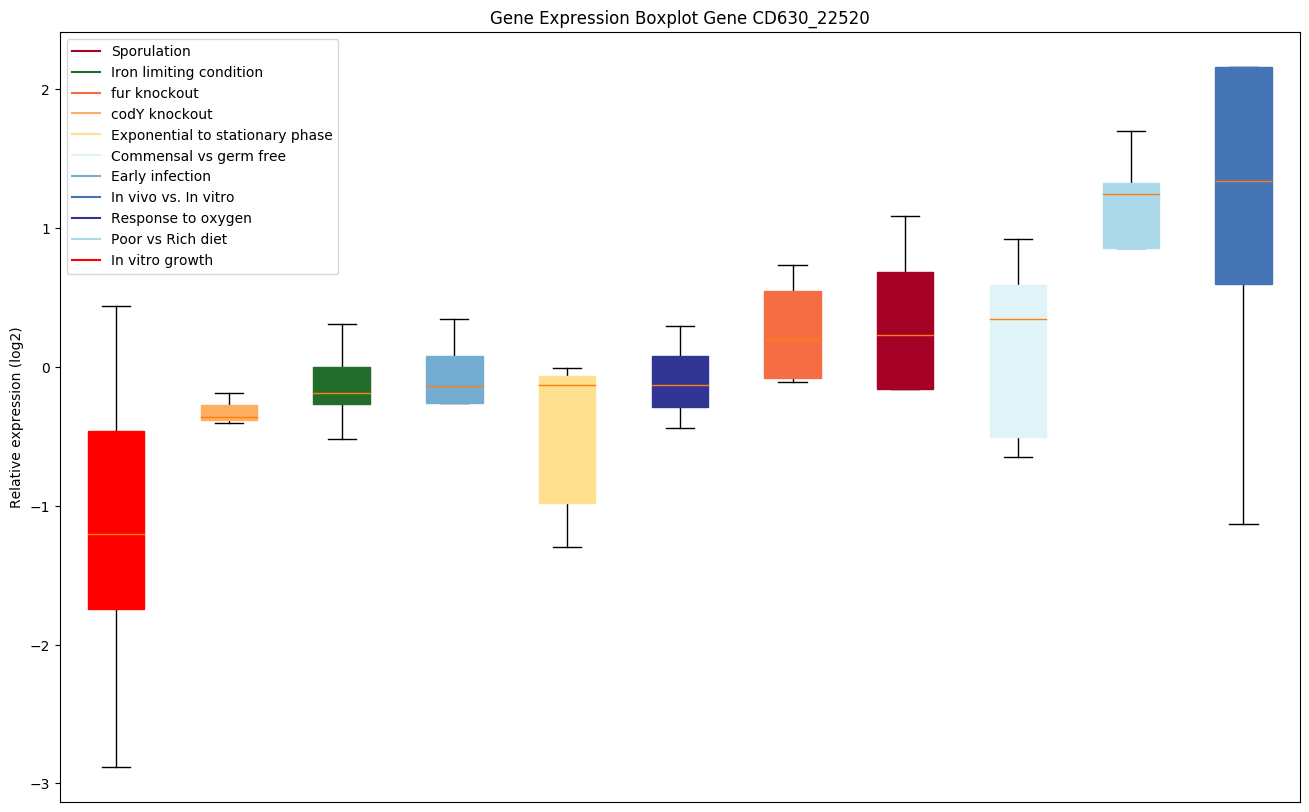 |
||||
| CD630_20260 | Putative acetyltransferase |
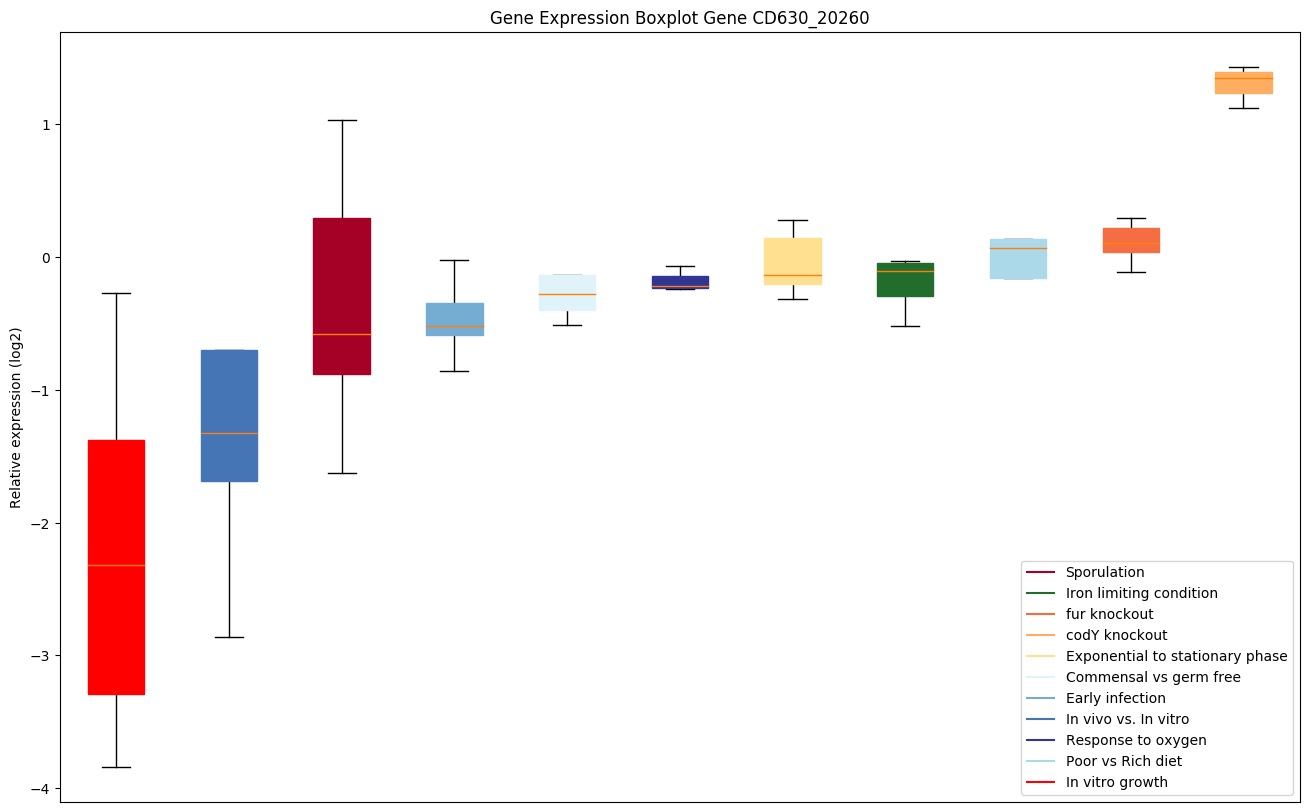 |
|||||
| CD630_24020 | Putative cell wall hydrolase;phosphatase-associated protein |
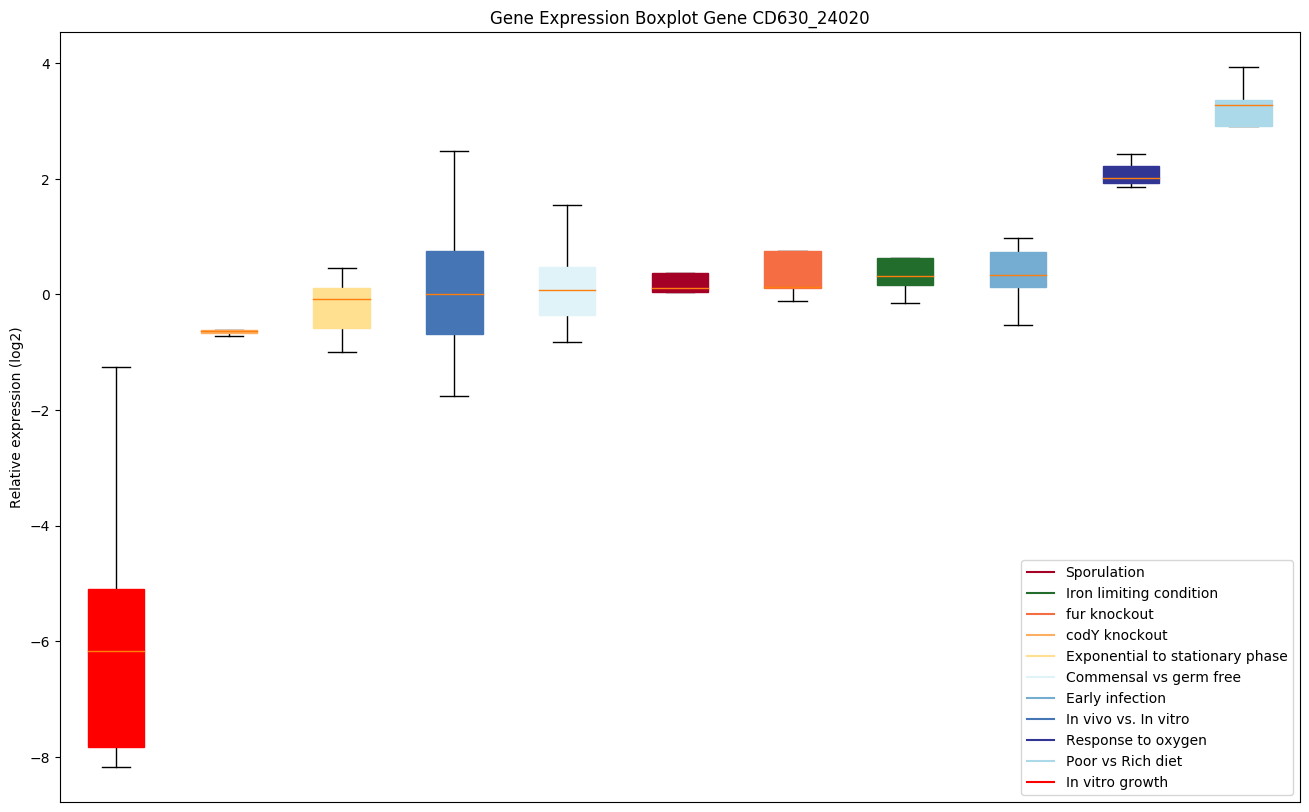 |
|||||
| CD630_24480 | Putative MiaB-like tRNA modifying enzyme |
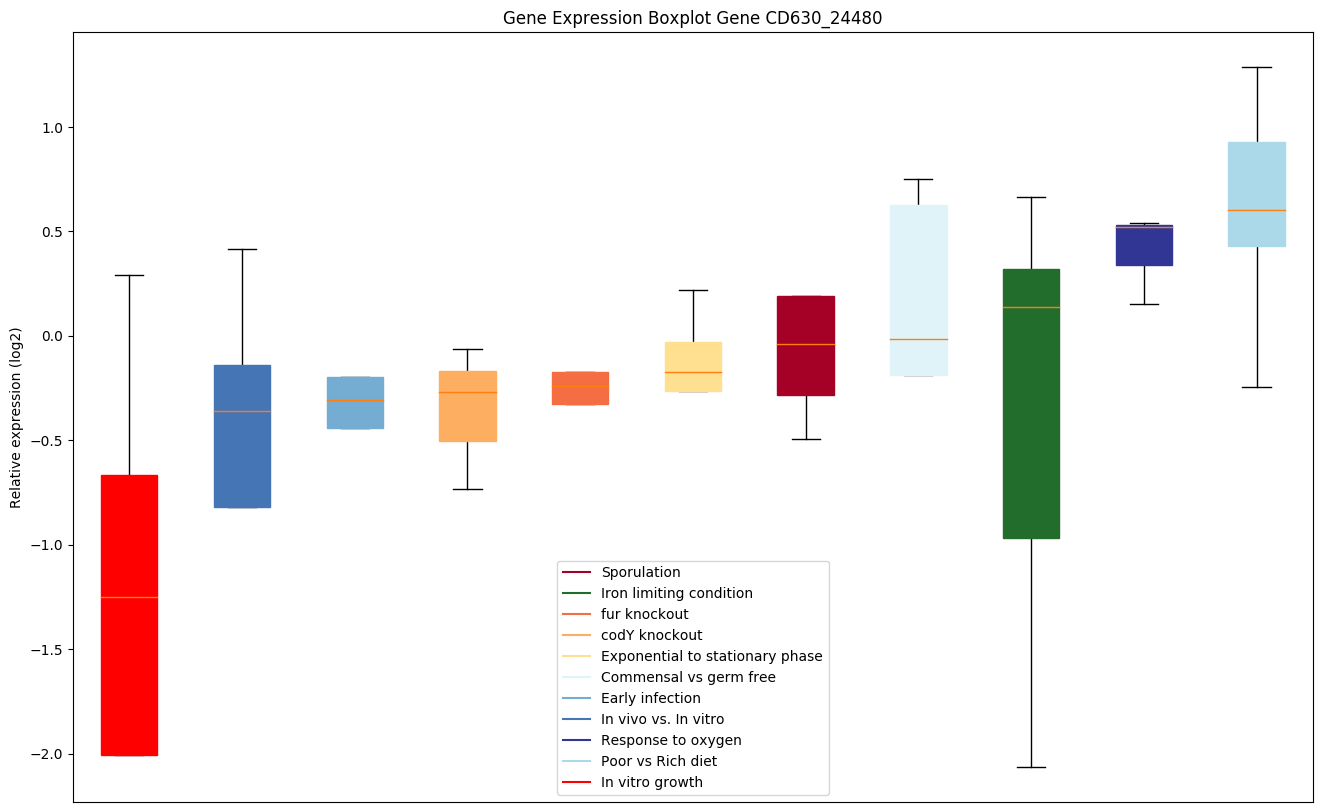 |
|||||
| CD630_33050 | clpP1 | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit 1 | Cleaves peptides in various proteins in a process that requires ATP hydrolysis. Has a chymotrypsin-like activity. Plays a major role in the degradation of misfolded proteins. |
 |
|||
| CD630_01910 | Putative DNA glycosylase |
 |
|||||
| CD630_34690 | atpG | ATP synthase gamma chain | Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The gamma chain is believed to be important in regulating ATPase activity and the flow of protons through the CF(0) complex. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_07550 | pilJ | Type IV pilus protein |
 |
||||
| CD630_34710 | atpH | ATP synthase subunit delta | F(1)F(0) ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton or sodium gradient. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. | Yes |
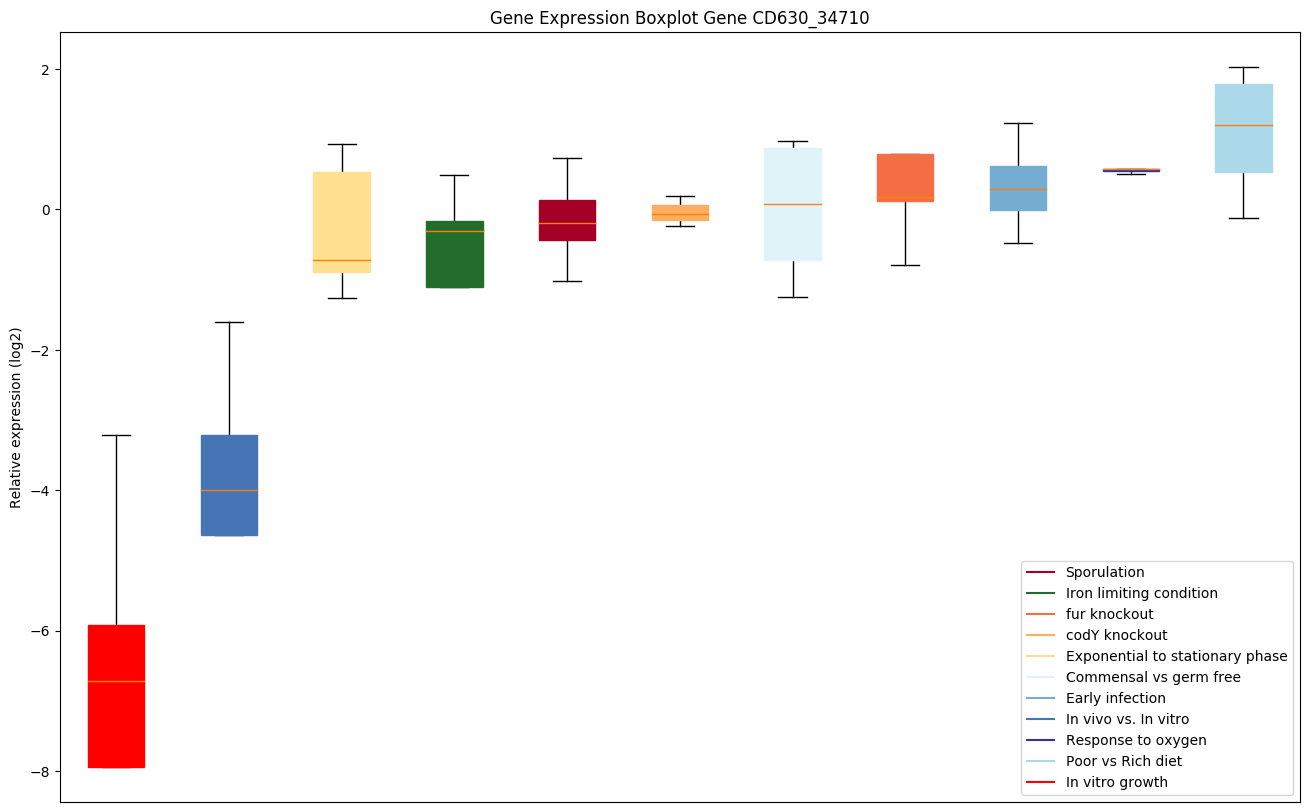 |
||
| CD630_34750 | atpI | ATP synthase subunit I | Yes |
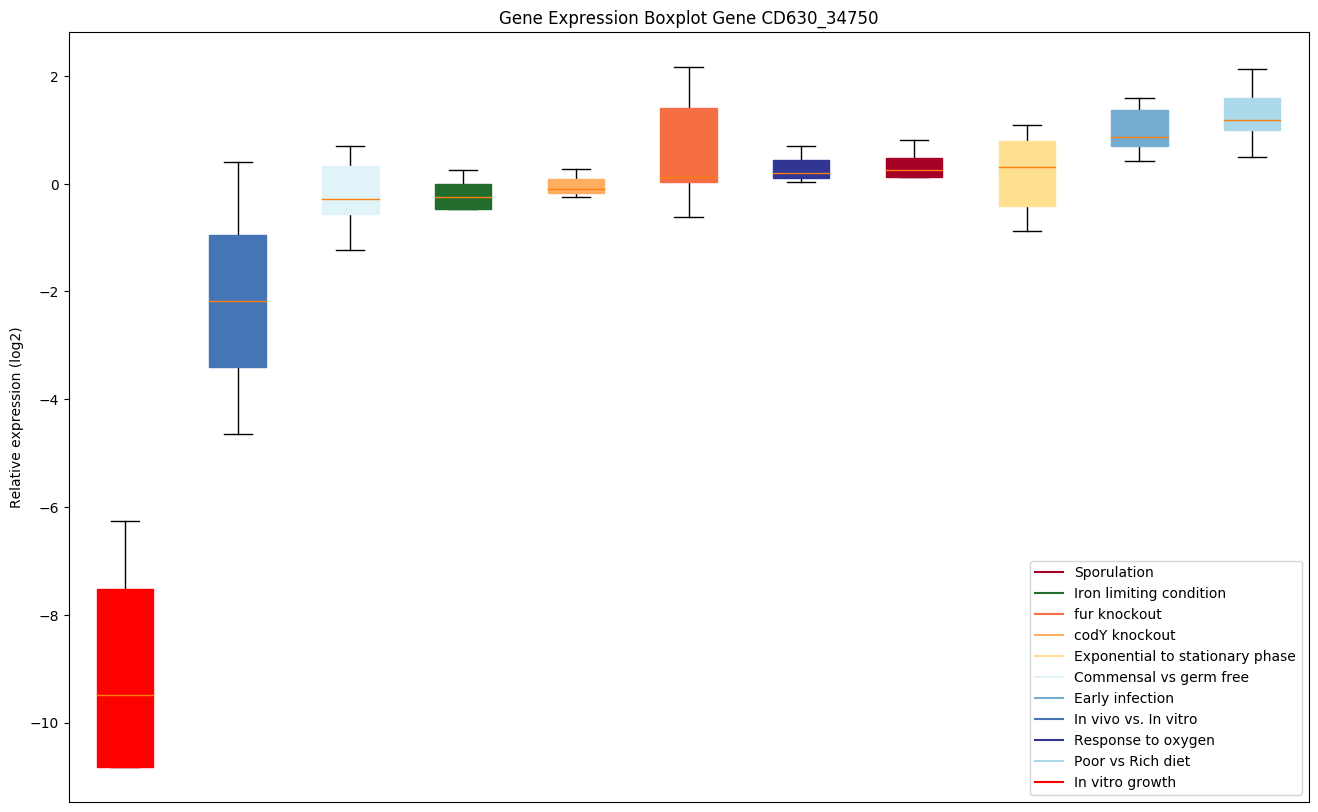 |
|||
| CD630_33080 | rph | Bifunctional enzyme, tRNA nucleotidyltransferase; Nucleoside-triphosphatase | Phosphorolytic 3'-5' exoribonuclease that plays an important role in tRNA 3'-end maturation. Removes nucleotide residues following the 3'-CCA terminus of tRNAs; can also add nucleotides to the ends of RNA molecules by using nucleoside diphosphates as substrates, but this may not be physiologically important. Probably plays a role in initiation of 16S rRNA degradation (leading to ribosome degradation) during starvation. |
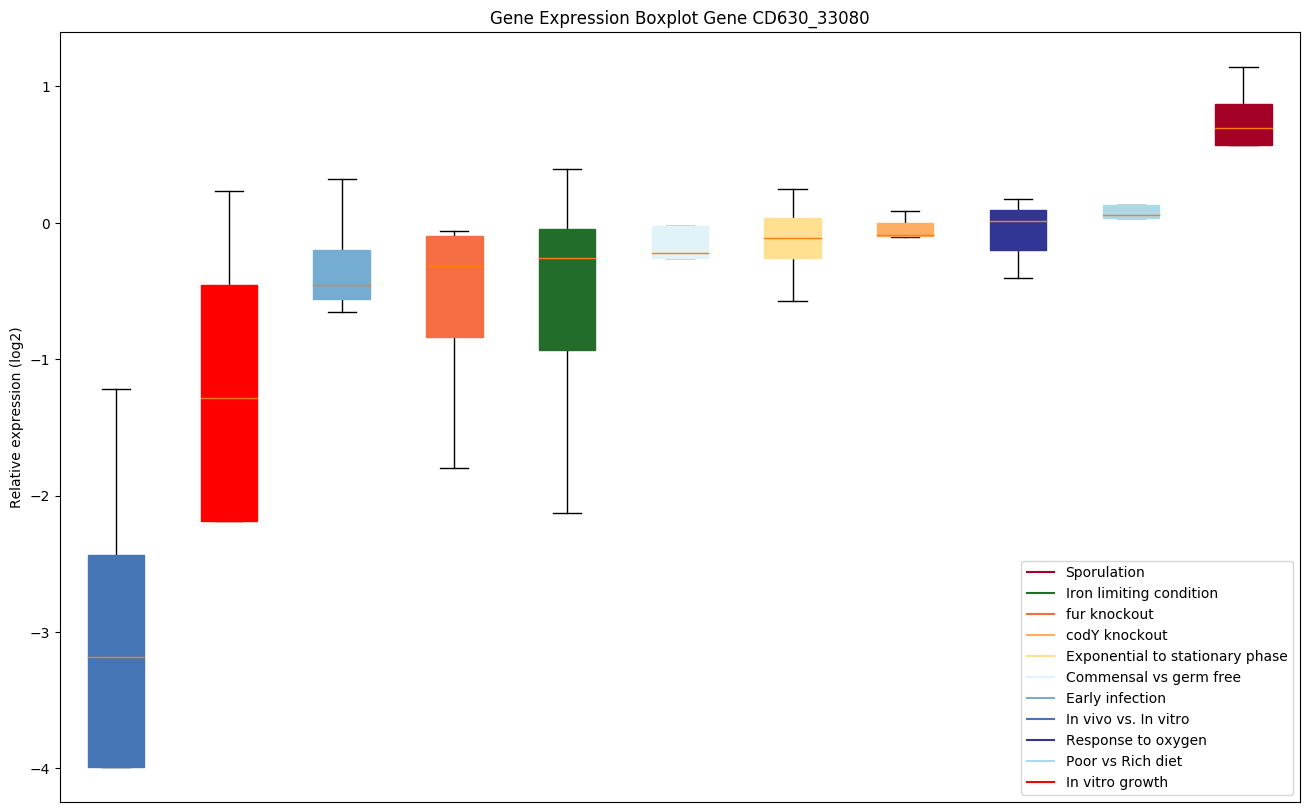 |
|||
| CD630_24470 | Putative histidine triad (HIT) protein |
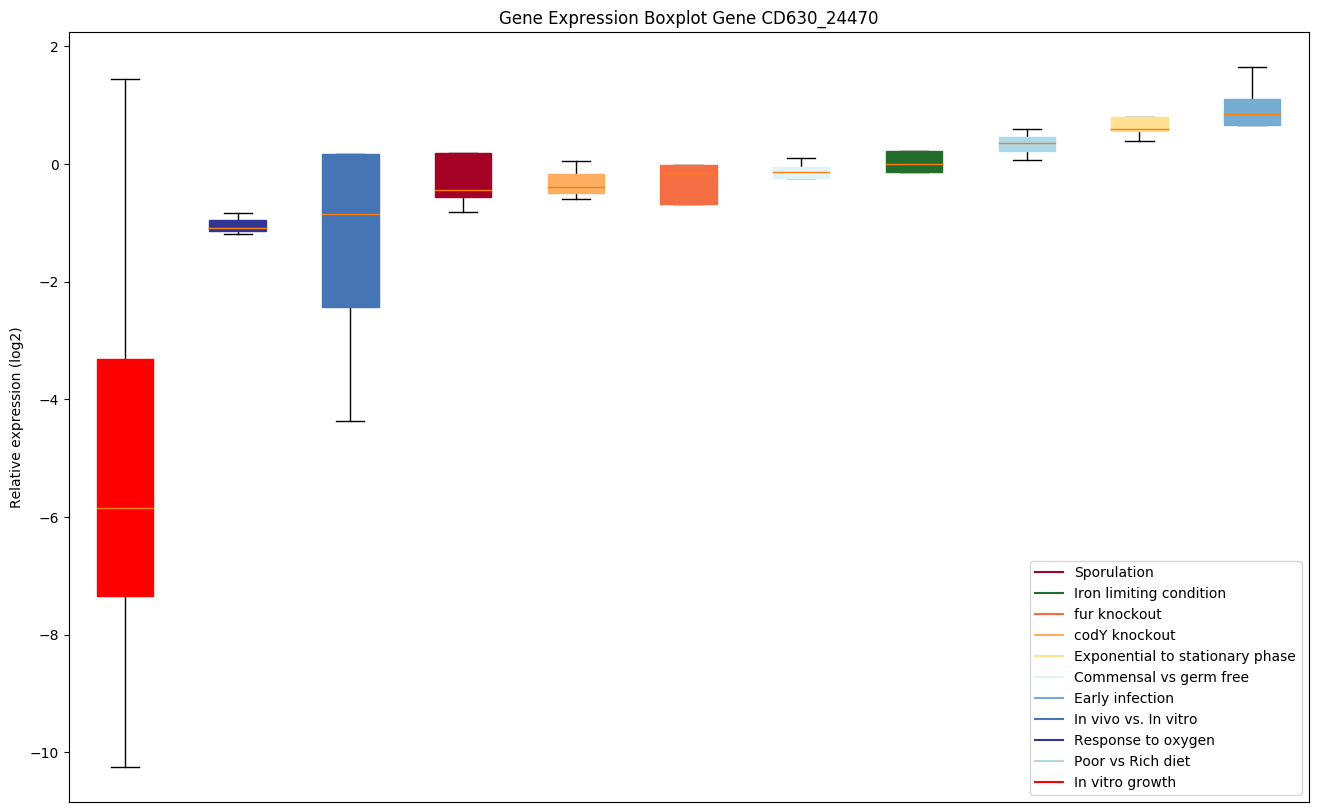 |
|||||
| CD630_22630 | prsA | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, PpiC-type |
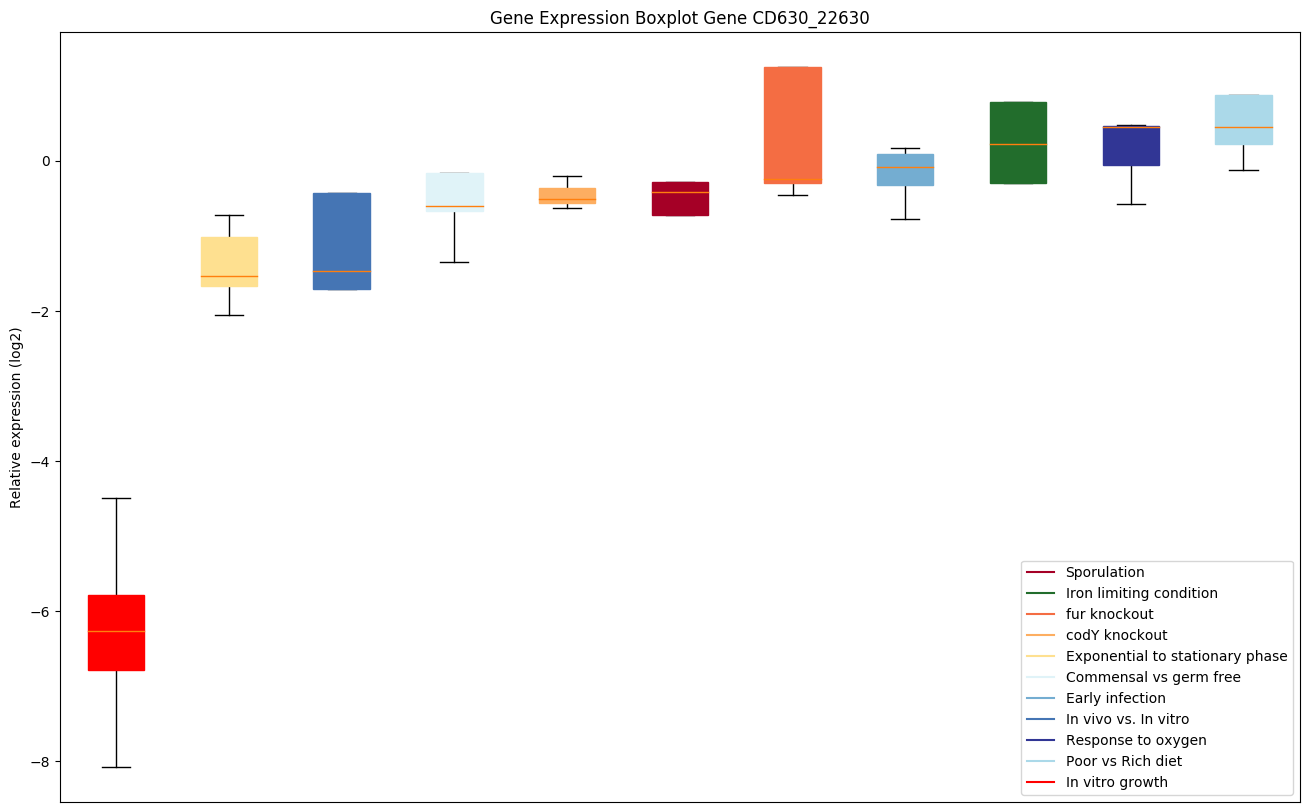 |
||||
| CD630_33060 | tig | Trigger factor (TF) | Involved in protein export. Acts as a chaperone by maintaining the newly synthesized protein in an open conformation. Functions as a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. |
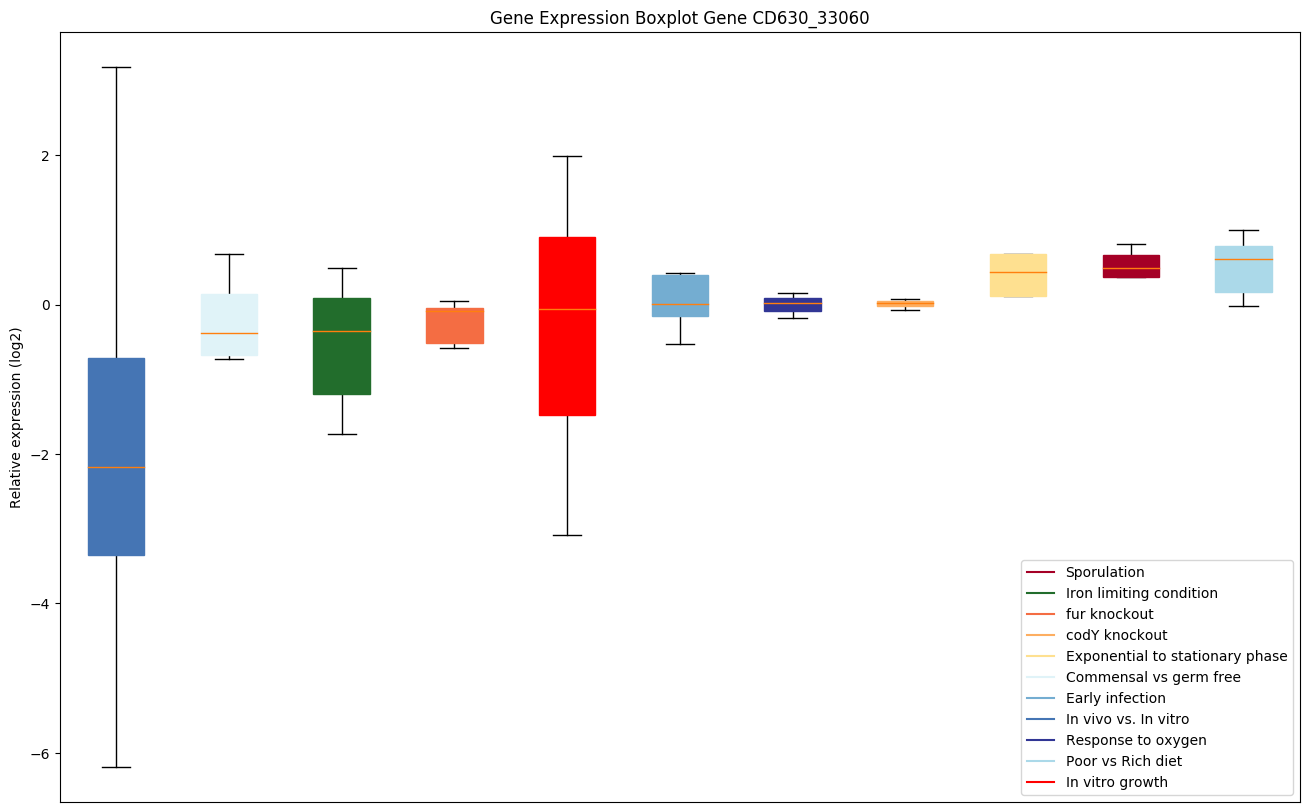 |
|||
| CD630_36130 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
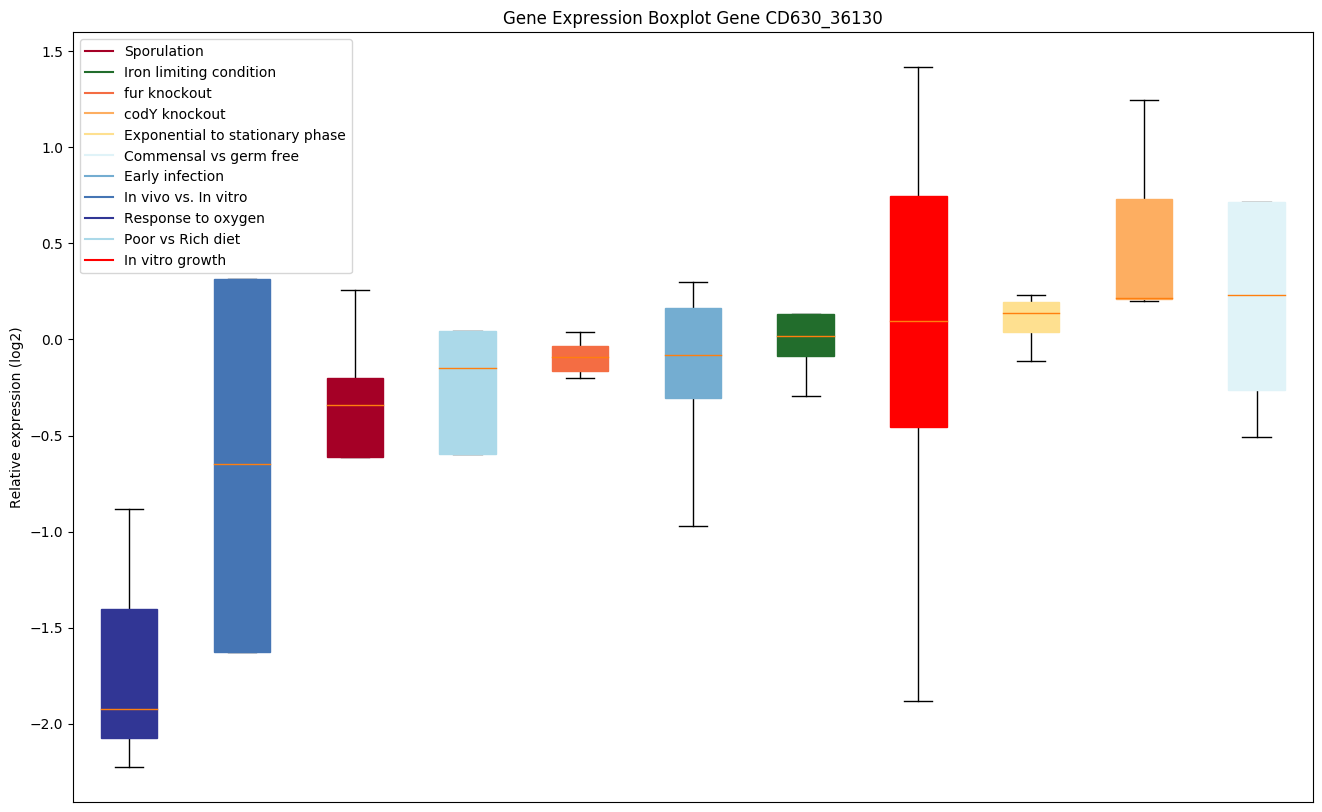 |
