Module 177
Summary
| Residual | Gene Count | Condition Count | 1st Q Condition Block * | 5th Q Condition Block * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.44 | 21 | 64 | NA | NA |
Bicluster expression profile
Expression of genes in subset of conditions included in bicluster on left side of red dashed line and out of bicluster on right of red dashed line. Each condition is represented as a boxplot, ordered by their median expression for the bicluster genes (smallest to largest) and colored according to condition blocks.
|
|
de novo identified motifs are listed below
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
1. Betas: correspond to the average coefficients of the Bayesian regressions between module expression and TF expression profiles. The values indicate the magnitude and direction (activation or repression for positive or negative values, respectively) of each TF-module interaction.
2. Confidence scores: indicate the likelihood of the TF-module interactions.
The module is significantly enriched with genes associated to the indicated functional terms
Genes that are included in this module
* "Gene essentiality is based on TnSeq Data from: Dembek M, Barquist L, Boinett CJ, et al. High-throughput analysis of gene essentiality and sporulation in Clostridium difficile. mBio. 2015;6(2):e02383. Published 2015 Feb 24.doi:10.1128/mBio.02383-14".
| Title | Short Name | Product | Function | Essentiality * | in vivo Essentiality | Rich broth Essentiality | Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD630_05690 | Putative lipoprotein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_24640 | hemN | Oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase(Coproporphyrinogenase) (Coprogen oxidase) | Probably acts as a heme chaperone, transferring heme to an unknown acceptor. Binds one molecule of heme per monomer, possibly covalently. Binds 1 [4Fe-4S] cluster. The cluster is coordinated with 3 cysteines and an exchangeable S-adenosyl-L-methionine. |
 |
|||
| CD630_24670 | lepA | GTP-binding protein LepA | Required for accurate and efficient protein synthesis under certain stress conditions. May act as a fidelity factor of the translation reaction, by catalyzing a one-codon backward translocation of tRNAs on improperly translocated ribosomes. Back-translocation proceeds from a post-translocation (POST) complex to a pre-translocation (PRE) complex, thus giving elongation factor G a second chance to translocate the tRNAs correctly. Binds to ribosomes in a GTP-dependent manner. |
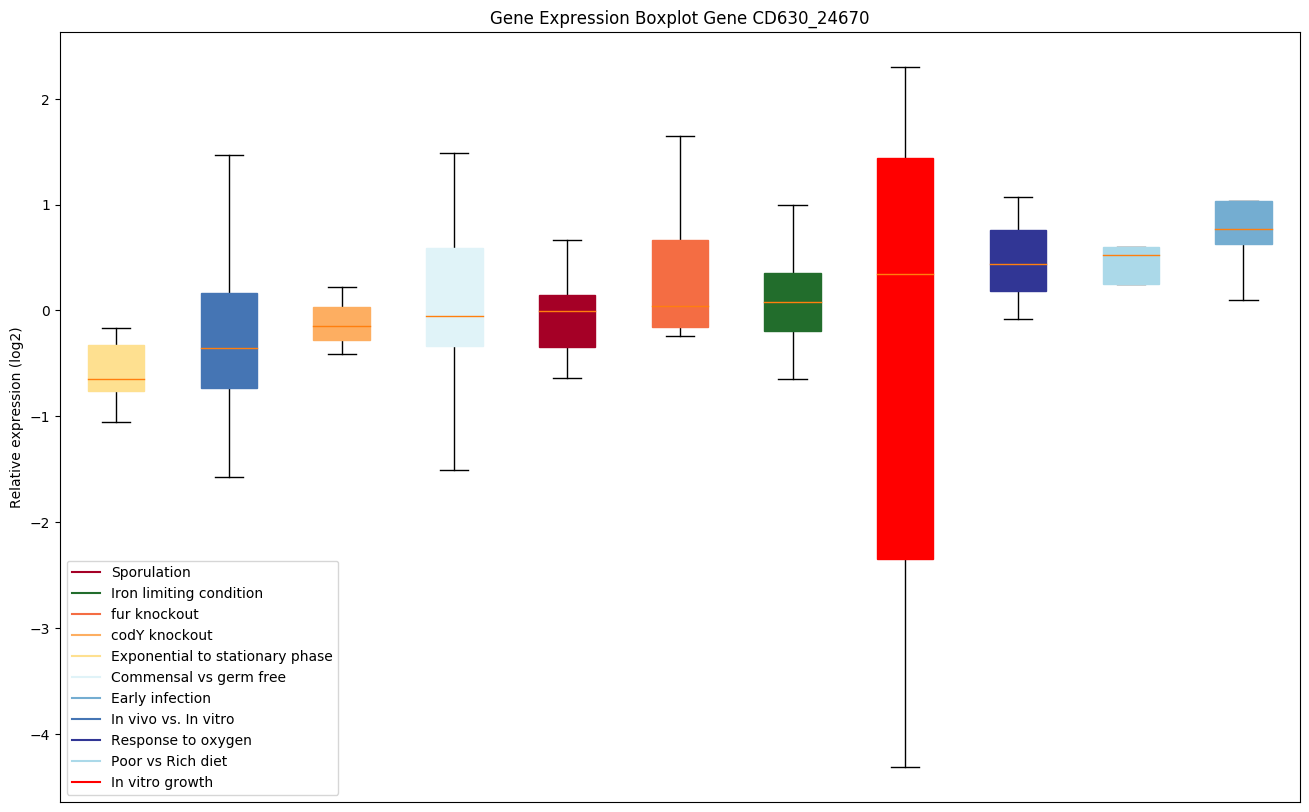 |
|||
| CD630_24620 | grpE | Protein grpE (HSP-70 cofactor) | Participates actively in the response to hyperosmotic and heat shock by preventing the aggregation of stress-denatured proteins, in association with DnaK and GrpE. It is the nucleotide exchange factor for DnaK and may function as a thermosensor. Unfolded proteins bind initially to DnaJ; upon interaction with the DnaJ-bound protein, DnaK hydrolyzes its bound ATP, resulting in the formation of a stable complex. GrpE releases ADP from DnaK; ATP binding to DnaK triggers the release of the substrate protein, thus completing the reaction cycle. Several rounds of ATP-dependent interactions between DnaJ, DnaK and GrpE are required for fully efficient folding. | Yes |
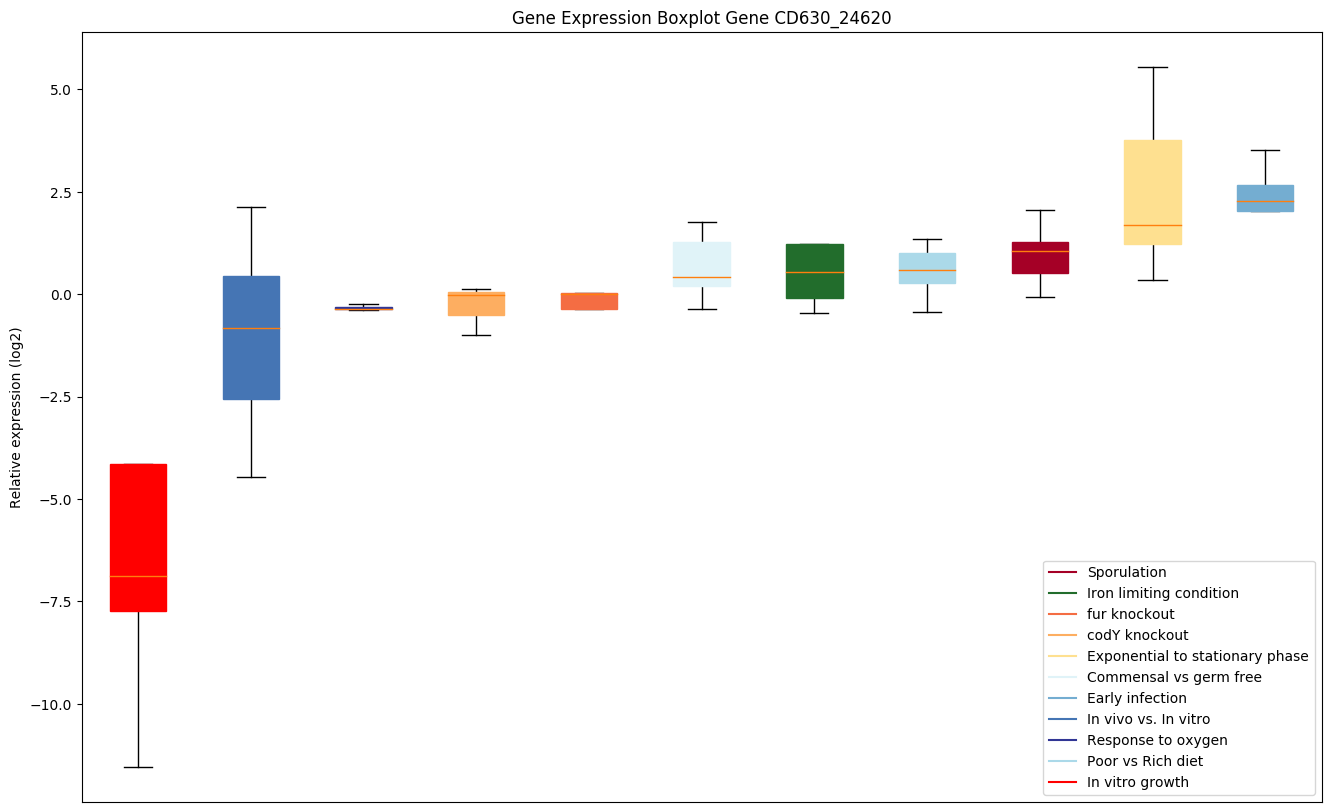 |
||
| CD630_27440 | relA | GTP pyrophosphokinase (RelA/SpoT) | In eubacteria ppGpp (guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5-' diphosphate) is a mediator of the stringent response that coordinates a variety of cellular activities in response to changes in nutritional abundance. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_27400 | hisS | Histidyl-tRNA synthetase (Histidine--tRNA ligase)(HisRS) | Yes |
 |
|||
| CD630_24660 | Putative tRNA-nucleotidyltransferase/Poly(A)polymerase family member |
 |
|||||
| CD630_27240 | Putative polysaccharide deacetylase |
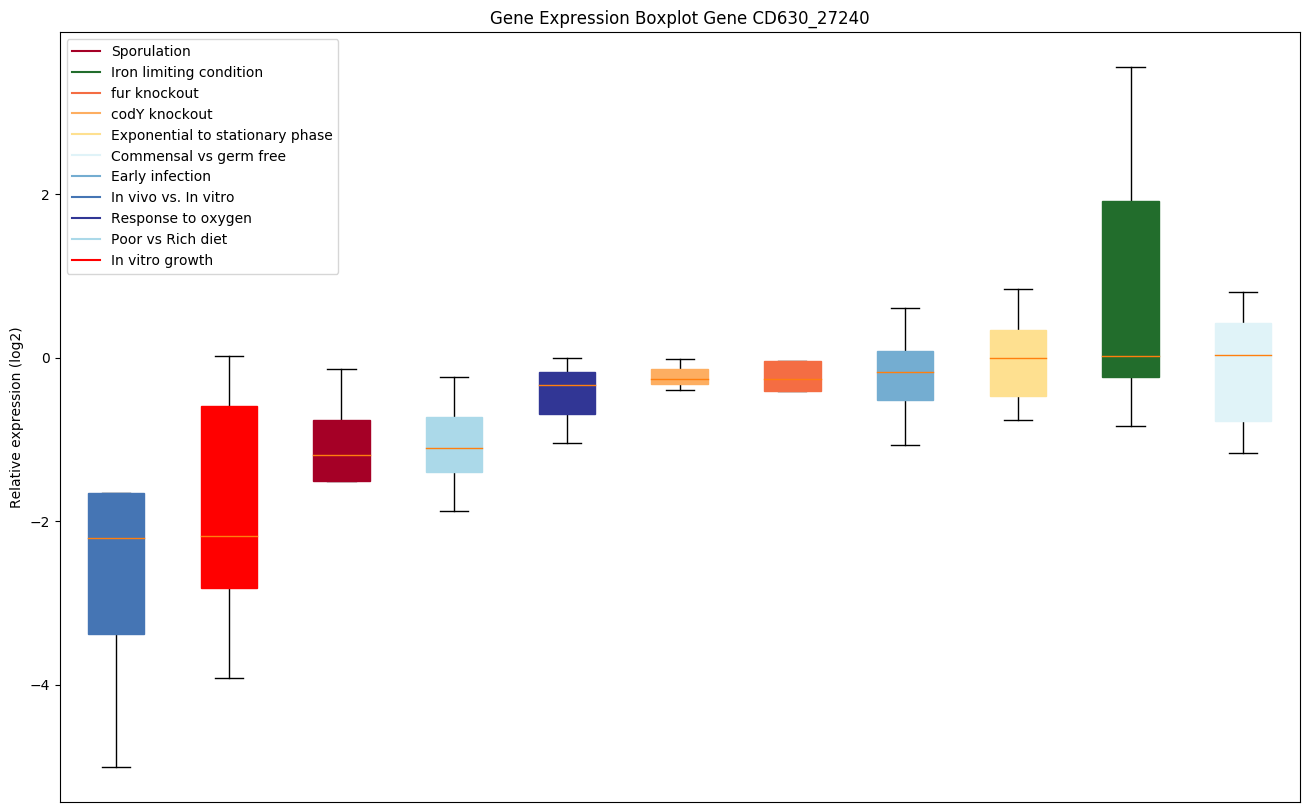 |
|||||
| CD630_01450 | Putative resolvase, S1 RNA-bindingdomain-containing protein |
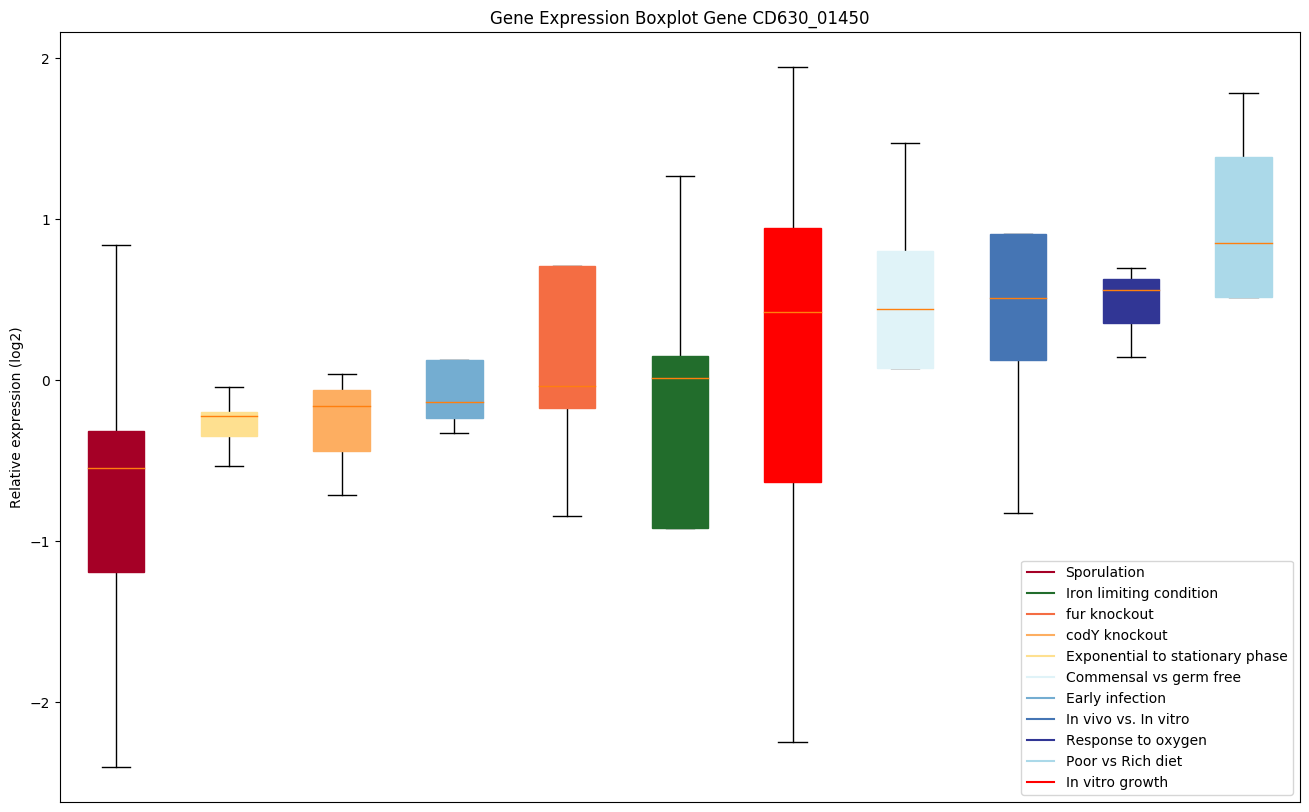 |
|||||
| CD630_27250 | Putative monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase |
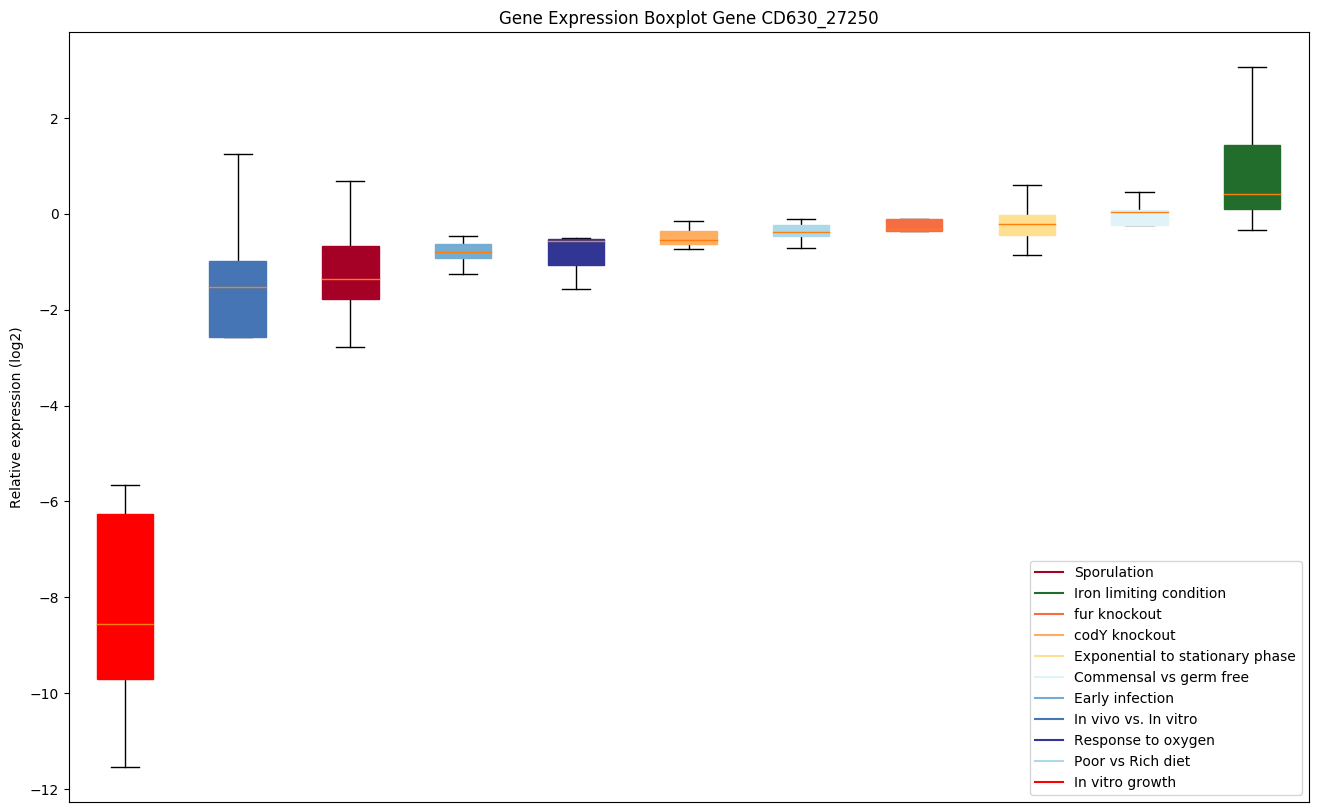 |
|||||
| CD630_05700 | Putative lipoprotein |
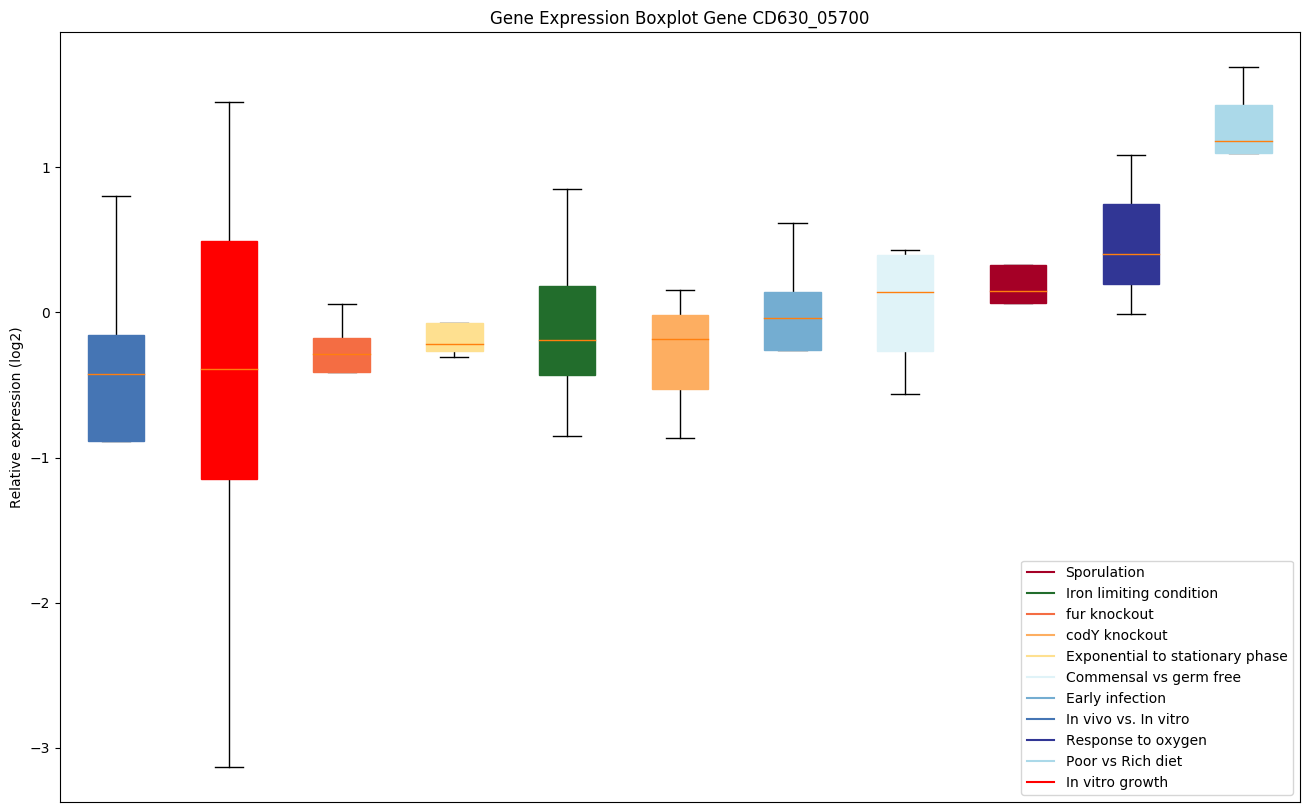 |
|||||
| CD630_24630 | hrcA | Transcriptional regulator, Heat-induciblerepressor HrcA | Negative regulator of class I heat shock genes (grpE-dnaK-dnaJ and groELS operons). Prevents heat-shock induction of these operons. |
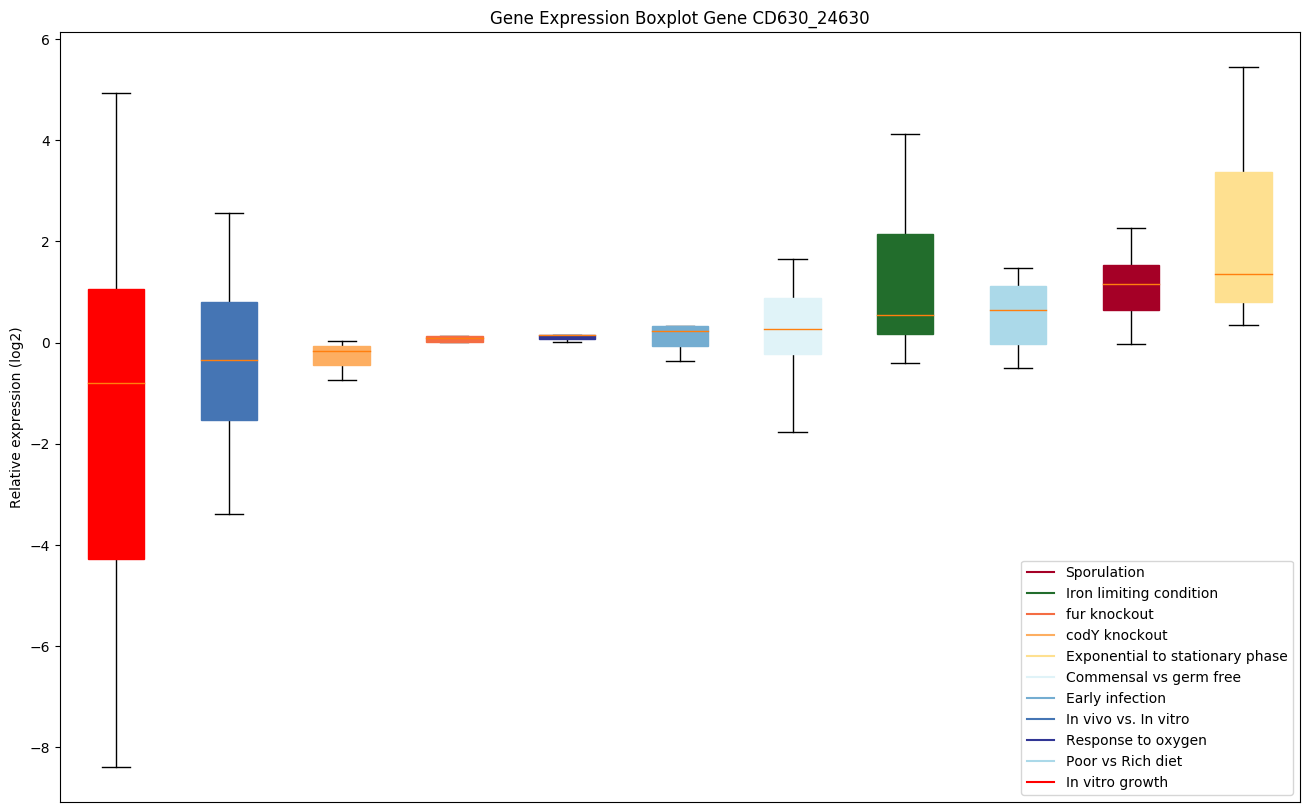 |
|||
| CD630_24600 | dnaJ | Chaperone protein DnaJ | Participates actively in the response to hyperosmotic and heat shock by preventing the aggregation of stress-denatured proteins and by disaggregating proteins, also in an autonomous, DnaK-independent fashion. Unfolded proteins bind initially to DnaJ; upon interaction with the DnaJ-bound protein, DnaK hydrolyzes its bound ATP, resulting in the formation of a stable complex. GrpE releases ADP from DnaK; ATP binding to DnaK triggers the release of the substrate protein, thus completing the reaction cycle. Several rounds of ATP-dependent interactions between DnaJ, DnaK and GrpE are required for fully efficient folding. Also involved, together with DnaK and GrpE, in the DNA replication of plasmids through activation of initiation proteins. |
 |
|||
| CD630_27410 | hemZ | Coproporphyrinogen III oxidase | Yes |
 |
|||
| CD630_01460 | Putative hydrolase |
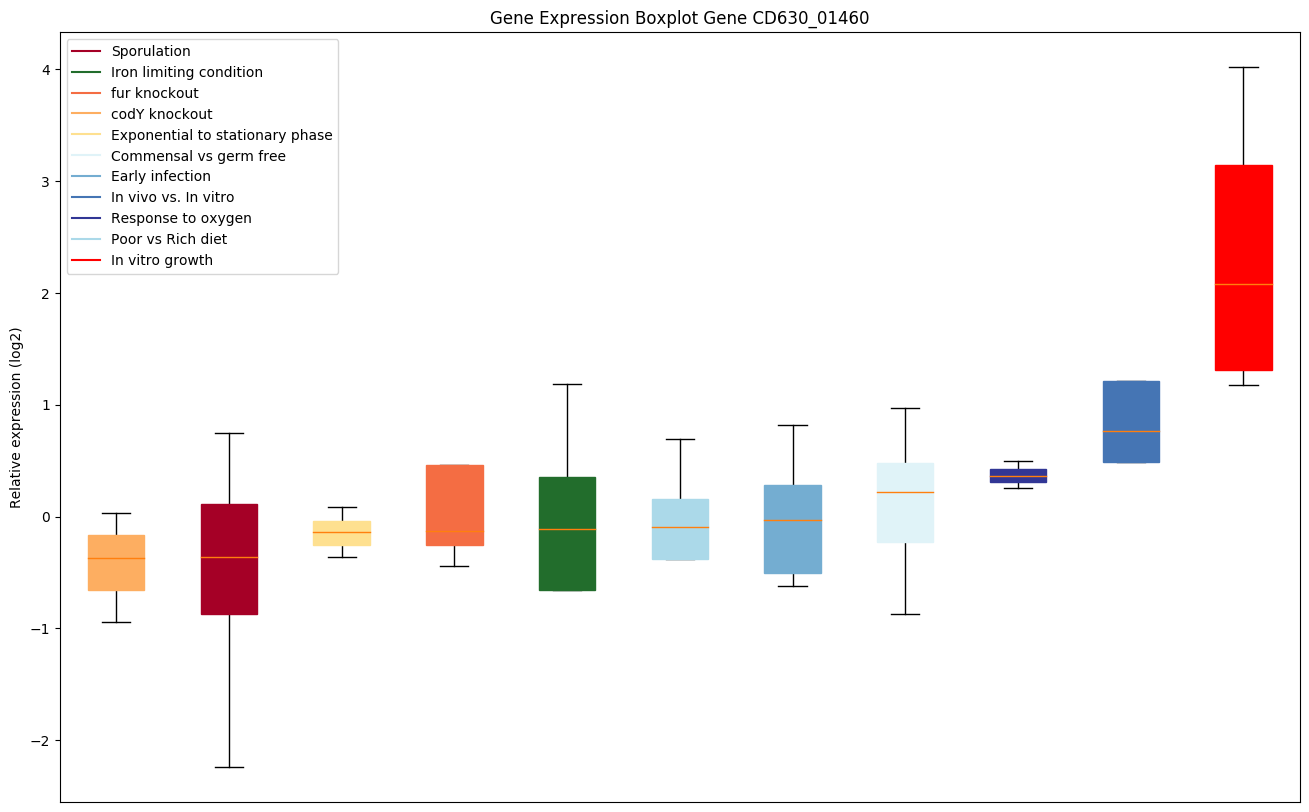 |
|||||
| CD630_28400 | serS1 | Seryl-tRNA synthetase 1 (Seryl-tRNA(Ser/Sec)synthetase 1) (Serine--tRNA ligase 1) (SerRS 1) | Catalyzes the attachment of serine to tRNA(Ser). Is also able to aminoacylate tRNA(Sec) with serine, to form the misacylated tRNA L-seryl-tRNA(Sec), which will be further converted into selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec). | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_24610 | dnaK | Chaperone protein dnaK (Heat shock protein 70)(Heat shock 70 kDa protein) (HSP70) | Acts as a chaperone. | Yes |
 |
||
| CD630_27450 | apt | Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) | Catalyzes a salvage reaction resulting in the formation of AMP, that is energically less costly than de novo synthesis. |
 |
|||
| CD630_27430 | dtd | D-tyrosyl-tRNA(Tyr) deacylase | An aminoacyl-tRNA editing enzyme that deacylates mischarged D-aminoacyl-tRNAs. Also deacylates mischarged glycyl-tRNA(Ala), protecting cells against glycine mischarging by AlaRS. Acts via tRNA-based rather than protein-based catalysis; rejects L-amino acids rather than detecting D-amino acids in the active site. By recycling D-aminoacyl-tRNA to D-amino acids and free tRNA molecules, this enzyme counteracts the toxicity associated with the formation of D-aminoacyl-tRNA entities in vivo and helps enforce protein L-homochirality. | Yes |
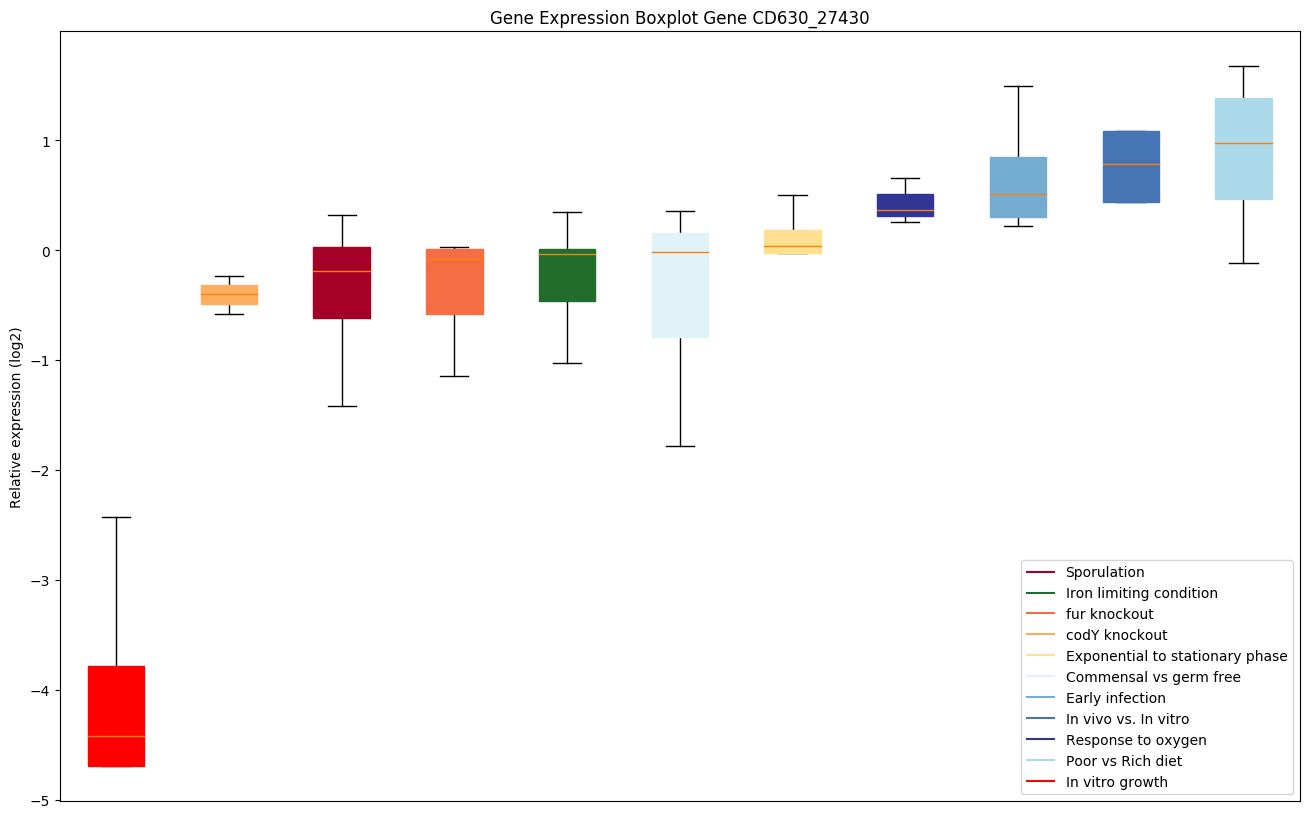 |
||
| CD630_27230 | Putative membrane protein | Catalyzes the transfer of a lysyl group from L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys) to membrane-bound phosphatidylglycerol (PG), which produces lysylphosphatidylglycerol (LPG), a major component of the bacterial membrane with a positive net charge. LPG synthesis contributes to bacterial virulence as it is involved in the resistance mechanism against cationic antimicrobial peptides (CAMP) produces by the host's immune system (defensins, cathelicidins) and by the competing microorganisms. |
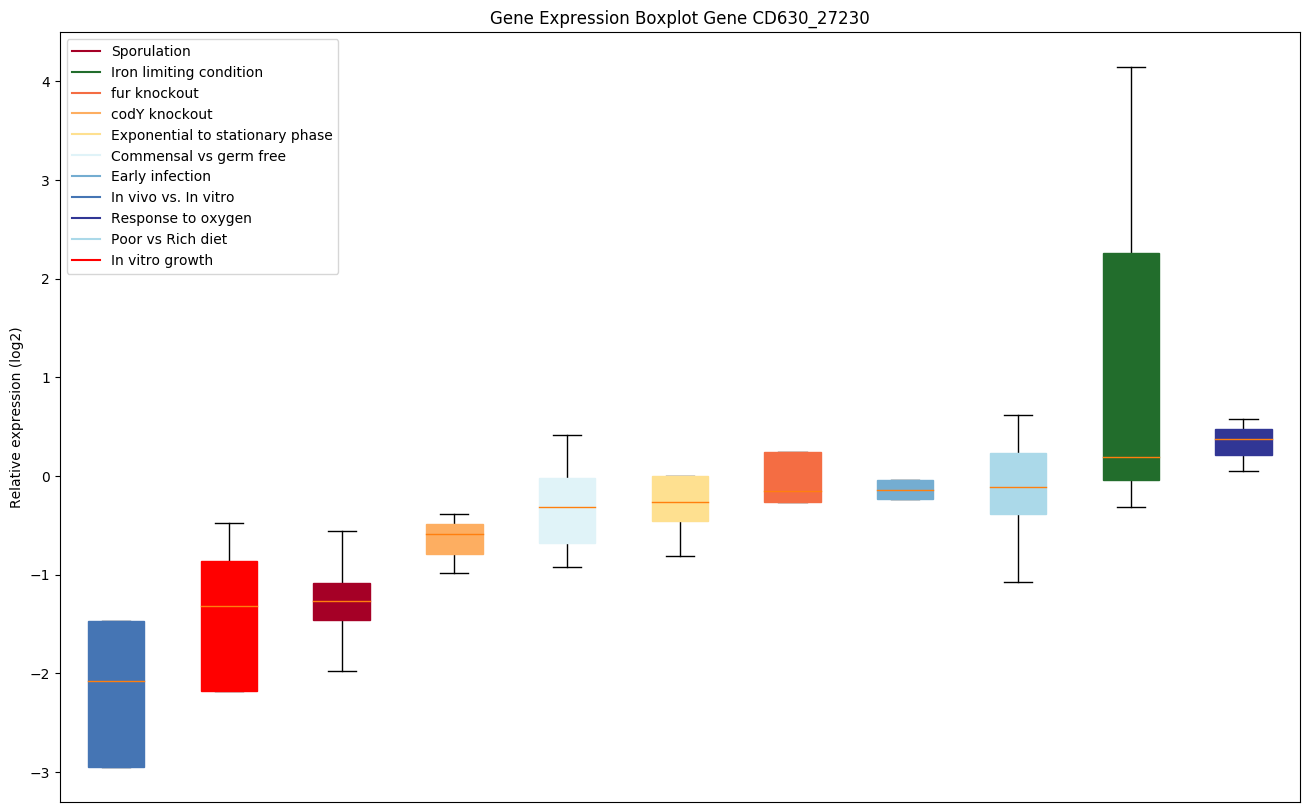 |
||||
| CD630_27420 | Putative hydrolase beta-lactamase-like |
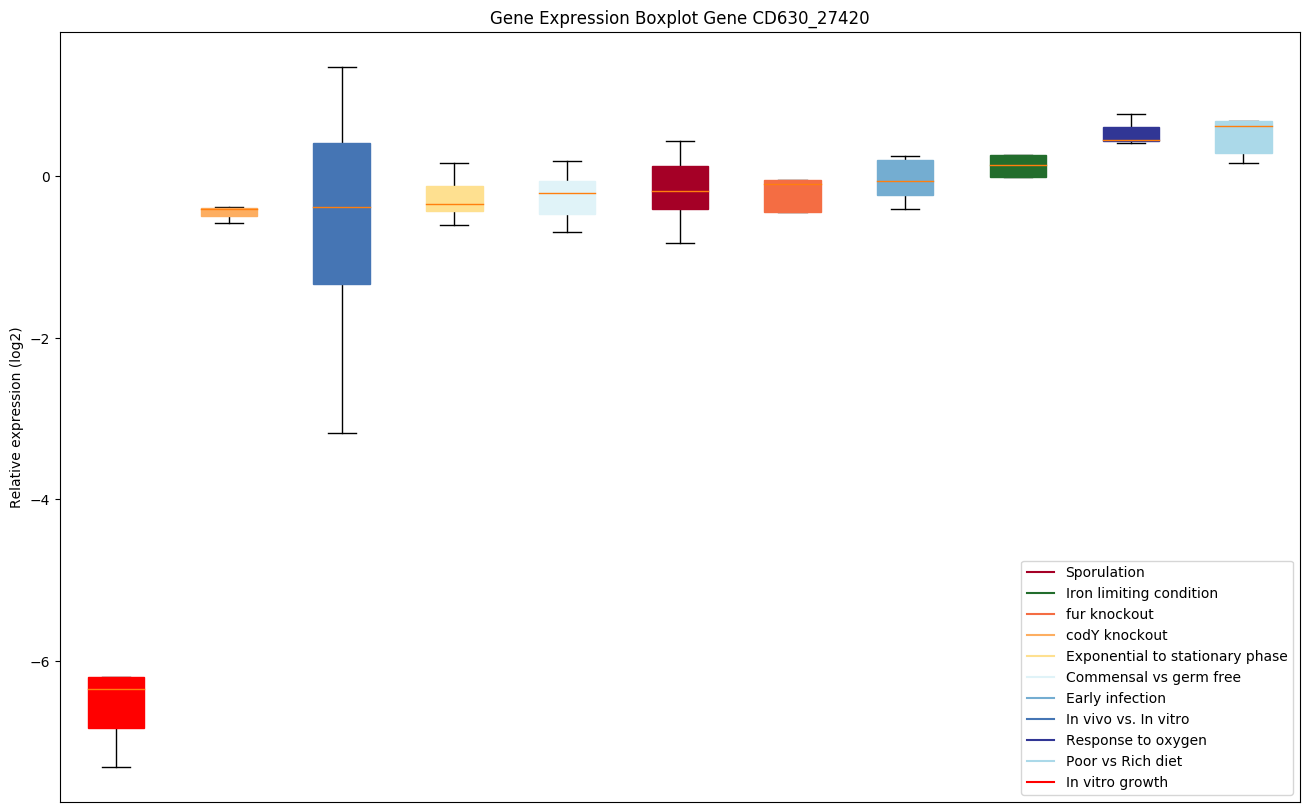 |