Module 393
Summary
| Residual | Gene Count | Condition Count | 1st Q Condition Block * | 5th Q Condition Block * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.46 | 26 | 62 | NA | NA |
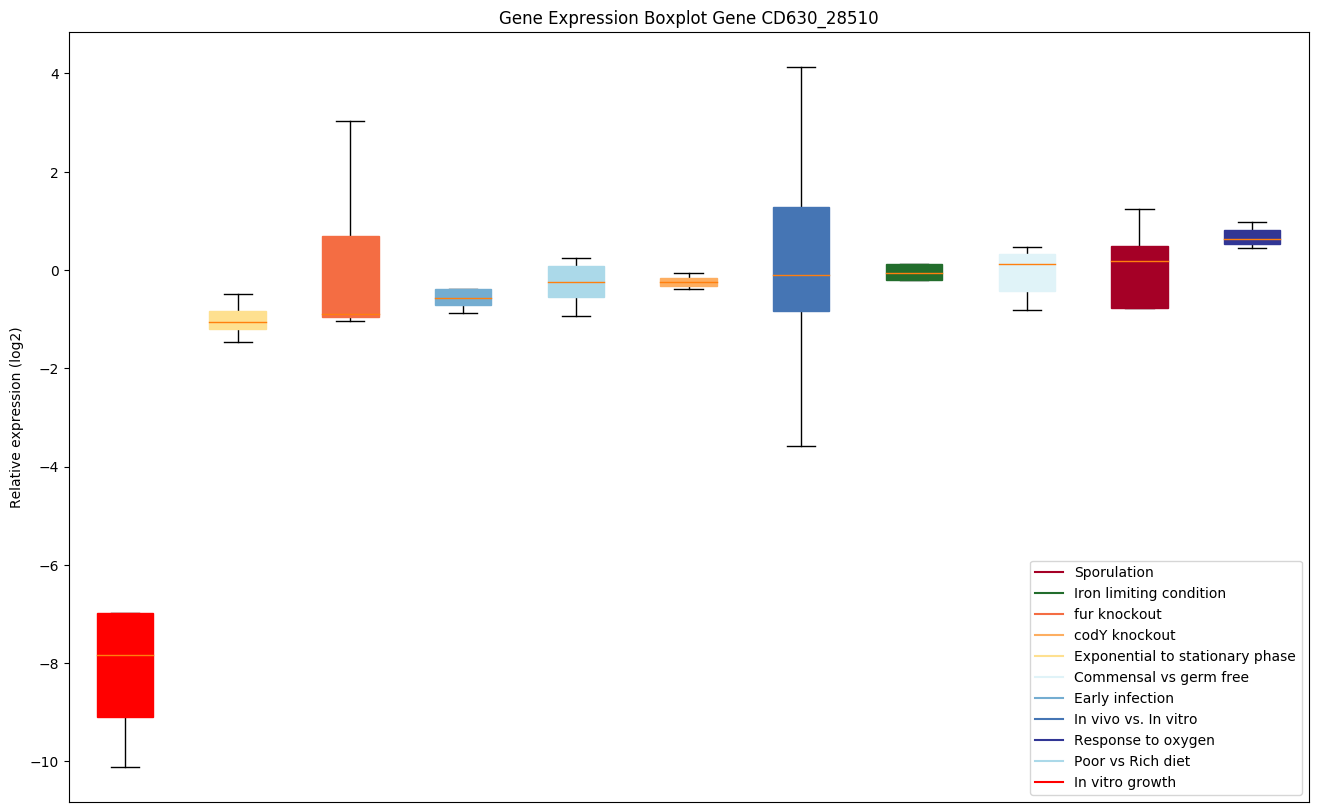
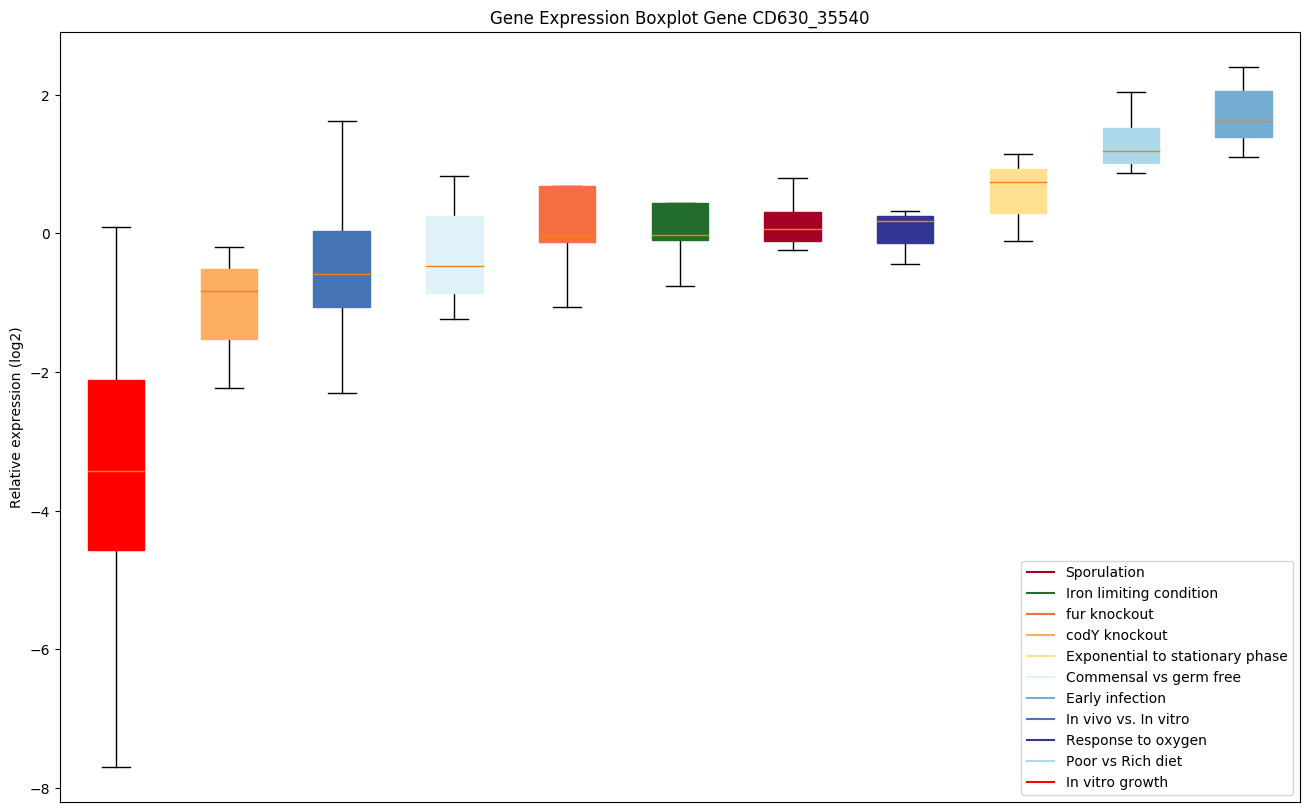
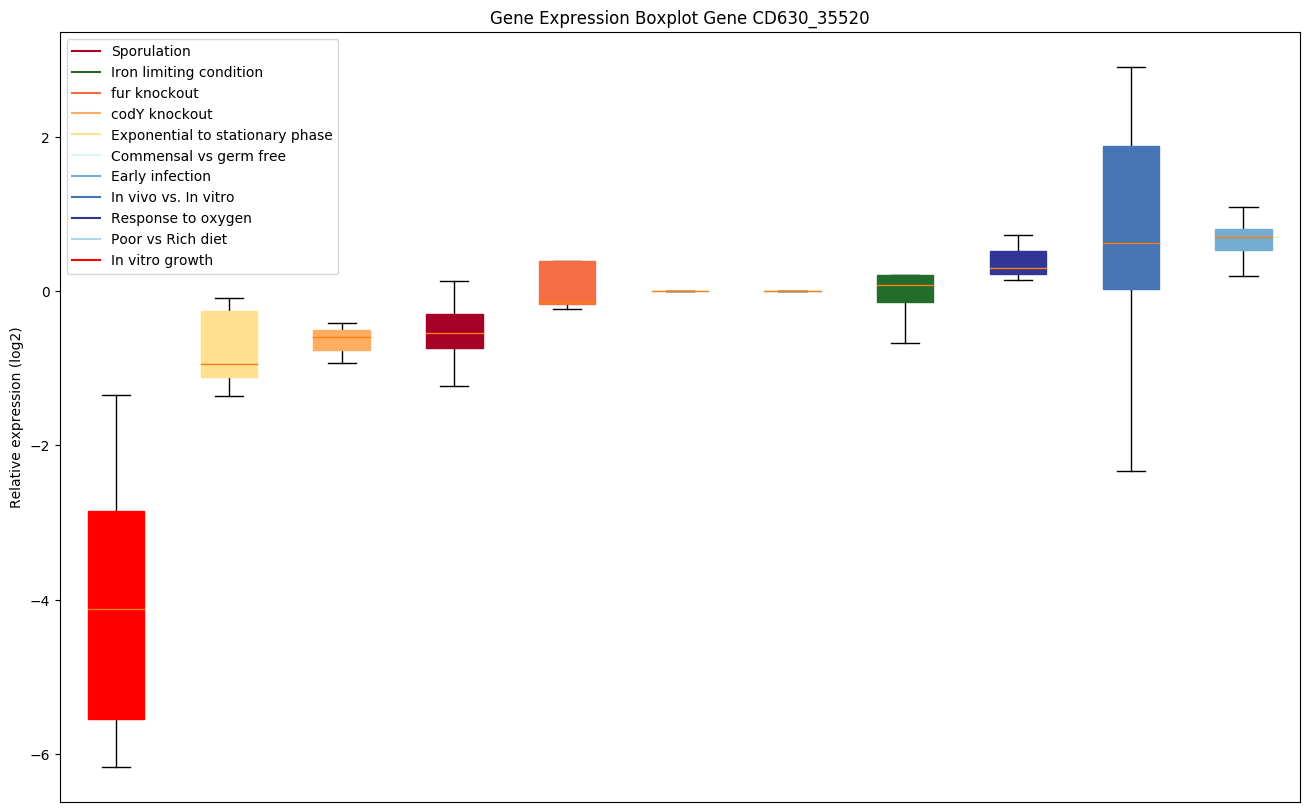
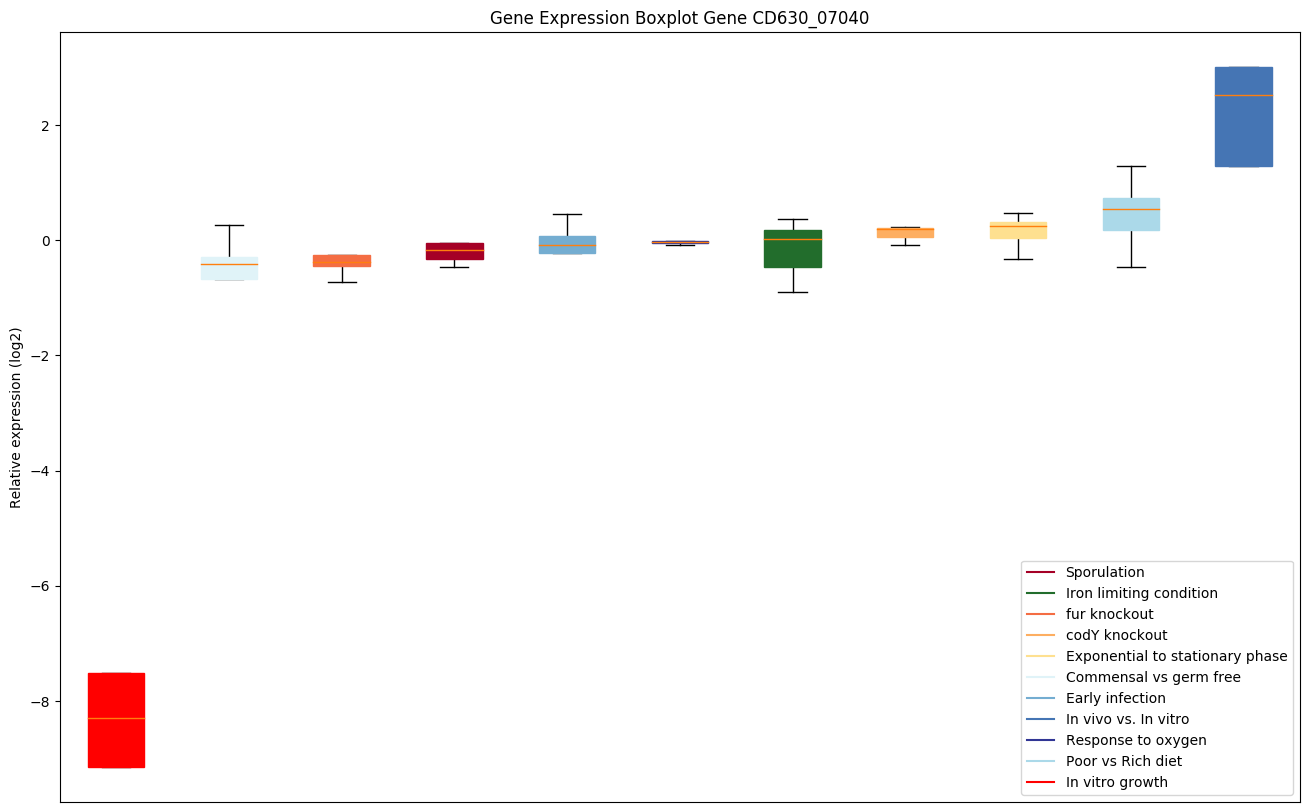
Bicluster expression profile
Expression of genes in subset of conditions included in bicluster on left side of red dashed line and out of bicluster on right of red dashed line. Each condition is represented as a boxplot, ordered by their median expression for the bicluster genes (smallest to largest) and colored according to condition blocks.
|
|
de novo identified motifs are listed below
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
1. Betas: correspond to the average coefficients of the Bayesian regressions between module expression and TF expression profiles. The values indicate the magnitude and direction (activation or repression for positive or negative values, respectively) of each TF-module interaction.
2. Confidence scores: indicate the likelihood of the TF-module interactions.
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
| TF | Module | Overlap | pvalue | Adjusted pvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
prdR Transcriptional regulator, sigma-54-dependent |
393 | 8 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
The module is significantly enriched with genes associated to the indicated functional terms
Genes that are included in this module
* "Gene essentiality is based on TnSeq Data from: Dembek M, Barquist L, Boinett CJ, et al. High-throughput analysis of gene essentiality and sporulation in Clostridium difficile. mBio. 2015;6(2):e02383. Published 2015 Feb 24.doi:10.1128/mBio.02383-14".
| Title | Short Name | Product | Function | Essentiality * | in vivo Essentiality | Rich broth Essentiality | Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
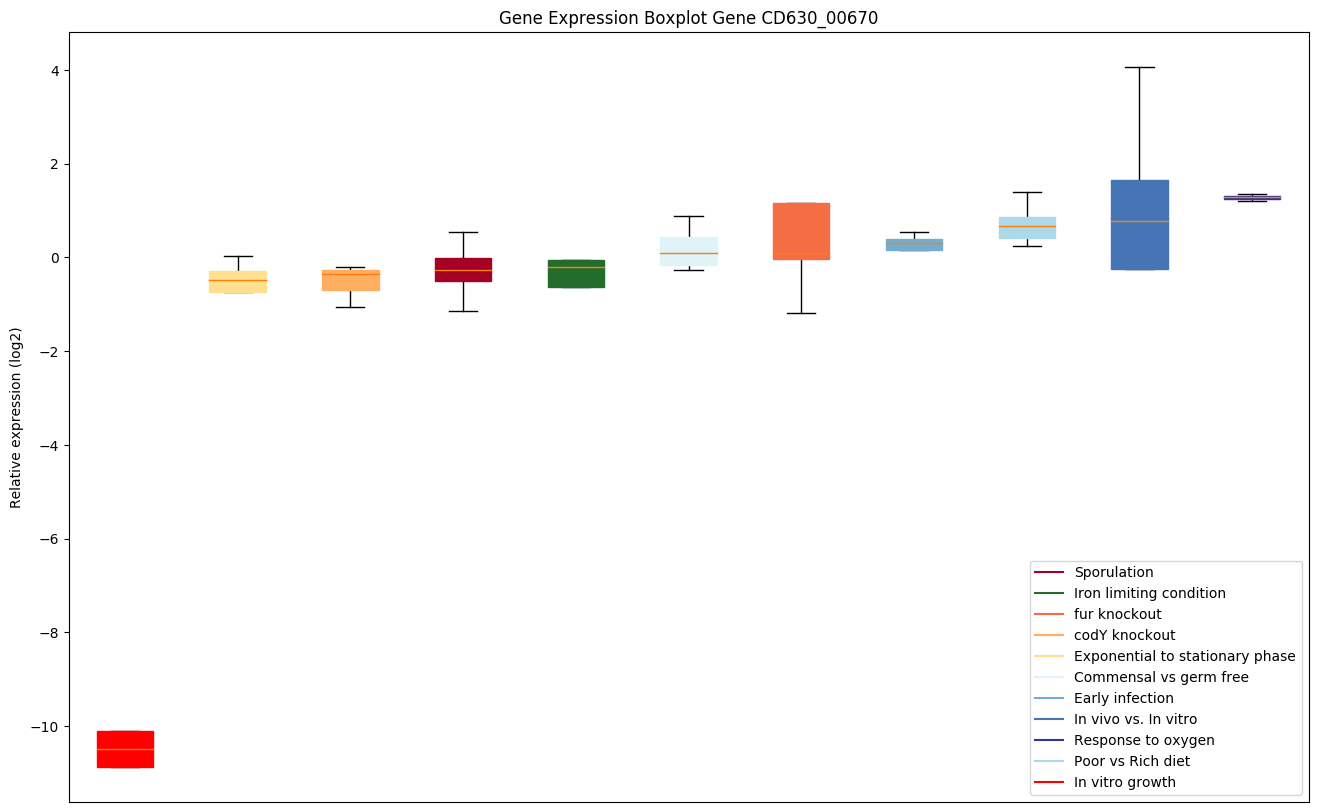
| CD630_00670 | rpoC | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta' | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. | Yes |
 |
||
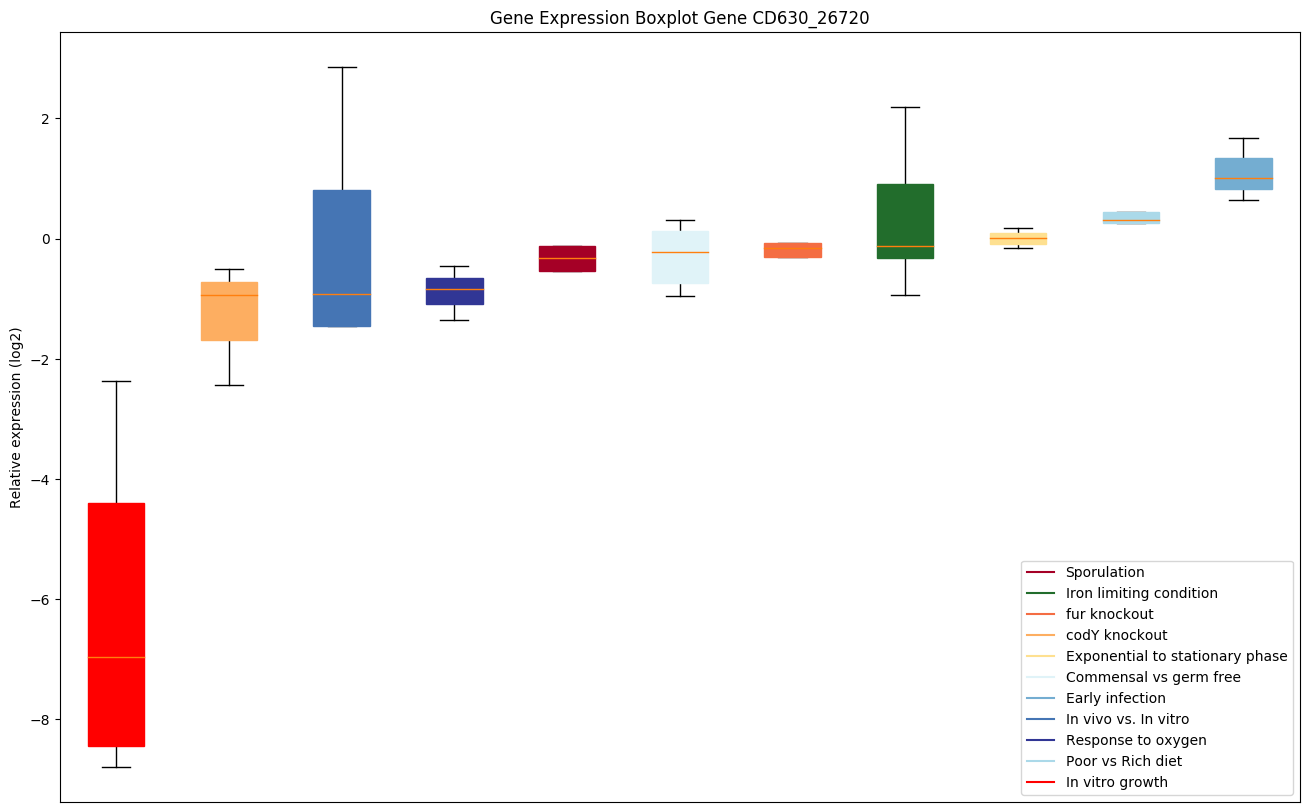
| CD630_26720 | appA | ABC-type transport system, oligopeptide-familysolute-binding protein |
 |
||||
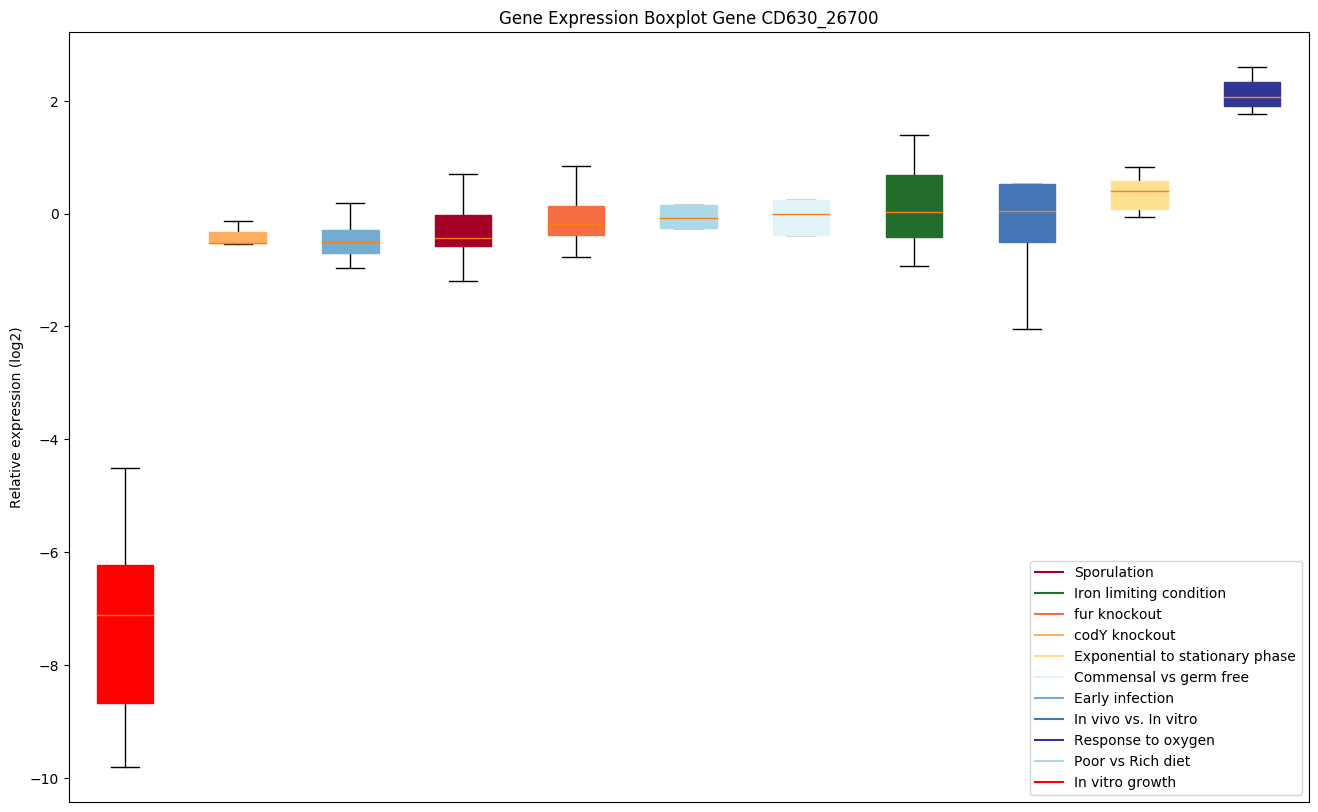
| CD630_26700 | appF | ABC-type transport system, ATP-binding protein |
 |
||||
| CD630_28520 | dltB | D-alanyl transferase DltB, MBOAT family | Could be involved in the transport of activated D-alanine through the membrane. |
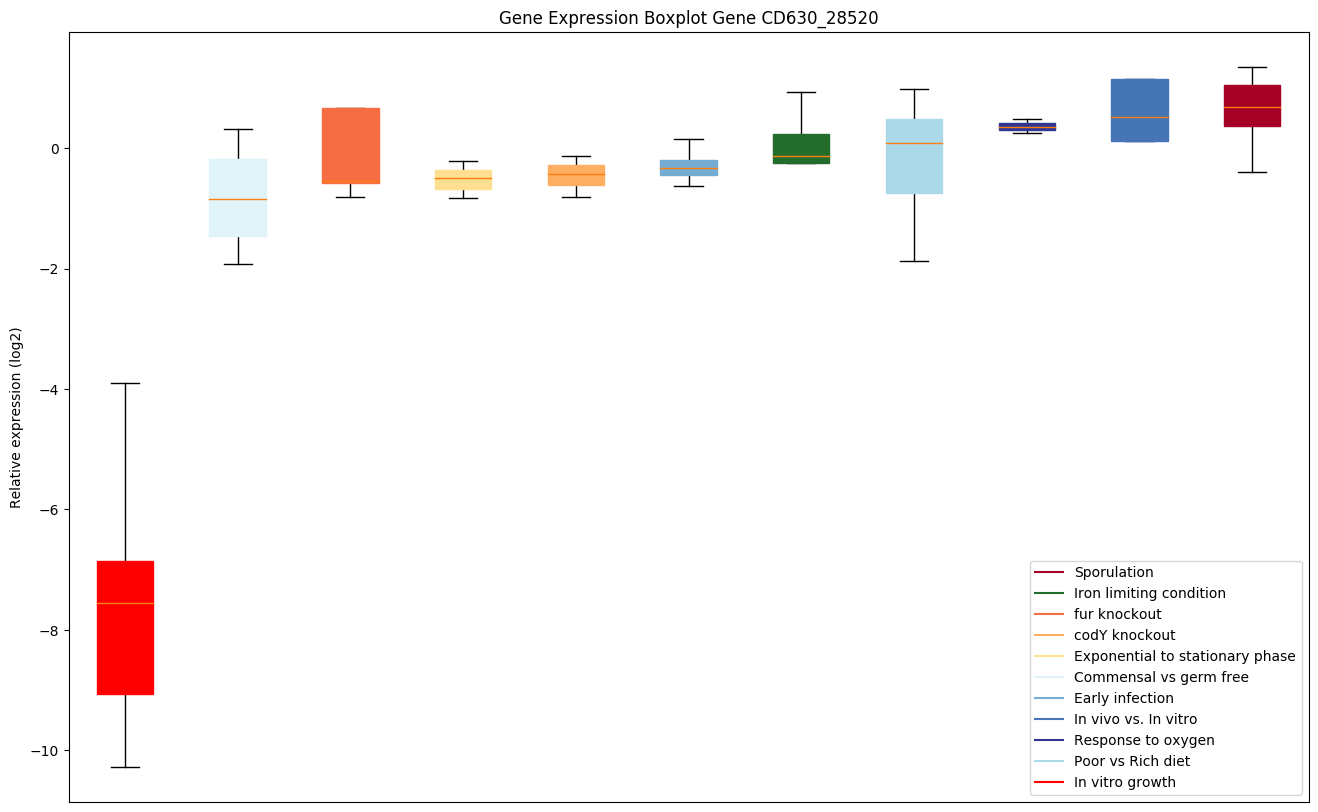 |
|||
| CD630_05480 | Putative penicillin-binding peptidase BlaR1-like,M56 family |
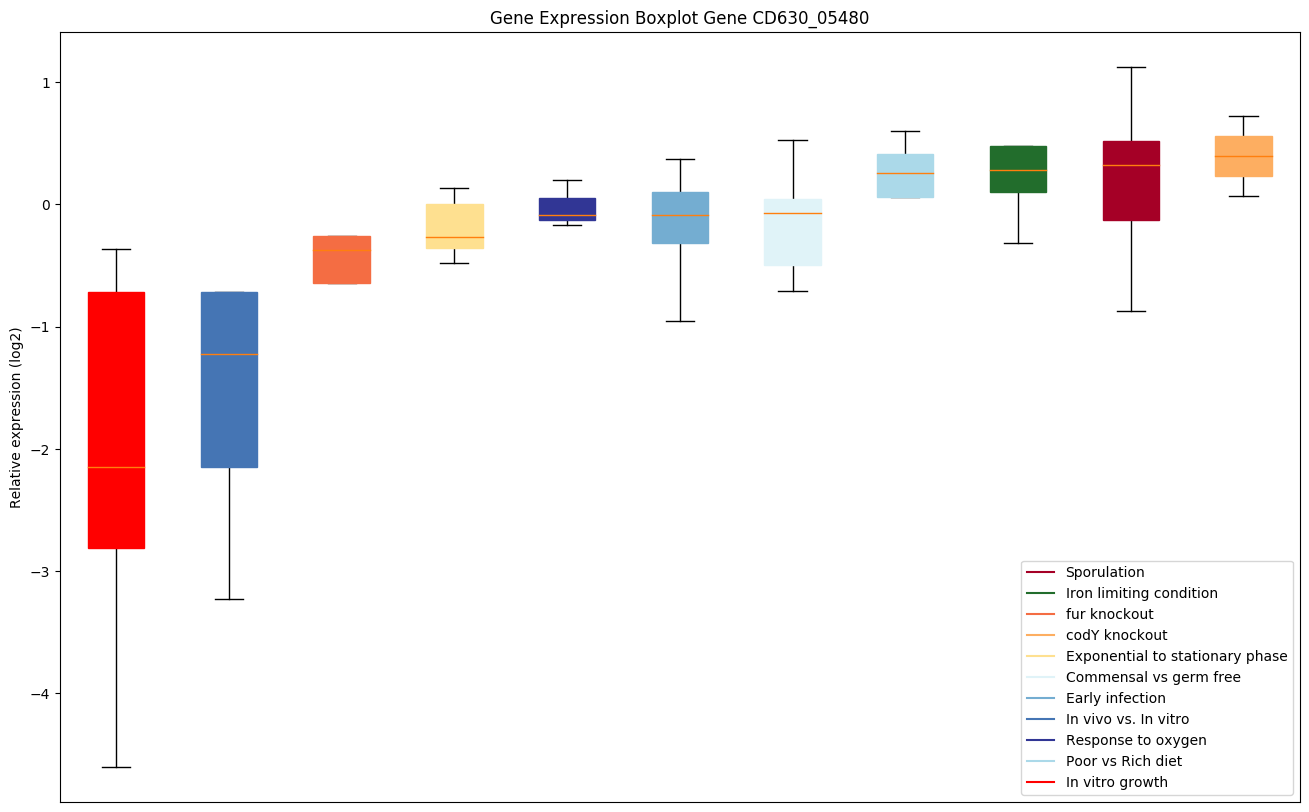 |
|||||
| CD630_28540 | dltD | D-alanine transferase |
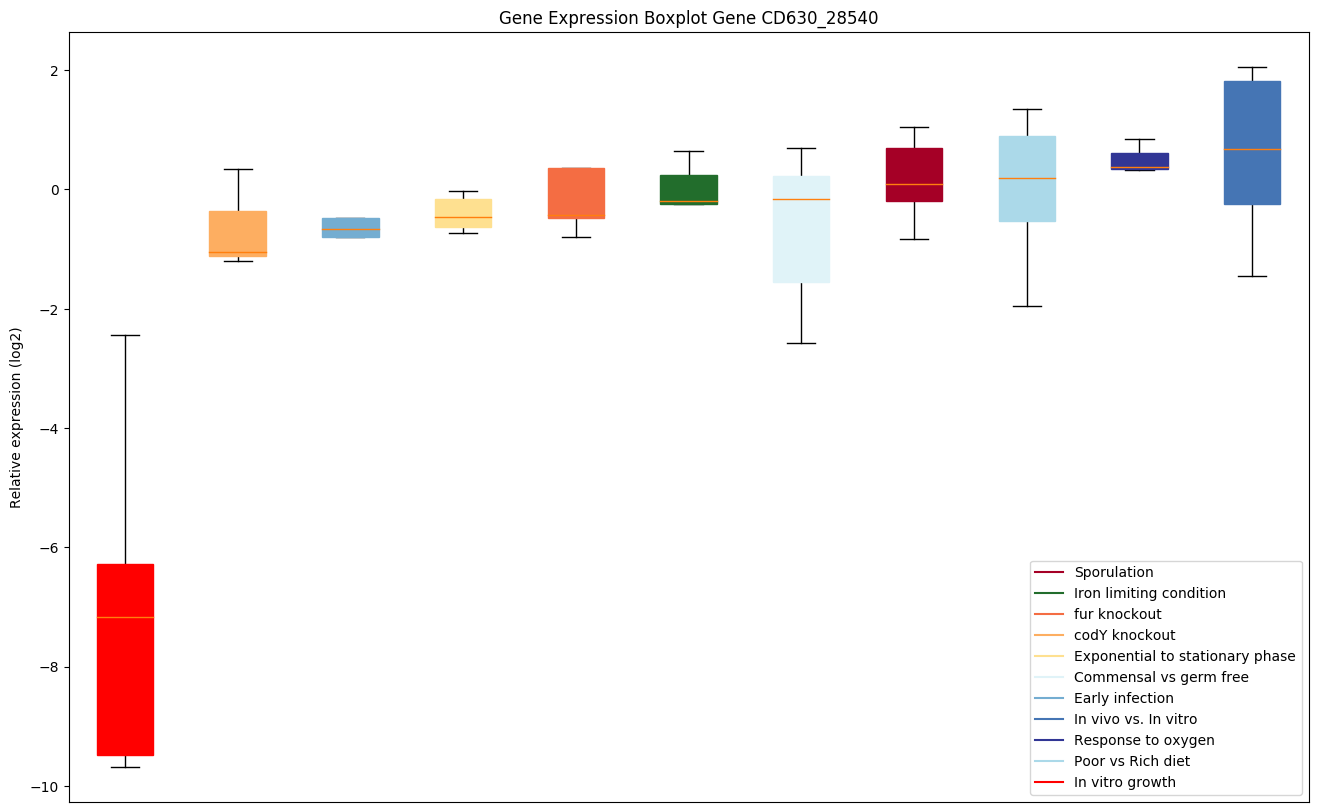 |
||||
| CD630_35560 | Putative membrane protein |
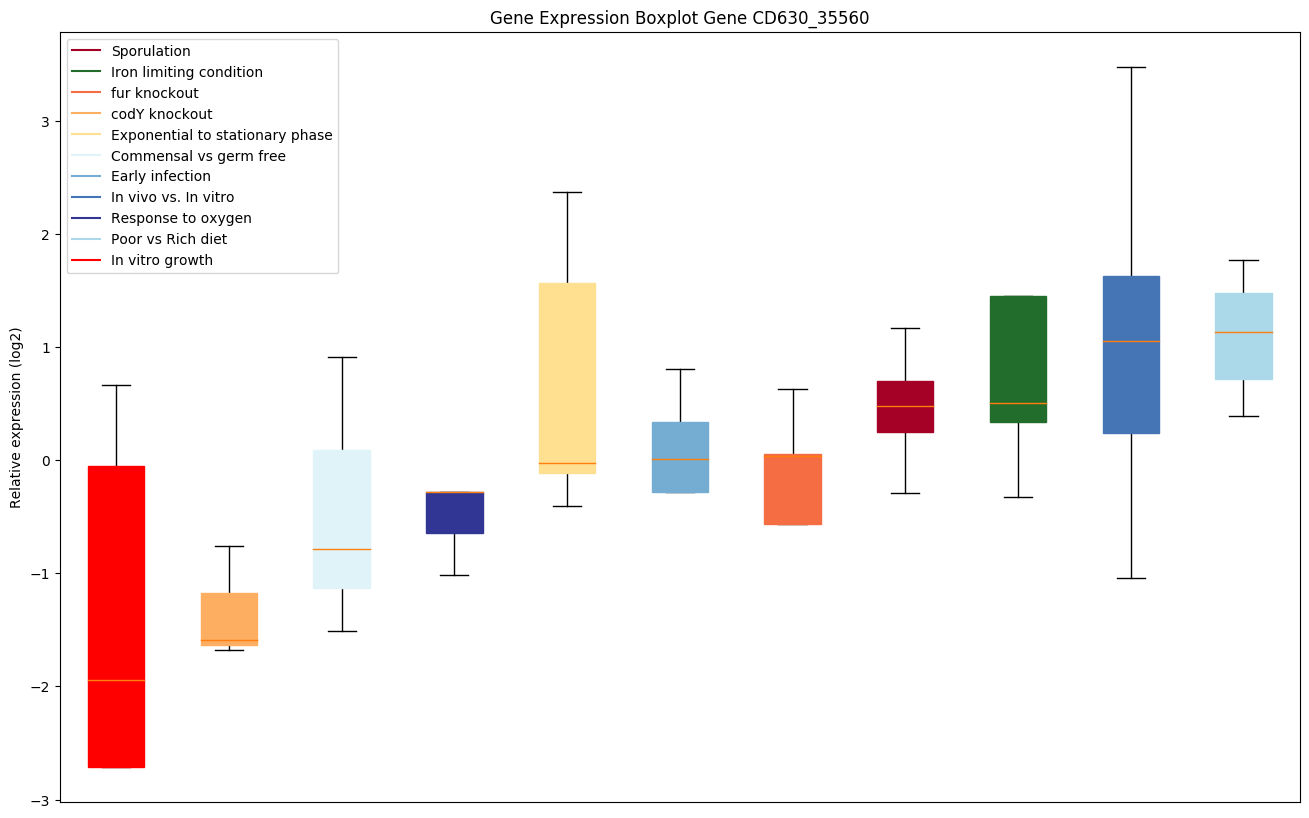 |
|||||
| CD630_28510 | dltC | D-alanine--poly(phosphoribitol) ligase subunit 2(D-alanyl carrier protein) (DCP) | Carrier protein involved in the D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid (LTA). The loading of thioester-linked D-alanine onto DltC is catalyzed by D-alanine--D-alanyl carrier protein ligase DltA. The DltC-carried D-alanyl group is further transferred to cell membrane phosphatidylglycerol (PG) by forming an ester bond, probably catalyzed by DltD. D-alanylation of LTA plays an important role in modulating the properties of the cell wall in Gram-positive bacteria, influencing the net charge of the cell wall. |
 |
|||
| CD630_35540 | dusB | tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase | Catalyzes the synthesis of 5,6-dihydrouridine (D), a modified base found in the D-loop of most tRNAs, via the reduction of the C5-C6 double bond in target uridines. |
 |
|||
| CD630_35520 | lysS | Lysyl-tRNA synthetase (Lysine--tRNA ligase)(LysRS) | Yes |
 |
|||
| CD630_18100 | Transcriptional regulator, beta-lactamsrepressor |
 |
|||||
| CD630_07040 | Putative metal-dependent phosphohydrolase |
 |
|||||
| CD630_26710 | appD | ABC-type transport system, ATP-binding protein |
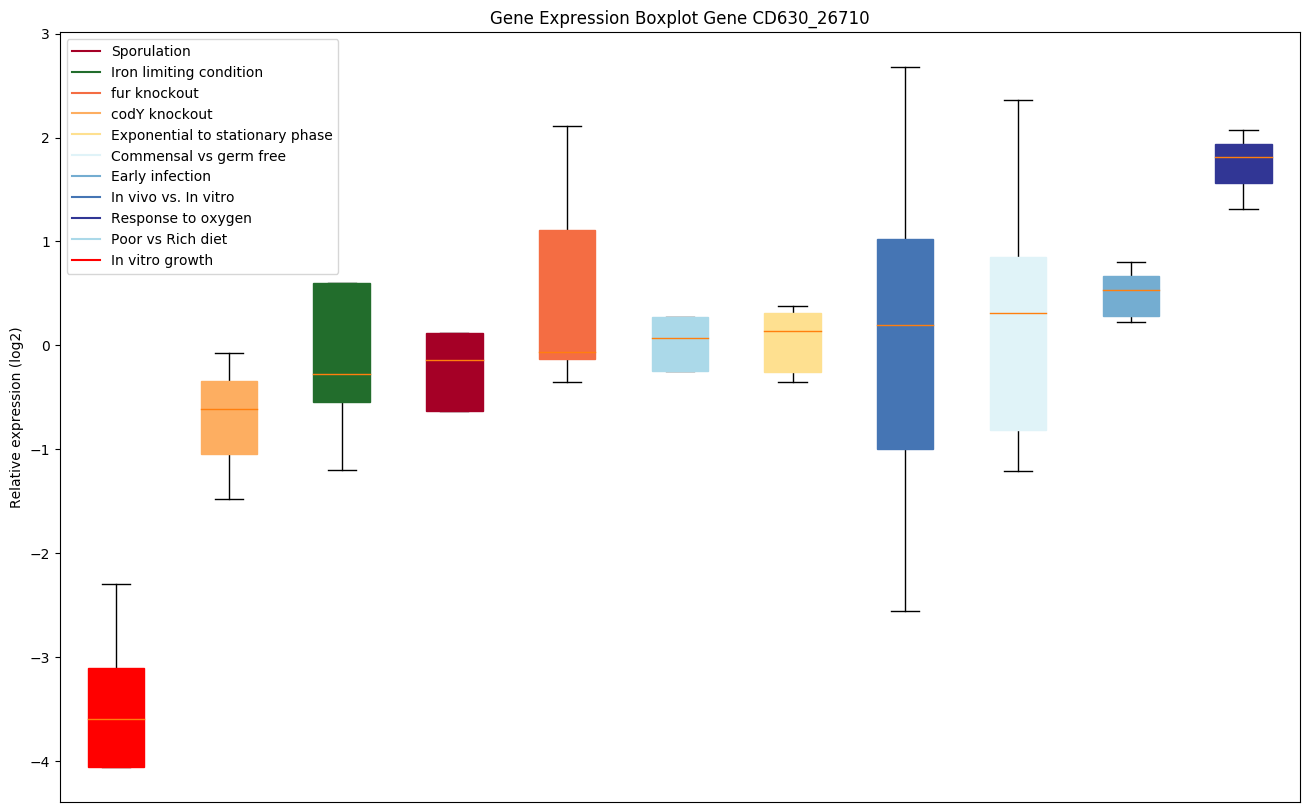 |
||||
| CD630_00660 | rpoB | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. | Yes |
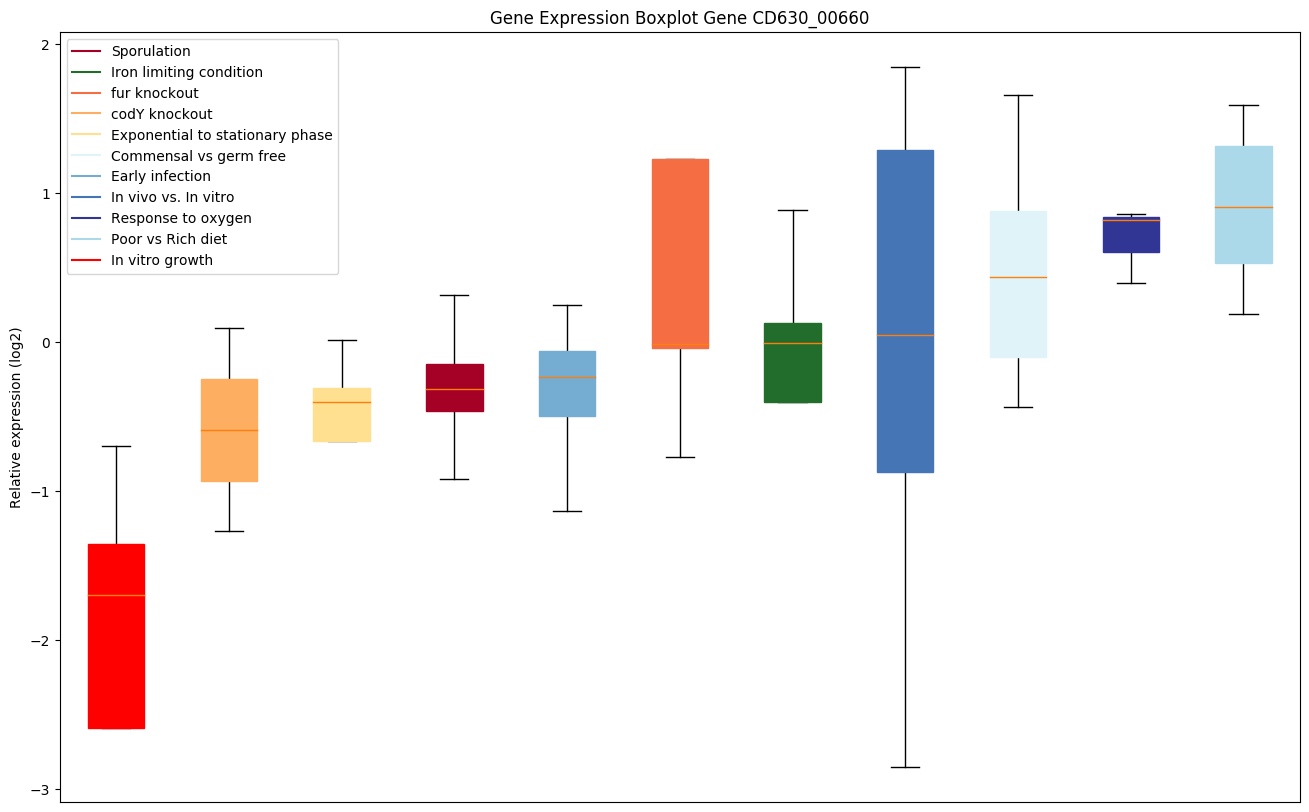 |
||
| CD630_35580 | birA | BirA bifunctional protein [Includes: biotinoperon repressor and biotin--[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase]synthetase | Acts both as a biotin--[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase and a repressor. |
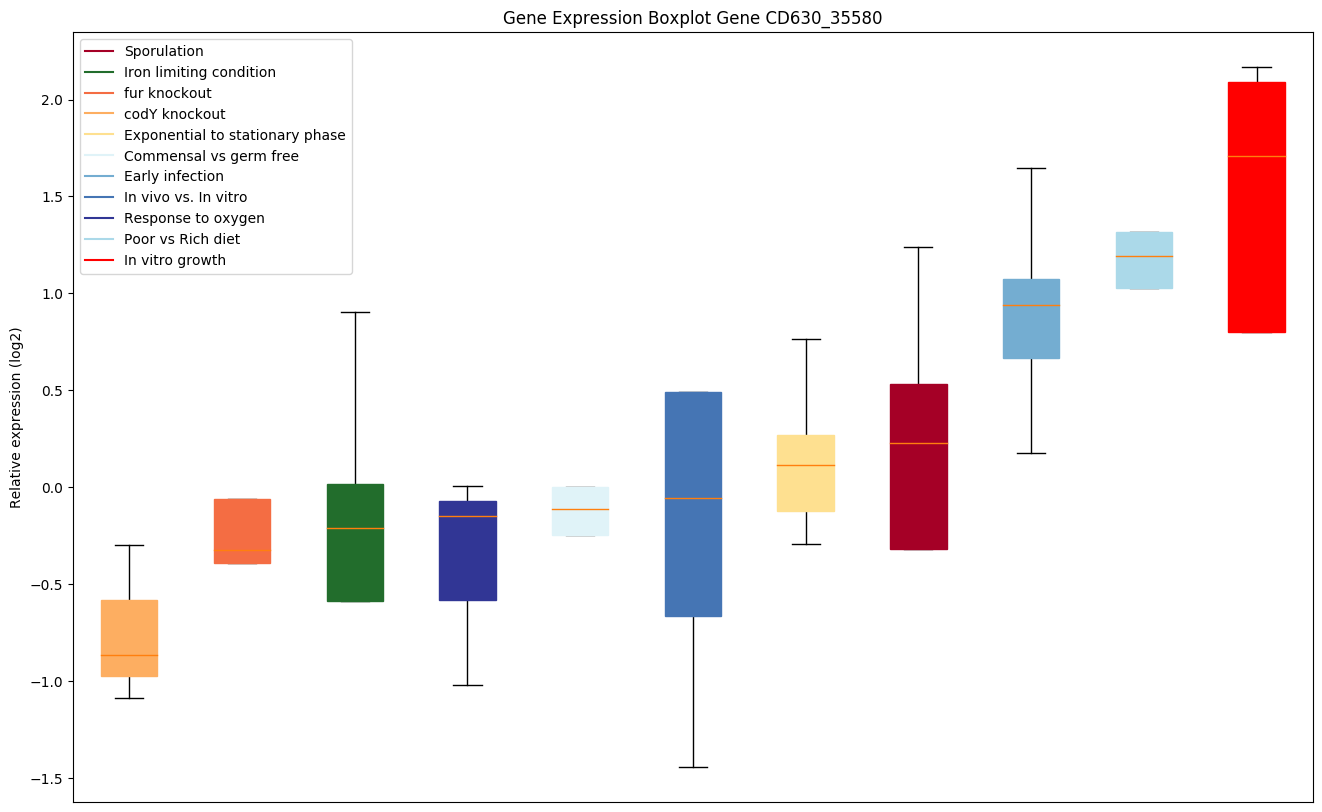 |
|||
| CD630_28530 | dltA | D-alanine--poly(phosphoribitol) ligase subunit 1 | Catalyzes the first step in the D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid (LTA), the activation of D-alanine and its transfer onto the D-alanyl carrier protein (Dcp) DltC. In an ATP-dependent two-step reaction, forms a high energy D-alanyl-AMP intermediate, followed by transfer of the D-alanyl residue as a thiol ester to the phosphopantheinyl prosthetic group of the Dcp. D-alanylation of LTA plays an important role in modulating the properties of the cell wall in Gram-positive bacteria, influencing the net charge of the cell wall. |
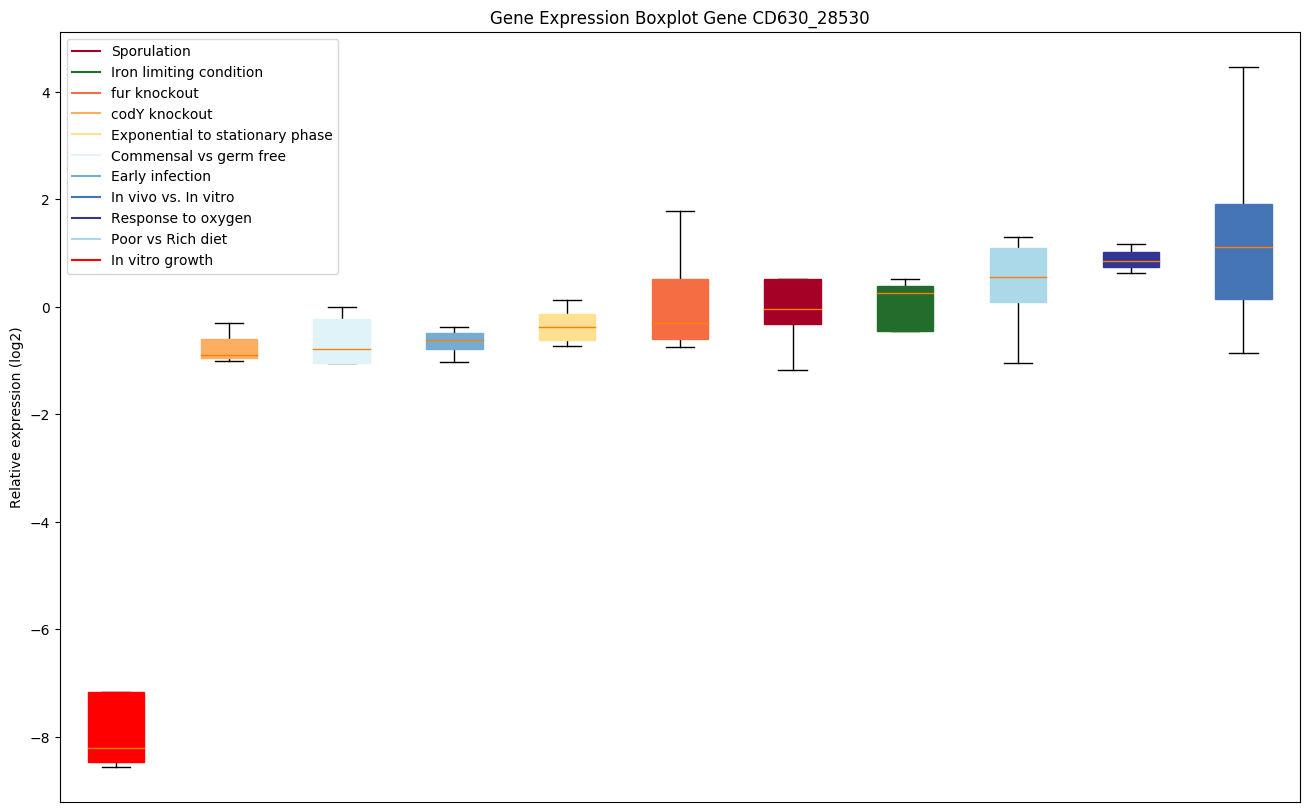 |
|||
| CD630_19630 | Putative methyltransferase |
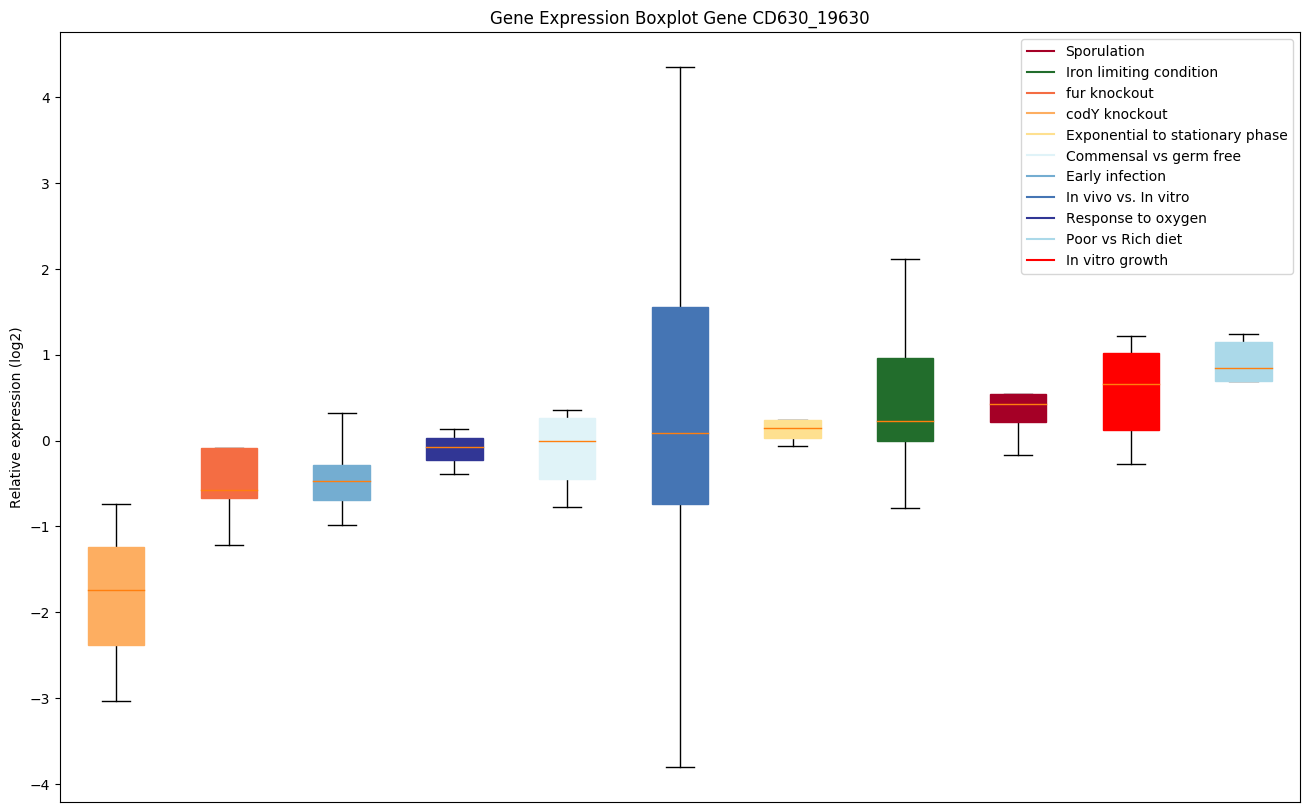 |
|||||
| CD630_35570 | Putative peptidase |
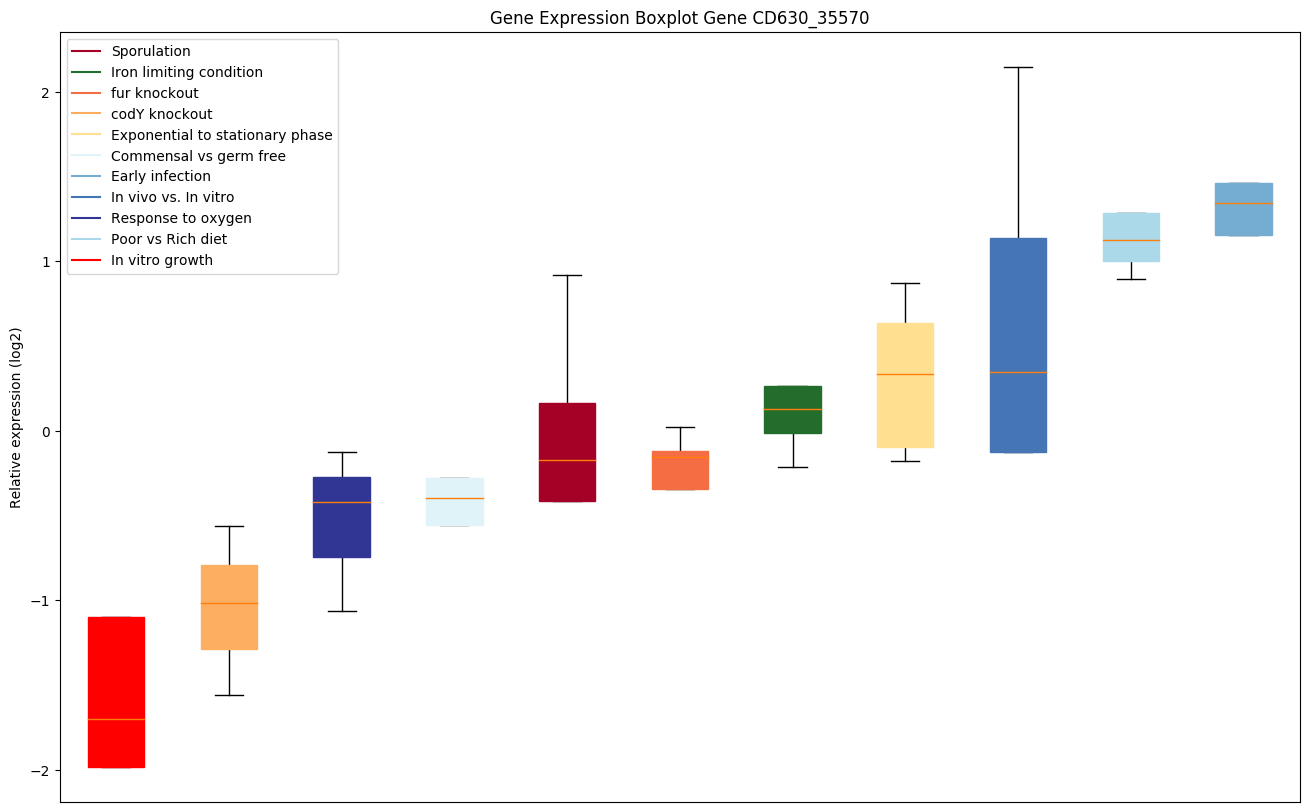 |
|||||
| CD630_35530 | greA | Transcription elongation factor greA (Transcriptcleavage factor GreA) | Necessary for efficient RNA polymerase transcription elongation past template-encoded arresting sites. The arresting sites in DNA have the property of trapping a certain fraction of elongating RNA polymerases that pass through, resulting in locked ternary complexes. Cleavage of the nascent transcript by cleavage factors such as GreA or GreB allows the resumption of elongation from the new 3'terminus. GreA releases sequences of 2 to 3 nucleotides. | Yes |
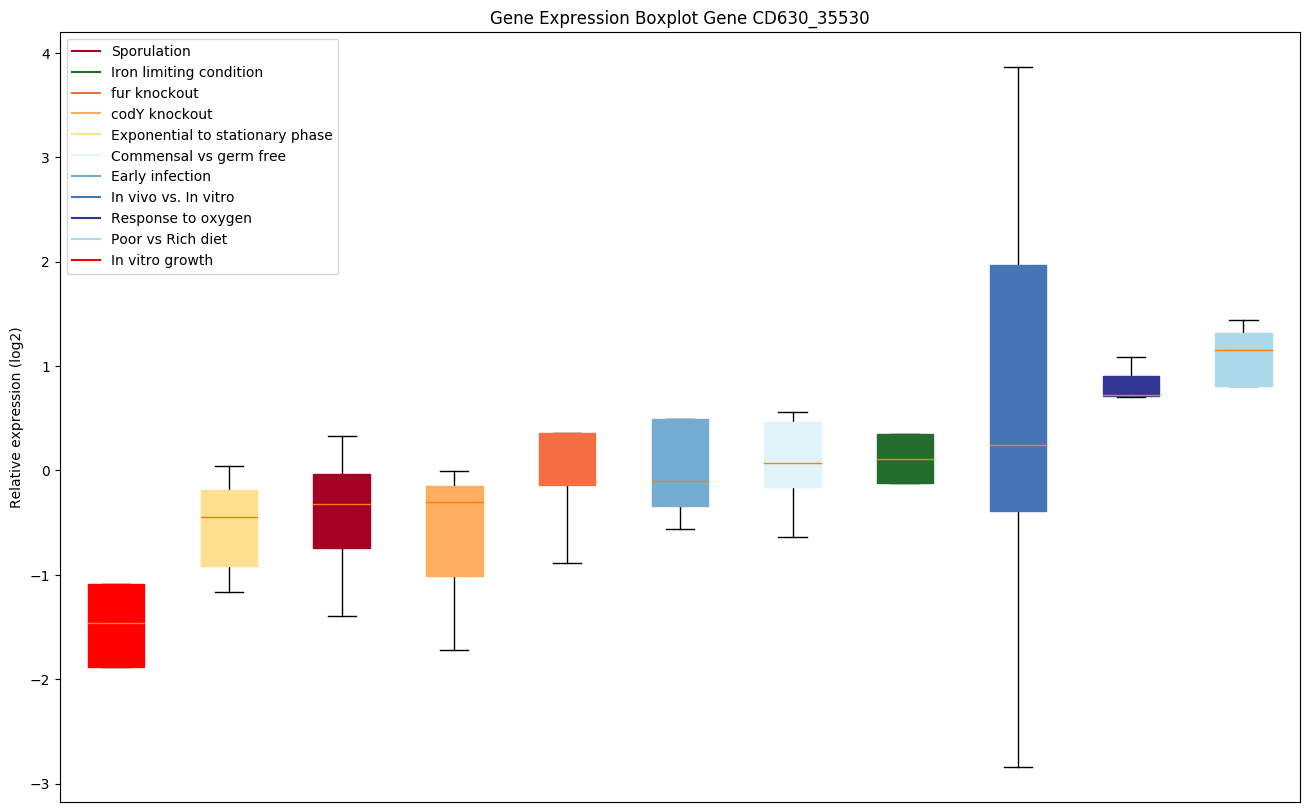 |
||
| CD630_35550 | coaX | Type III pantothenate kinase (Pantothenic acidkinase) (PanK-III) | Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pantothenate (Pan), the first step in CoA biosynthesis. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
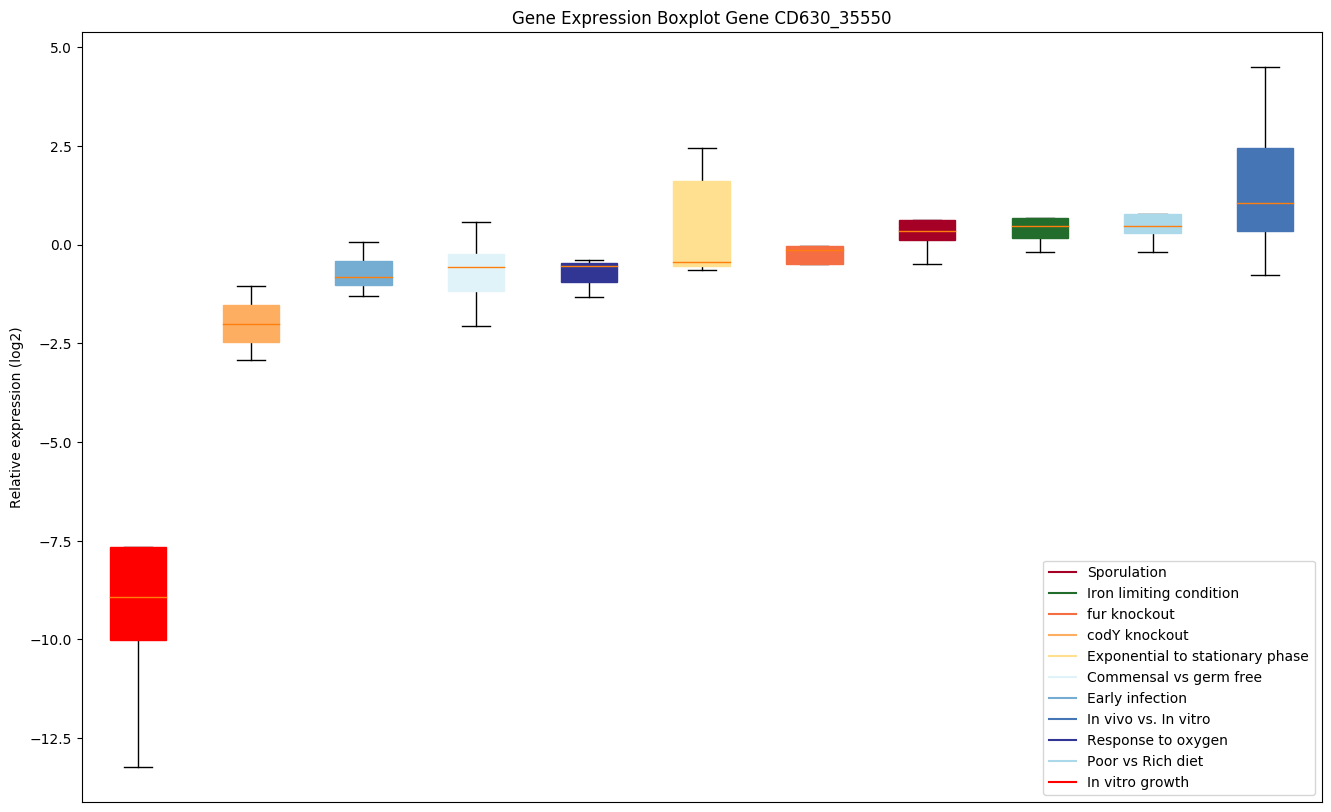 |
| CD630_02030 | Putative UvrABC system protein A 1 (UvrA protein1) (Excinuclease ABC subunit A 1) | The UvrABC repair system catalyzes the recognition and processing of DNA lesions. UvrA is an ATPase and a DNA-binding protein. A damage recognition complex composed of 2 UvrA and 2 UvrB subunits scans DNA for abnormalities. When the presence of a lesion has been verified by UvrB, the UvrA molecules dissociate. |
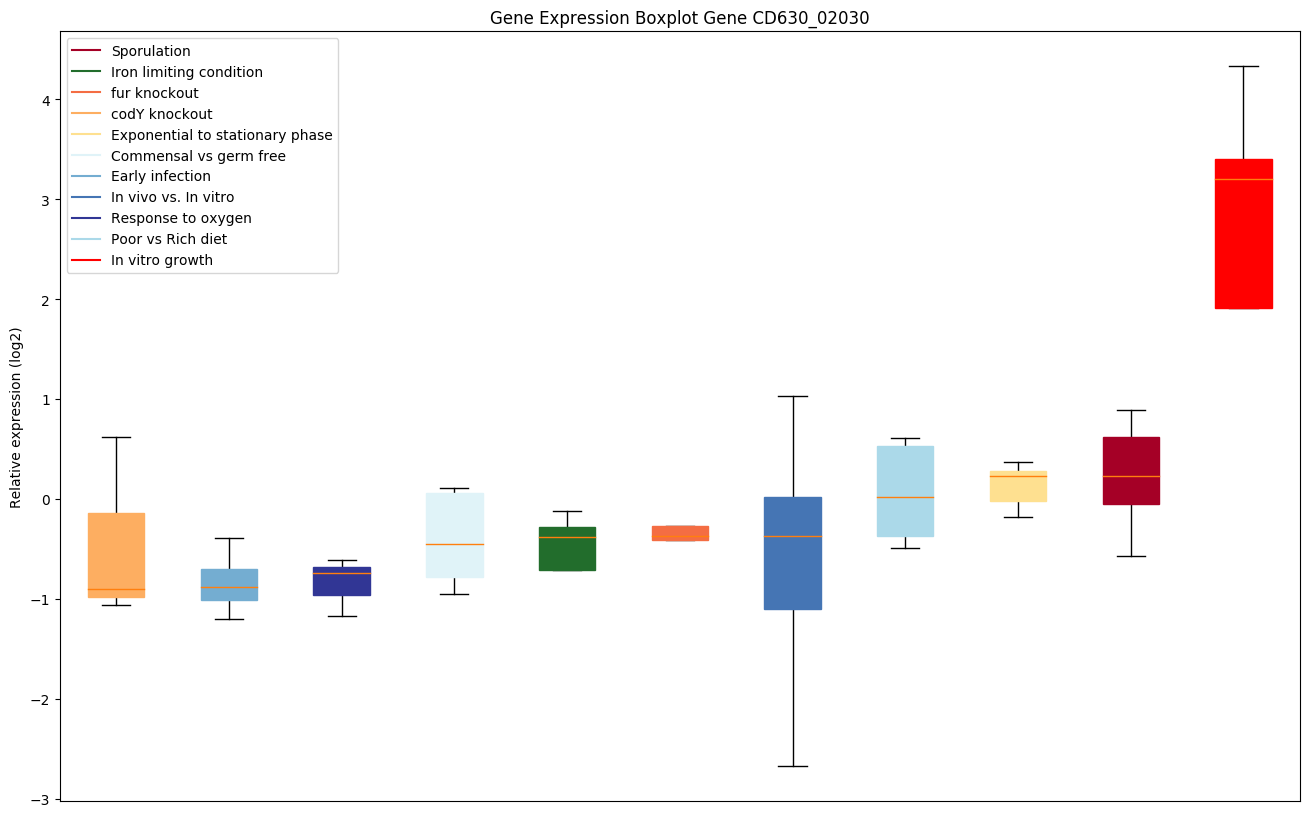 |
||||
| CD630_07030 | Putative peptidase, U32 family |
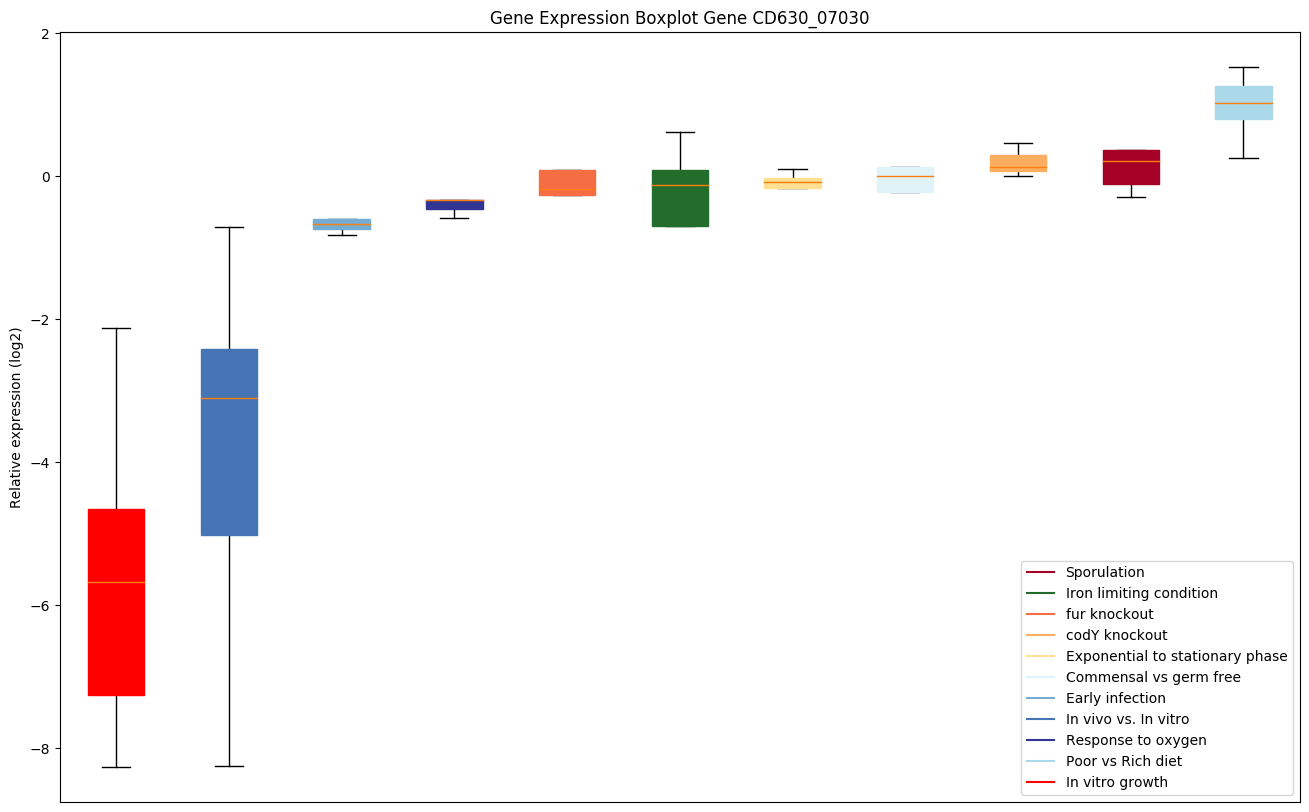 |
|||||
| CD630_07050 | Putative hydrolase, NUDIX family |
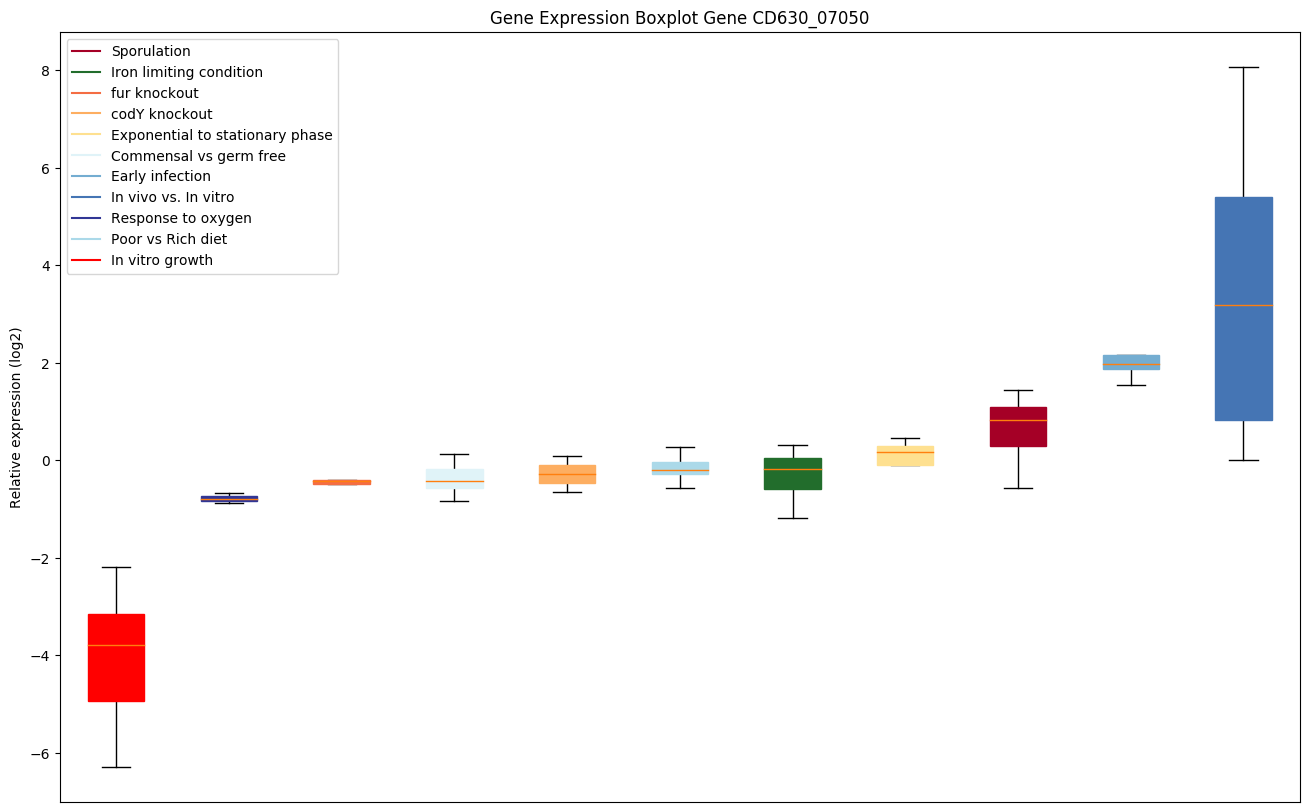 |
|||||
| CD630_36690 | Putative lipoprotein |
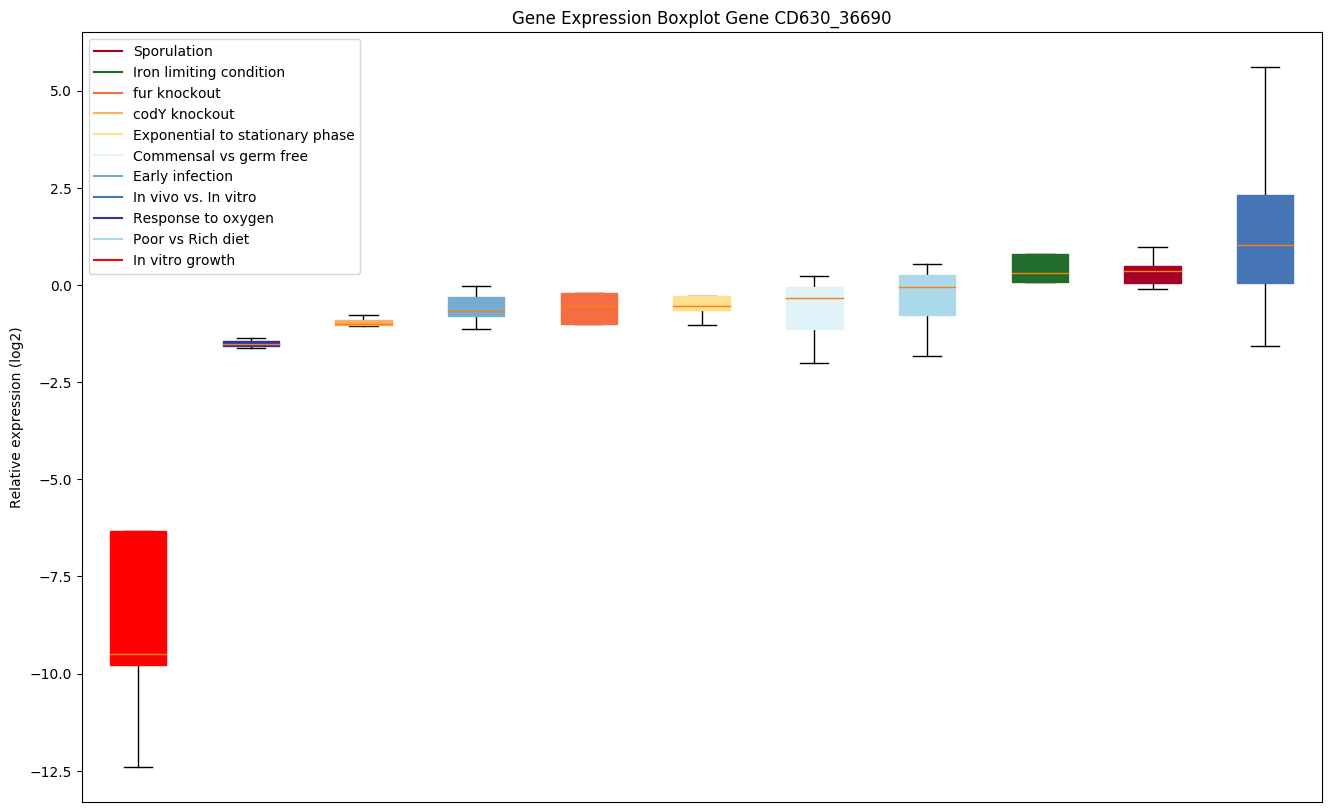 |
|||||
| CD630_05470 | Transcriptional regulator, beta-lactamsrepressor | Yes |
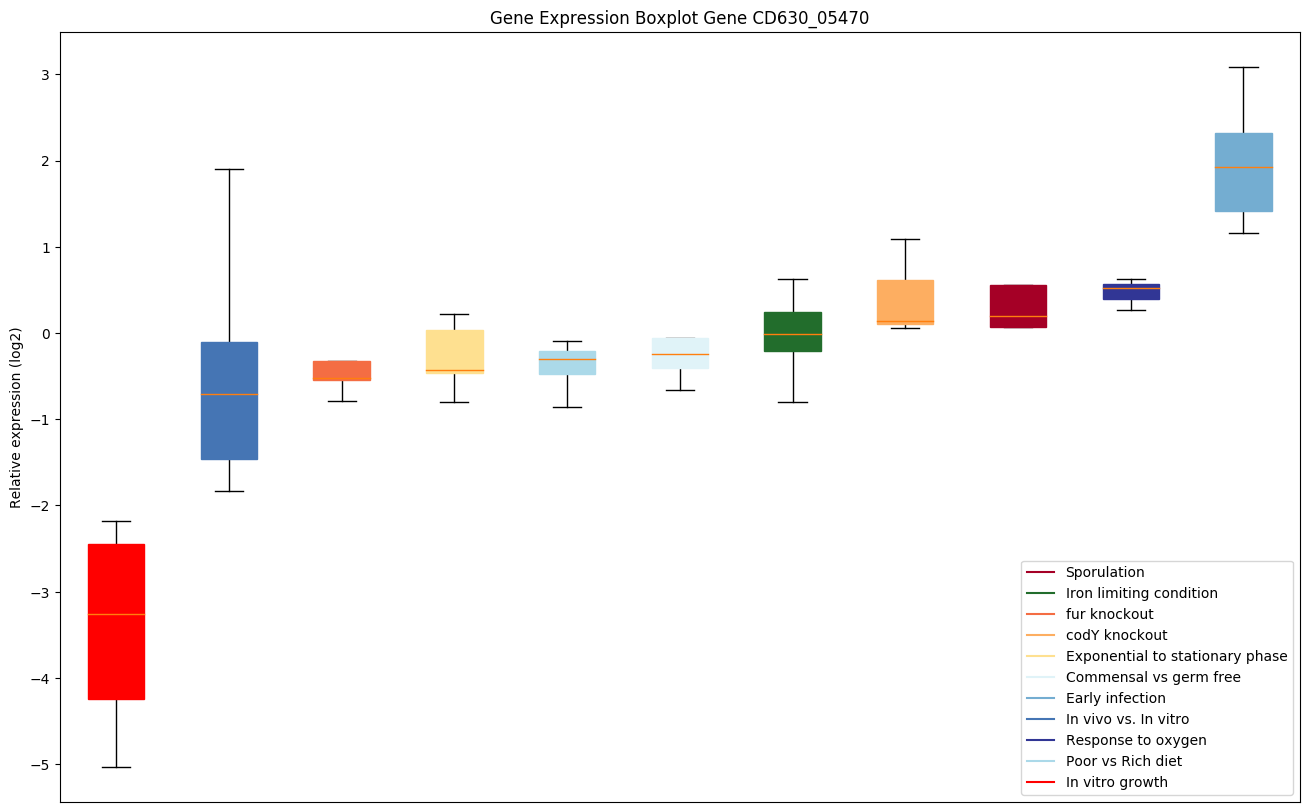 |
||||
| CD630_26740 | appC | ABC-type transport system, oligopeptide-familypermease protein |
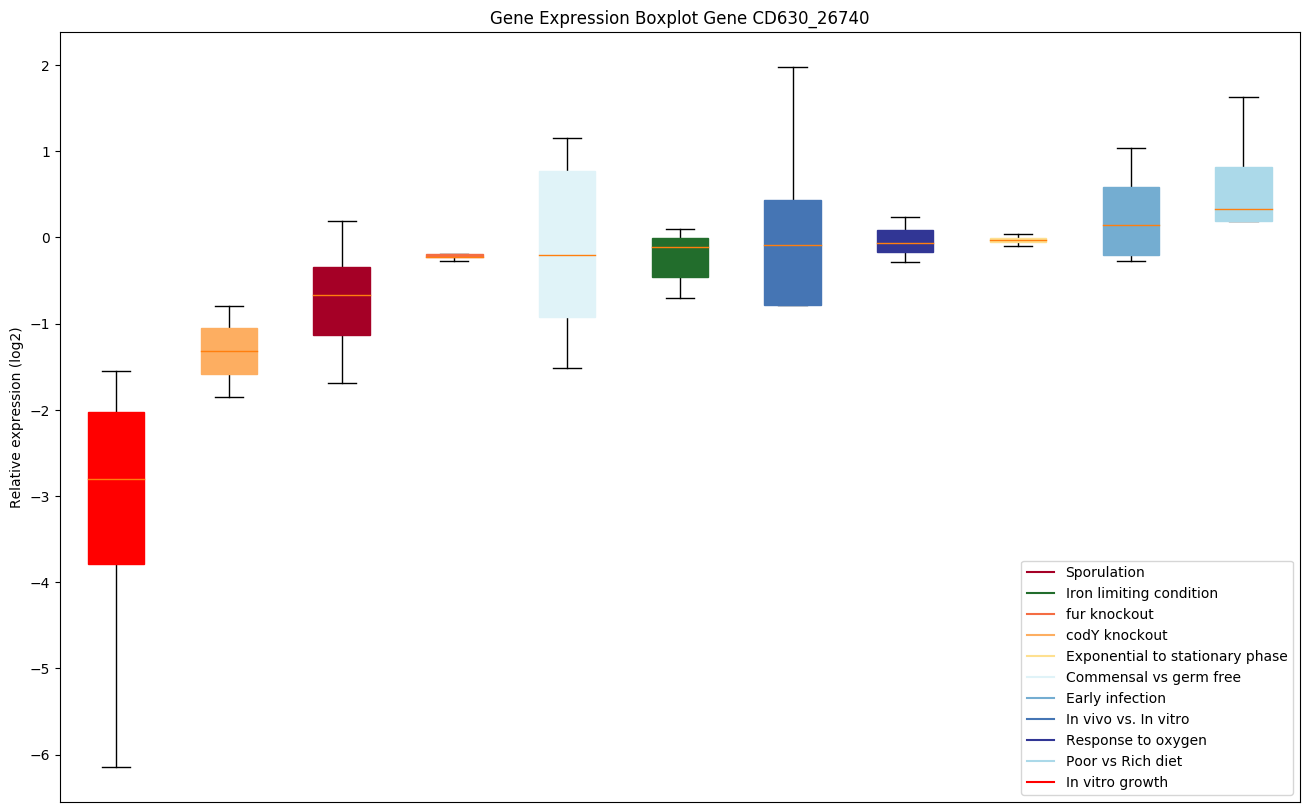 |