Organism : Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough
| Module List :

Regulation information for DVU2918
(Mouseover regulator name to see its description)
| Regulator | Module | Operator |
|---|---|---|
| DVU1949 DVU0569 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2036 DVU2275 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2036 DVU2633 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2275 | 109 | tf |
| DVU2547 DVU0539 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2547 DVU2675 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2644 | 109 | tf |
| DVU2675 | 109 | tf |
| DVU2675 DVU0539 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2886 DVU2195 |
109 | combiner |
| DVU2960 DVU0569 |
109 | combiner |
| DVUA0024 | 109 | tf |
| DVU0057 | 238 | tf |
| DVU0653 DVU2251 |
238 | combiner |
| DVU0936 DVU0653 |
238 | combiner |
| DVU1754 DVU3334 |
238 | combiner |
| DVU2111 DVU1517 |
238 | combiner |
| DVU2788 DVU0936 |
238 | combiner |
| DVU2886 DVU0525 |
238 | combiner |

Motif information (de novo identified motifs for modules)
There are 4 motifs predicted.
Click on the RegPredict links to explore the motif in RegPredict.
| Motif Id | e-value | Consensus | Motif Logo | RegPredict |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 209 | 5.60e-02 | caCgggGcaACAgGccAtGCa |
 |
RegPredict |
| 210 | 1.20e+01 | cGgc.tg.TGC |
 |
RegPredict |
| 455 | 1.20e+02 | GcGCGAcgTGTgccgggccatGTG |
 |
RegPredict |
| 456 | 5.60e+02 | GgATgccgtcT |
 |
RegPredict |

Module neighborhood information for DVU2918
| Gene | Common Name | Description | Module membership |
|---|---|---|---|
| DVU0010 | TRAP transporter subunit DctQ | 182, 238 | |
| DVU0011 | TRAP transporter solute receptor DctP | 238, 260 | |
| DVU0053 | sulfate permease | 109, 205 | |
| DVU0125 | hypothetical protein DVU0125 | 26, 109 | |
| DVU0137 | hypothetical protein DVU0137 | 109, 175 | |
| DVU0164 | cation efflux family protein | 109, 261 | |
| DVU0171 | hemolysin-like protein | 82, 238 | |
| DVU0188 | hypothetical protein DVU0188 | 106, 238 | |
| DVU0406 | hypothetical protein DVU0406 | 127, 238 | |
| DVU0423 | universal stress protein | 60, 109 | |
| DVU0424 | cls | cardiolipin synthetase | 26, 109 |
| DVU0435 | hypothetical protein DVU0435 | 161, 238 | |
| DVU0437 | RND family efflux transporter MFP subunit | 68, 238 | |
| DVU0457 | EAL domain-containing protein | 238, 322 | |
| DVU0568 | tRNA 2-selenouridine synthase | 51, 238 | |
| DVU0586 | hypothetical protein DVU0586 | 109, 189 | |
| DVU0611 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 26, 109 | |
| DVU0631 | hypothetical protein DVU0631 | 109, 112 | |
| DVU0770 | hypothetical protein DVU0770 | 109, 256 | |
| DVU0981 | multiphosphoryl transfer protein | 109, 269 | |
| DVU1088 | hypothetical protein DVU1088 | 26, 109 | |
| DVU1216 | hypothetical protein DVU1216 | 238, 305 | |
| DVU1253 | hypothetical protein DVU1253 | 25, 238 | |
| DVU1358 | HAD superfamily hydrolase | 109, 123 | |
| DVU1420 | Hpt domain-containing protein | 109, 192 | |
| DVU1421 | hypothetical protein DVU1421 | 68, 238 | |
| DVU1436 | hypothetical protein DVU1436 | 109, 123 | |
| DVU1657 | hypothetical protein DVU1657 | 26, 109 | |
| DVU1920 | hypothetical protein DVU1920 | 109, 320 | |
| DVU1924 | hypC | hydrogenase assembly chaperone HypC/HupF | 109, 229 |
| DVU1925 | GDSL family lipase | 109, 229 | |
| DVU1926 | hypothetical protein DVU1926 | 14, 109 | |
| DVU2081 | hypothetical protein DVU2081 | 238, 302 | |
| DVU2093 | thiH | thiamine biosynthesis protein ThiH | 46, 238 |
| DVU2242 | asparaginase family protein | 84, 238 | |
| DVU2297 | glycine/betaine/L-proline ABC transporter periplasmic-binding protein | 109, 179 | |
| DVU2321 | hypothetical protein DVU2321 | 238, 316 | |
| DVU2411 | EF hand domain-containing protein | 109, 224 | |
| DVU2414 | hypothetical protein DVU2414 | 109, 281 | |
| DVU2429 | hypothetical protein DVU2429 | 105, 109 | |
| DVU2450 | tatA | twin arginine translocase protein A | 7, 109 |
| DVU2610 | hypothetical protein DVU2610 | 238, 316 | |
| DVU2629 | hypothetical protein DVU2629 | 161, 238 | |
| DVU2775 | hypothetical protein DVU2775 | 109, 205 | |
| DVU2918 | hypothetical protein DVU2918 | 109, 238 | |
| DVU2936 | hypothetical protein DVU2936 | 26, 109 | |
| DVU3063 | mviN-2 | integral membrane protein MviN | 238, 305 |
| DVU3137 | fabG | 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase | 109, 123 |
| DVU3217 | hypothetical protein DVU3217 | 109, 192 | |
| DVU3256 | mutM | formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase | 238, 320 |
| DVU3282 | ADP-ribosylglycohydrolase family protein | 109, 192 | |
| DVU3376 | sulfatase family protein | 238, 254 | |
| DVU3377 | dgkA | diacylglycerol kinase | 25, 238 |
| DVU3394 | hypothetical protein DVU3394 | 25, 238 |
Gene Page Help
Network Tab
If the gene is associated with a module(s), its connection to given modules along with other members of that module are shown as network by using CytoscapeWeb. In this view, each green colored circular nodes represent module member genes, purple colored diamonds represent module motifs and red triangles represent regulators. Each node is connected to module (Bicluster) via edges. This representation provides quick overview of all genes, regulators and motifs for modules. It also allows one to see shared genes/motifs/regulators among diferent modules.
Network representation is interactive. You can zoom in/out and move nodes/edges around. Clicking on a node will open up a window to give more details. For genes, Locus tag, organism, genomic coordinates, NCBI gene ID, whether it is transcription factor or not and any associated functional information will be shown. For regulators, number of modules are shown in addition to gene details. For motifs, e-value, consensus sequence and sequence logo will be shown. For modules, expression profile plot, motif information, functional associations and motif locations for each member of the module will be shown.
You can pin information boxes by using button in the box title and open up additional ones on the same screen for comparative analysis.
Regulation Tab
Regulation tab for each gene includes regulatory influences such as environmental factors or transcription factors or their combinations identified by regulatory network inference algorithms.
If the gene is a member of a module, regulators influencing that module are also considered to regulate the gene. Regulators table list total number of regulatory influences, regulators, modules and type of the influence.
You can see description of the regulator inside the tooltip when you mouseover. In certain cases the regulatory influence is predicted to be the result of the combination of two influences. These are indicated as combiner in the column labeled "Operator".
For transcription factors, an additional table next to regulator table will be show. This table show modules that are influenced by the transcription factor.
Motifs Tab
Network inference algorithm uses de novo motif prediction for assigning genes to modules. If there are any motifs identified in the upstream region of a gene, the motif will be shown here. For each motif sequence logo, consensus and e-value will be shown.
Functions Tab
Identification of functional enrichment for the module members is important in associating predicted motifs and regulatory influences with pathways. As described above, the network inference pipeline includes a functional enrichment module by which hypergeometric p-values are used to identify over representation of functional ontology terms among module members.
Network Portal presents functional ontologies from KEGG, GO, TIGRFAM, and COG as separate tables that include function name, type, corrected and uncorrected hypergeometric p-values, and the number of genes assigned to this category out of total number of genes in the module.
Module Members Tab
Identity of gene members in a module may help to identify potential interactions between different functional modules. Therefore, neighbor genes that share the same module(s) with gene under consideration are shown here. For each memebr, gene name, description and modules that contain it are listed.
Help Tab
This help page. More general help can be accessed by clicking help menu in the main navigation bar.
CircVis
Our circular module explorer is adapted from visquick originally developed by Dick Kreisberg of Ilya Shmulevich lab at ISB for The Cancer Genome Atlas. We use simplified version of visquick to display distribution of module members and their interactions across the genome. This view provides summary of regulation information for a gene. The main components are;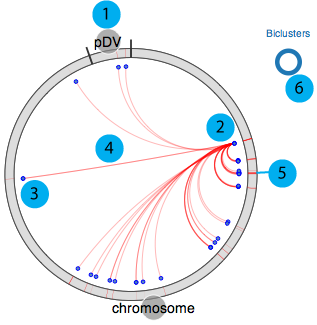
- 1. All genomic elements for the organism are represented as a circle and each element is separated by black tick marks. In this example chromosome and pDV represent main chromosome and plasmid for D. vulgaris Hildenborough, respectively.
- 2. Source gene
- 3. Target genes (other module members)
- 4. Interactions between source and target genes for a particular module
- 5. Module(s) that source gene and target genes belong to
- 6. Visualisation legend


 Module member
Module member 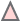 Regulator
Regulator 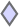 Motif
Motif 
Social Tab
Network Portal is designed to promote collaboration through social interactions. Therefore interested researchers can share information, questions and updates for a particular gene.
Users can use their Disqus, Facebook, Twitter or Google accounts to connect to this page (We recommend Google). Each module and gene page includes comments tab that lists history of the interactions for that gene. You can browse the history, make updates, raise questions and share these activities with social web.
In the next releases of the network portal, we are planning to create personal space for each user where you can share you space that contains all the analysis steps you did along with relevant information.