Module 310
Summary
| Residual | Gene Count | Condition Count | 1st Q Condition Block * | 5th Q Condition Block * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.54 | 23 | 64 | NA | NA |
Bicluster expression profile
Expression of genes in subset of conditions included in bicluster on left side of red dashed line and out of bicluster on right of red dashed line. Each condition is represented as a boxplot, ordered by their median expression for the bicluster genes (smallest to largest) and colored according to condition blocks.
|
|
de novo identified motifs are listed below
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
1. Betas: correspond to the average coefficients of the Bayesian regressions between module expression and TF expression profiles. The values indicate the magnitude and direction (activation or repression for positive or negative values, respectively) of each TF-module interaction.
2. Confidence scores: indicate the likelihood of the TF-module interactions.
| TF | Module | Confidence Score | Beta |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Two-component response regulator |
310 | 0.45 | 0.3236 |
The module is significantly enriched with genes associated to the indicated functional terms
Genes that are included in this module
* "Gene essentiality is based on TnSeq Data from: Dembek M, Barquist L, Boinett CJ, et al. High-throughput analysis of gene essentiality and sporulation in Clostridium difficile. mBio. 2015;6(2):e02383. Published 2015 Feb 24.doi:10.1128/mBio.02383-14".
| Title | Short Name | Product | Function | Essentiality * | in vivo Essentiality | Rich broth Essentiality | Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
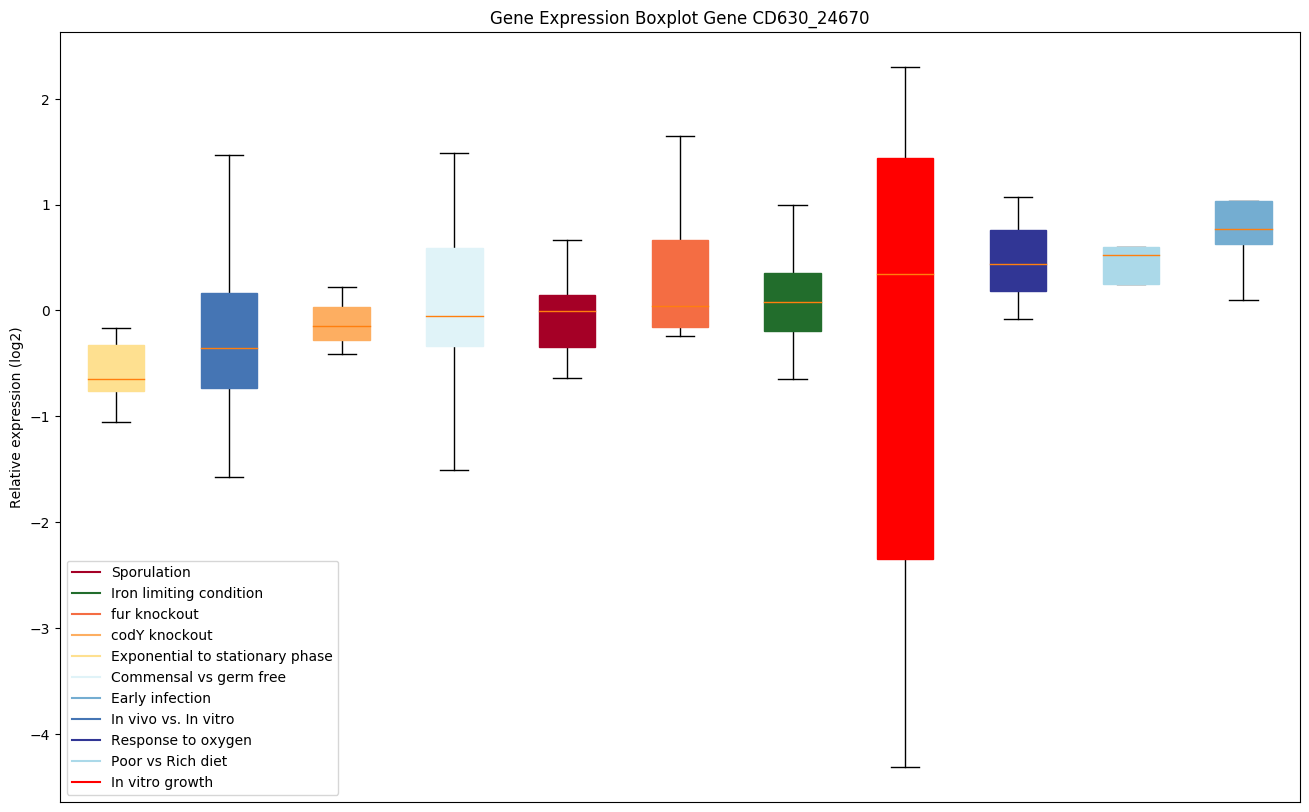
| CD630_24670 | lepA | GTP-binding protein LepA | Required for accurate and efficient protein synthesis under certain stress conditions. May act as a fidelity factor of the translation reaction, by catalyzing a one-codon backward translocation of tRNAs on improperly translocated ribosomes. Back-translocation proceeds from a post-translocation (POST) complex to a pre-translocation (PRE) complex, thus giving elongation factor G a second chance to translocate the tRNAs correctly. Binds to ribosomes in a GTP-dependent manner. |
 |
|||
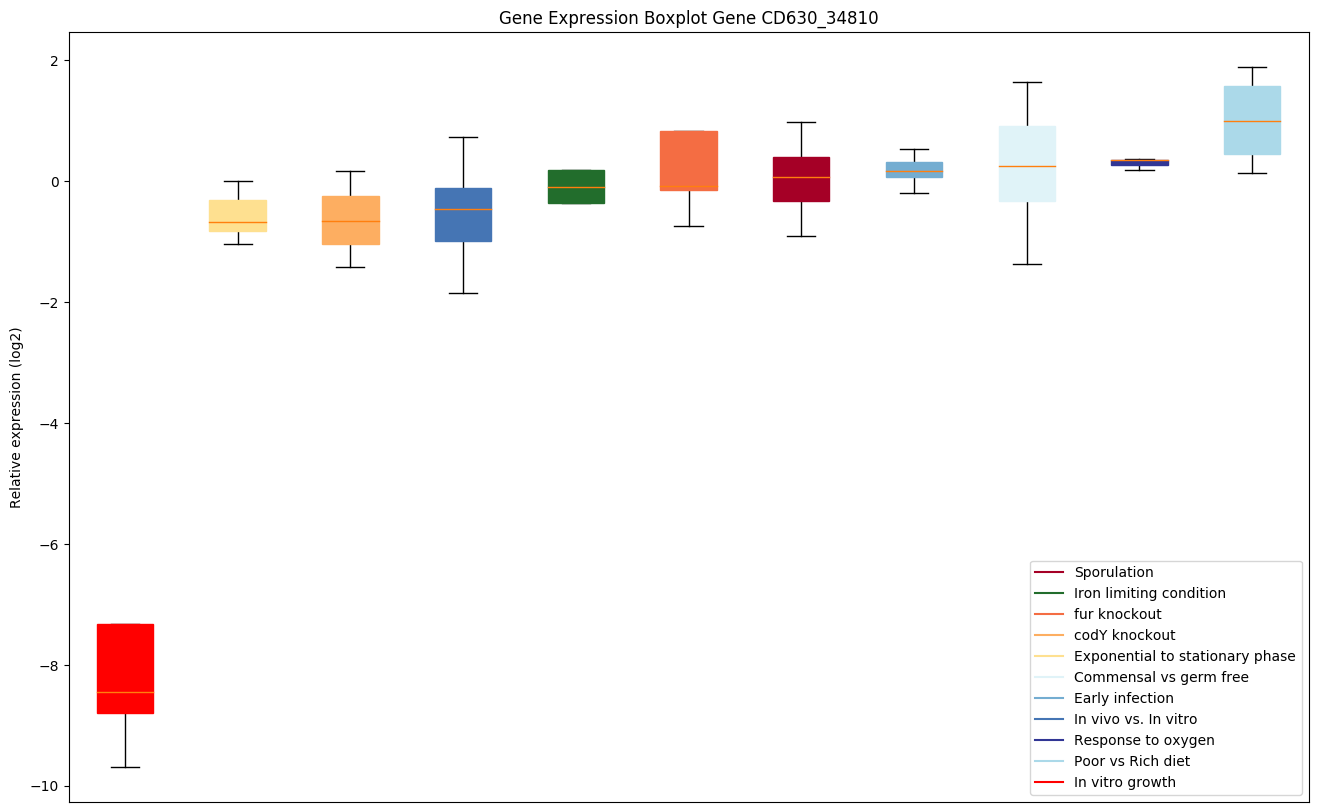
| CD630_34810 | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase reductase |
 |
|||||
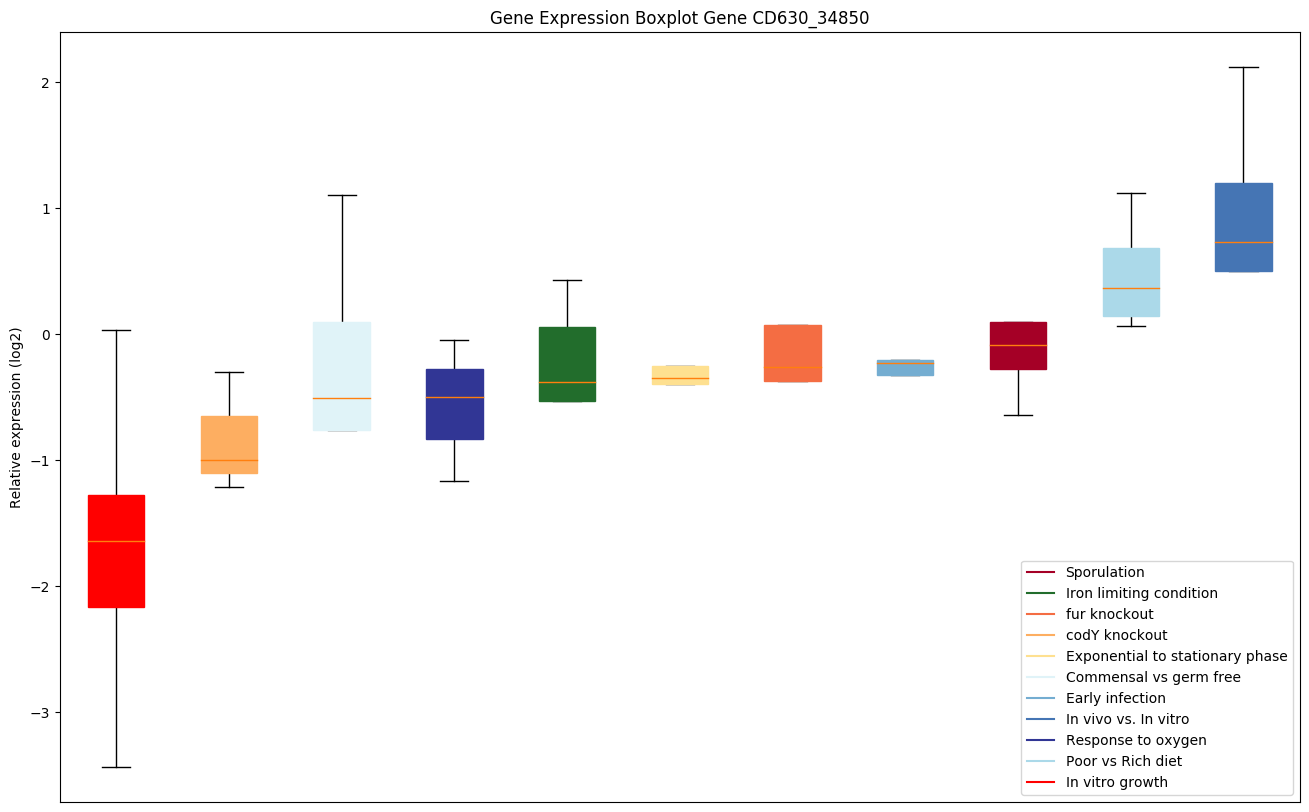
| CD630_34850 | hemK | Modification methylase HemK | Methylates the class 1 translation termination release factors RF1/PrfA and RF2/PrfB on the glutamine residue of the universally conserved GGQ motif. |
 |
|||
| CD630_34830 | Putative zinc/iron permease |
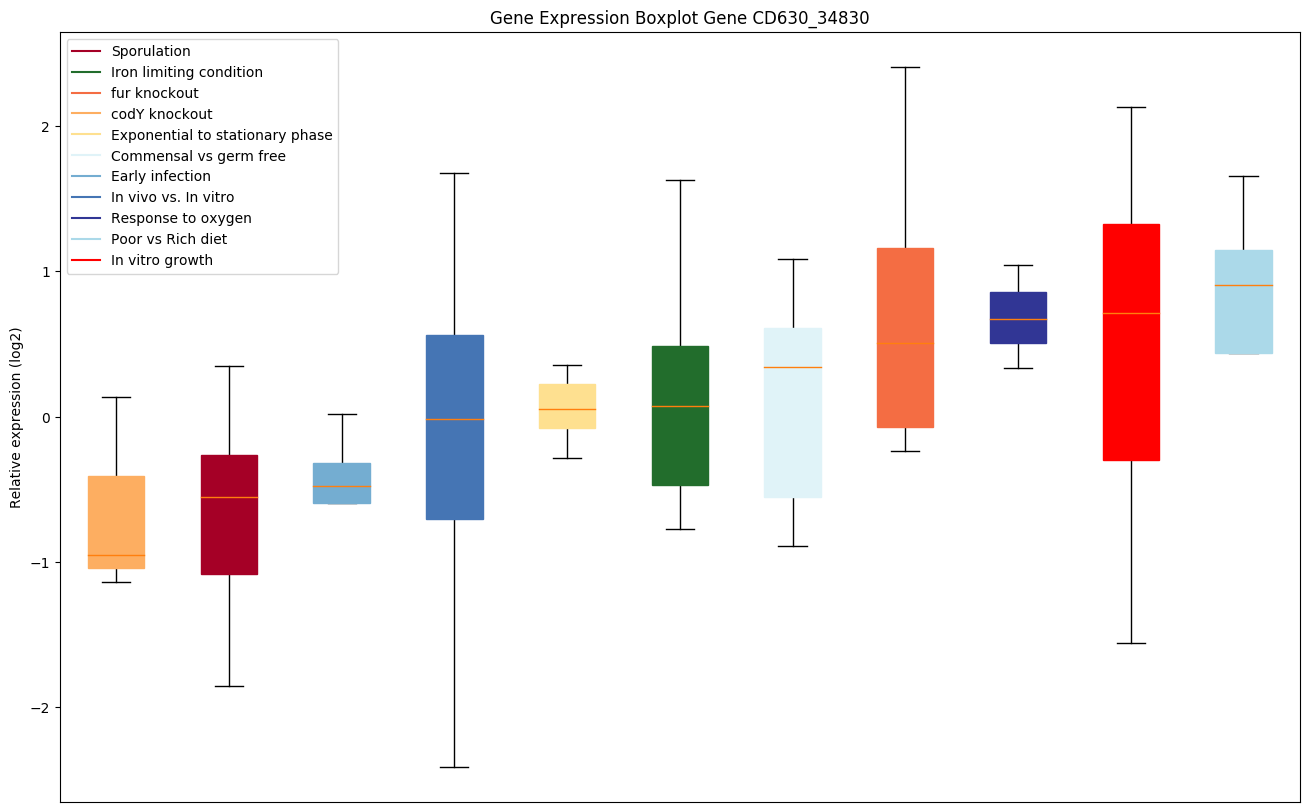 |
|||||
| CD630_34870 | rho | Transcription termination factor Rho | Facilitates transcription termination by a mechanism that involves Rho binding to the nascent RNA, activation of Rho's RNA-dependent ATPase activity, and release of the mRNA from the DNA template. |
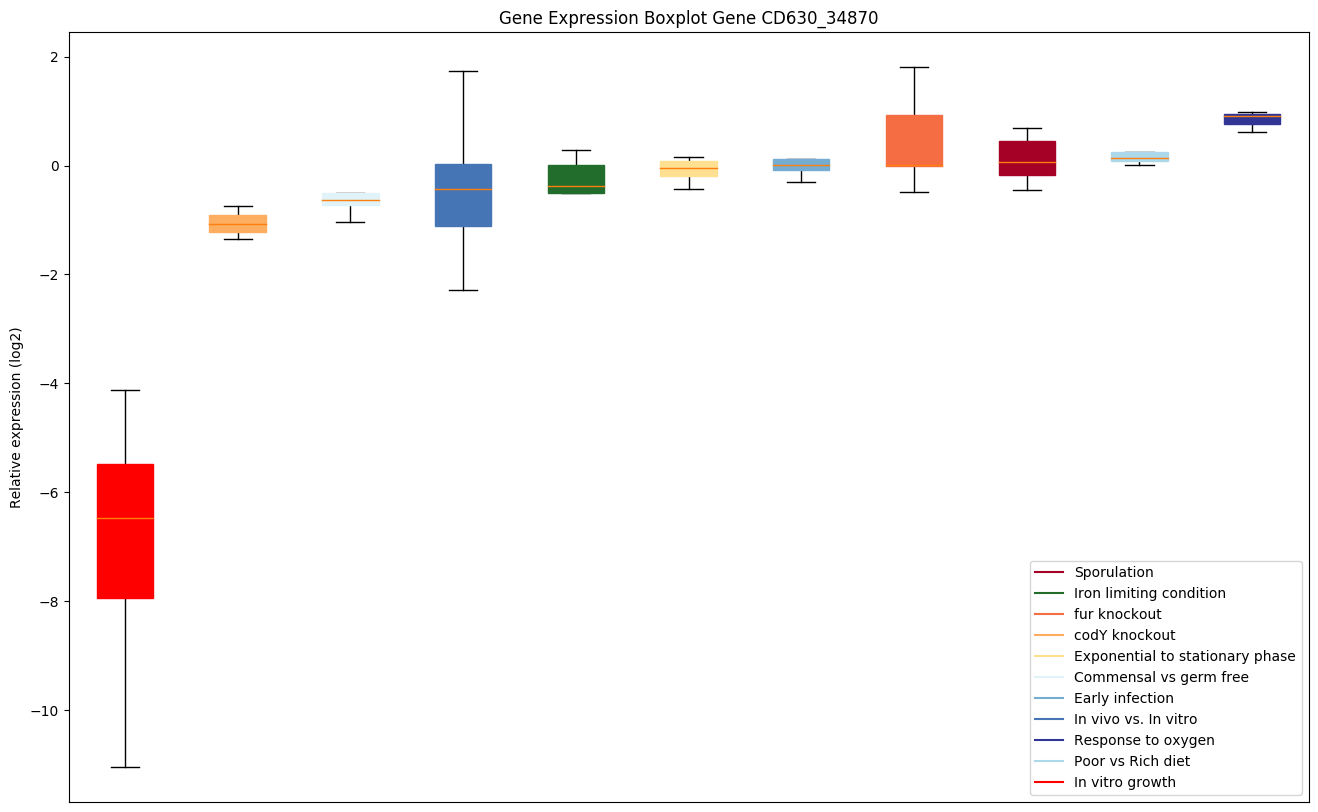 |
|||
| CD630_34840 | prfA | Peptide chain release factor 1 (RF-1) | Peptide chain release factor 1 directs the termination of translation in response to the peptide chain termination codons UAG and UAA. | Yes |
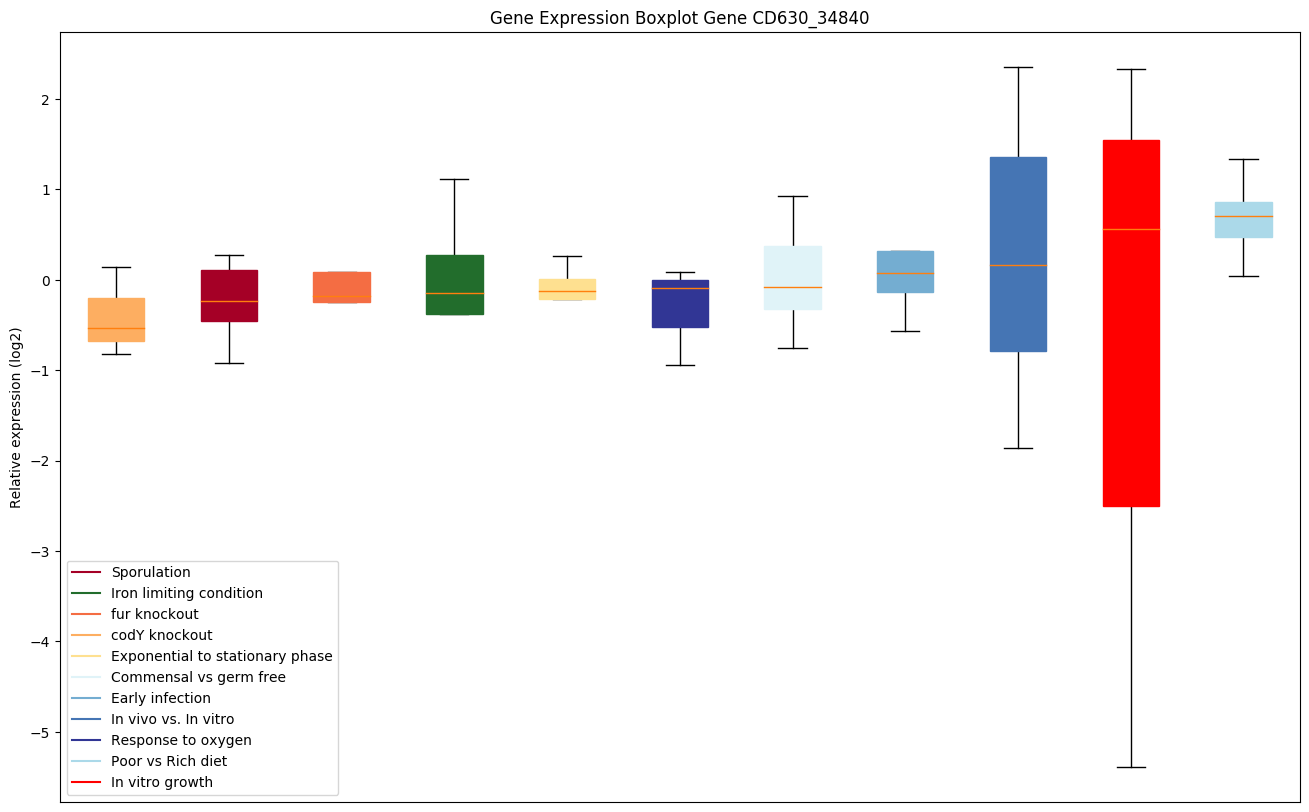 |
||
| CD630_27250 | Putative monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase |
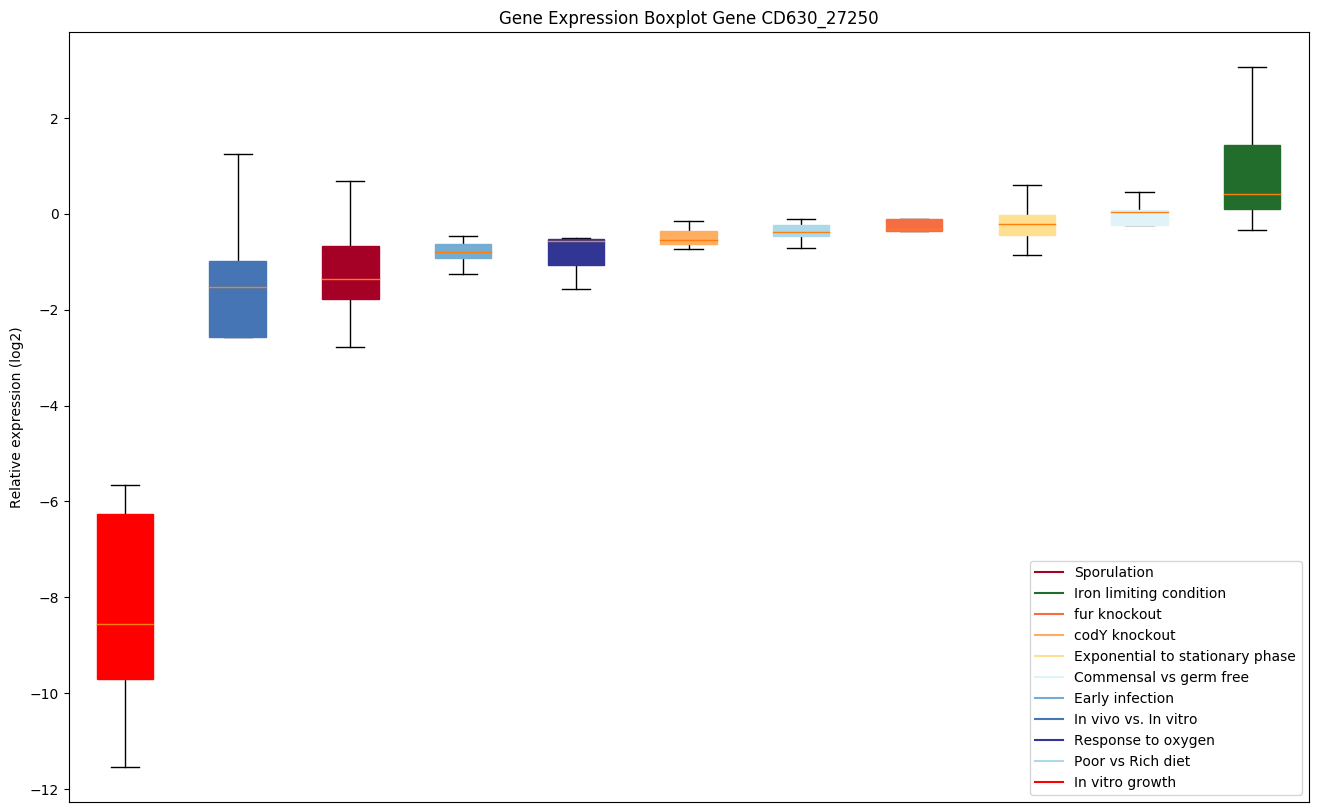 |
|||||
| CD630_03090 | Putative hydrolase, HAD superfamily, subfamilyIB |
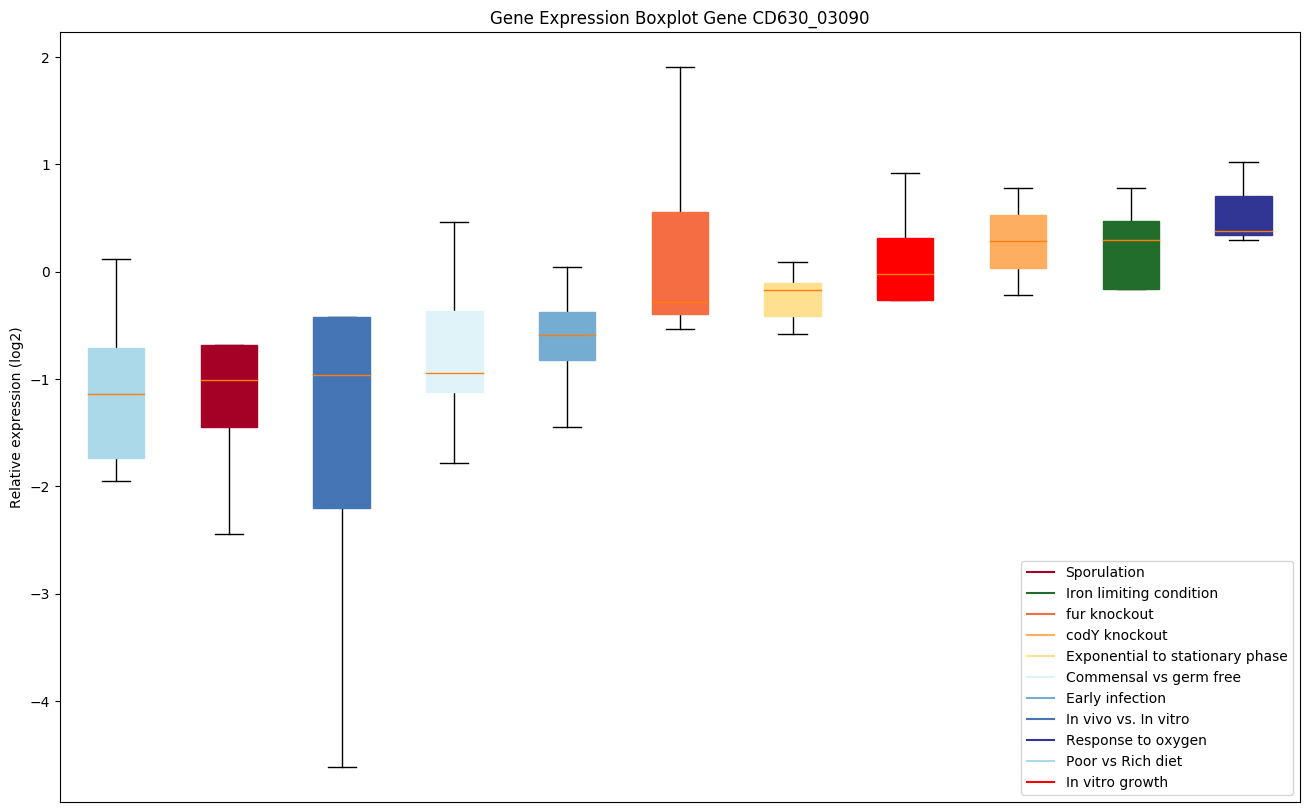 |
|||||
| CD630_27230 | Putative membrane protein | Catalyzes the transfer of a lysyl group from L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys) to membrane-bound phosphatidylglycerol (PG), which produces lysylphosphatidylglycerol (LPG), a major component of the bacterial membrane with a positive net charge. LPG synthesis contributes to bacterial virulence as it is involved in the resistance mechanism against cationic antimicrobial peptides (CAMP) produces by the host's immune system (defensins, cathelicidins) and by the competing microorganisms. |
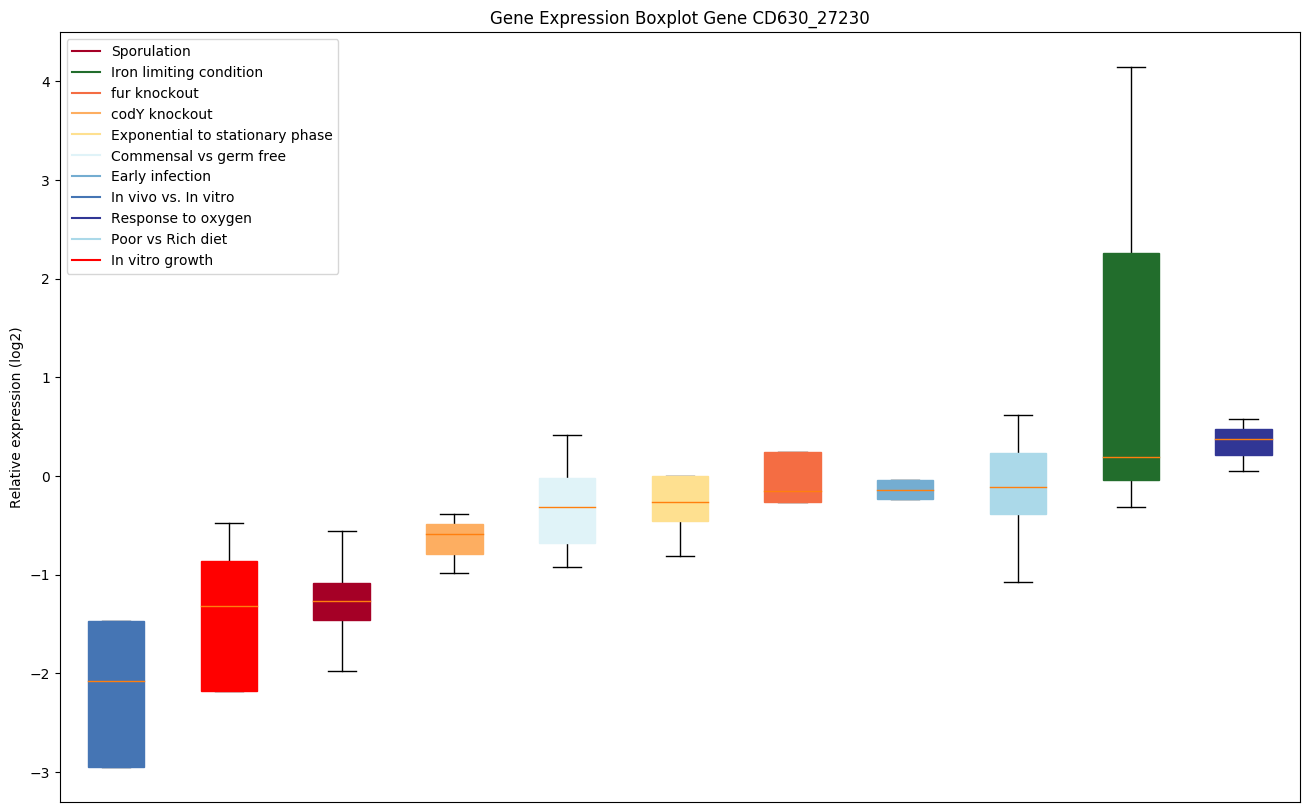 |
||||
| CD630_00290 | Putative membrane protein |
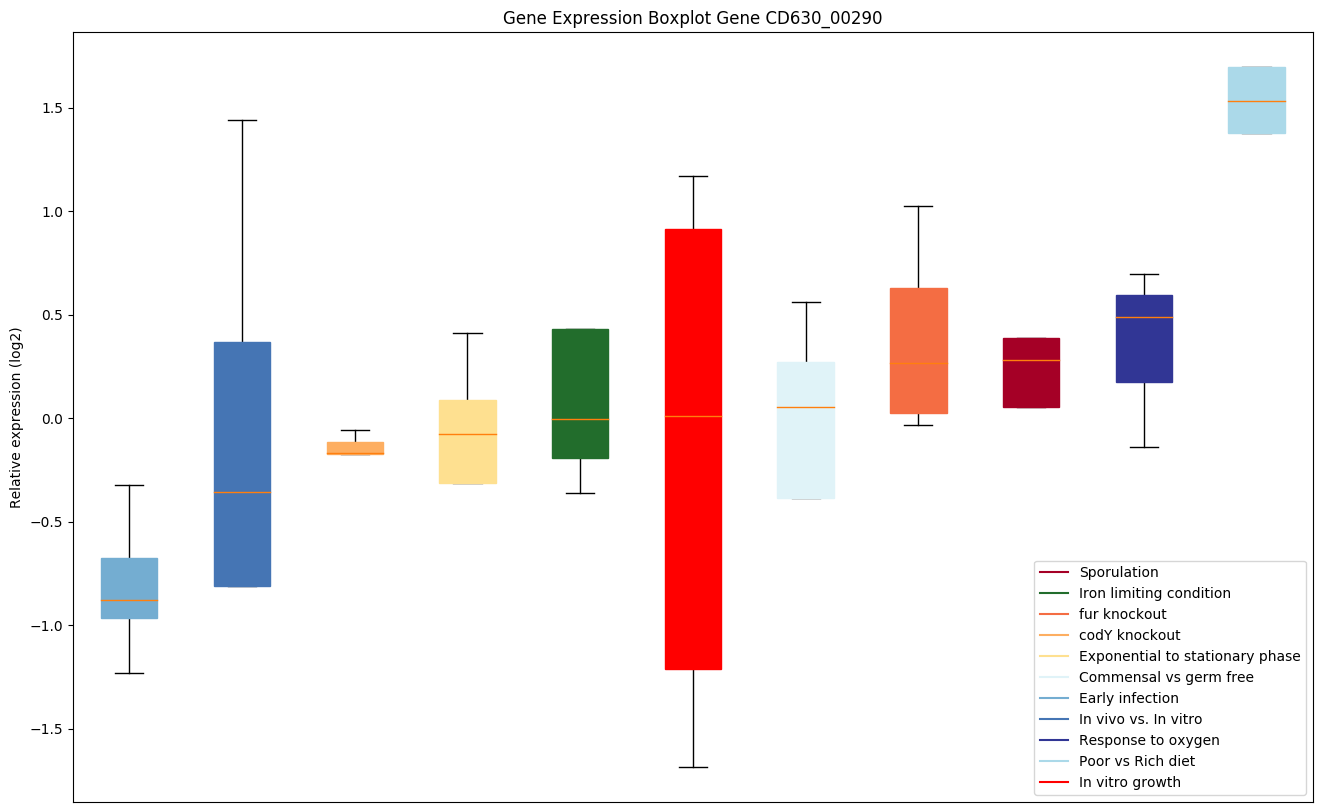 |
|||||
| CD630_27240 | Putative polysaccharide deacetylase |
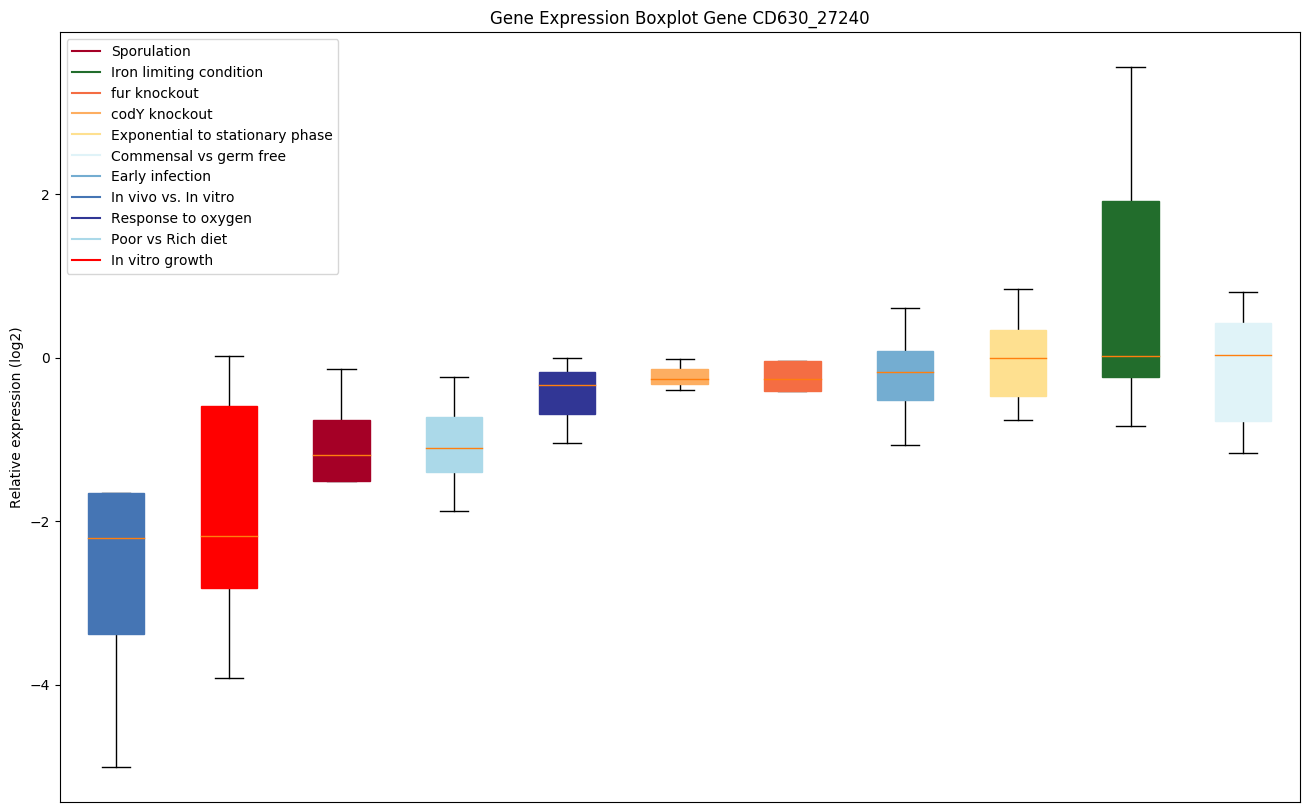 |
|||||
| CD630_24660 | Putative tRNA-nucleotidyltransferase/Poly(A)polymerase family member |
 |
|||||
| CD630_34800 | rpiB2 | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase 2 |
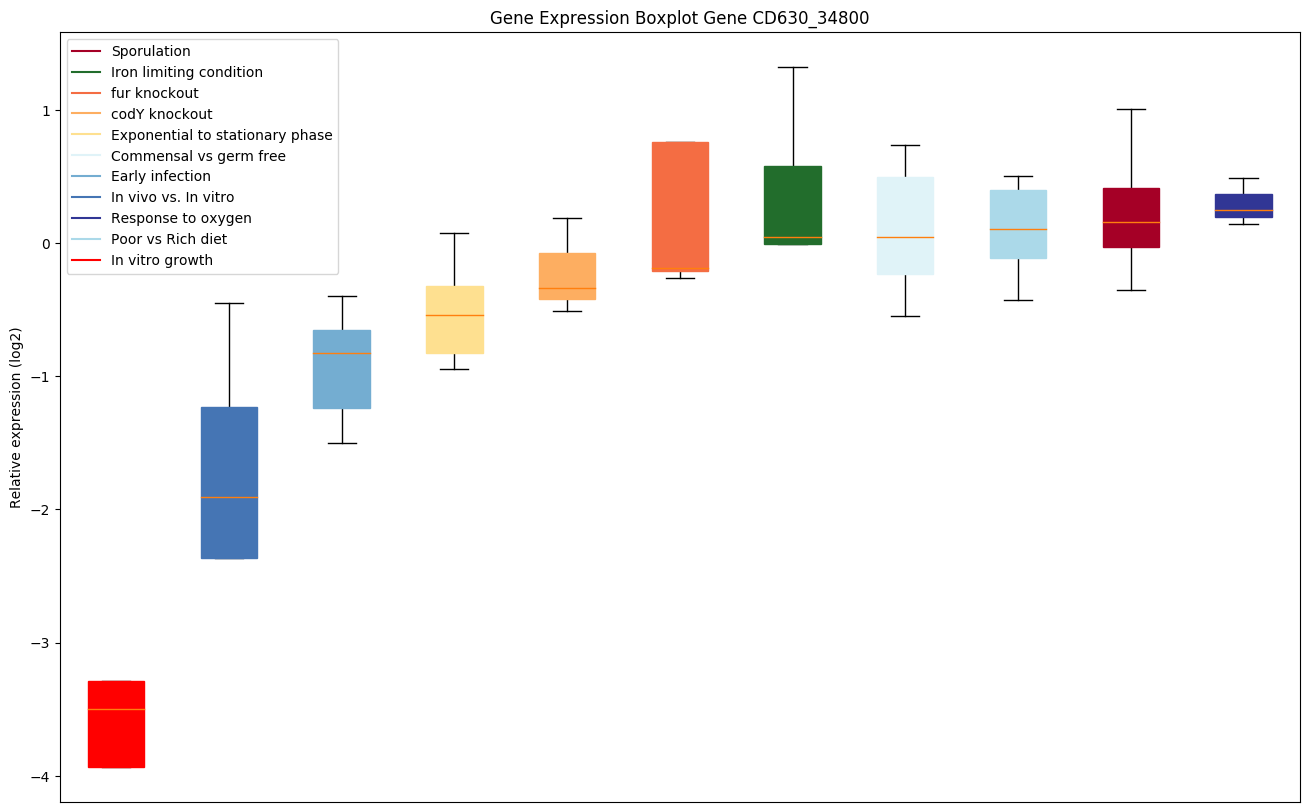 |
||||
| CD630_34790 | upp | Uracil phosphoribosyltransferase (UMPpyrophosphorylase) (UPRTase) | Catalyzes the conversion of uracil and 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate (PRPP) to UMP and diphosphate. |
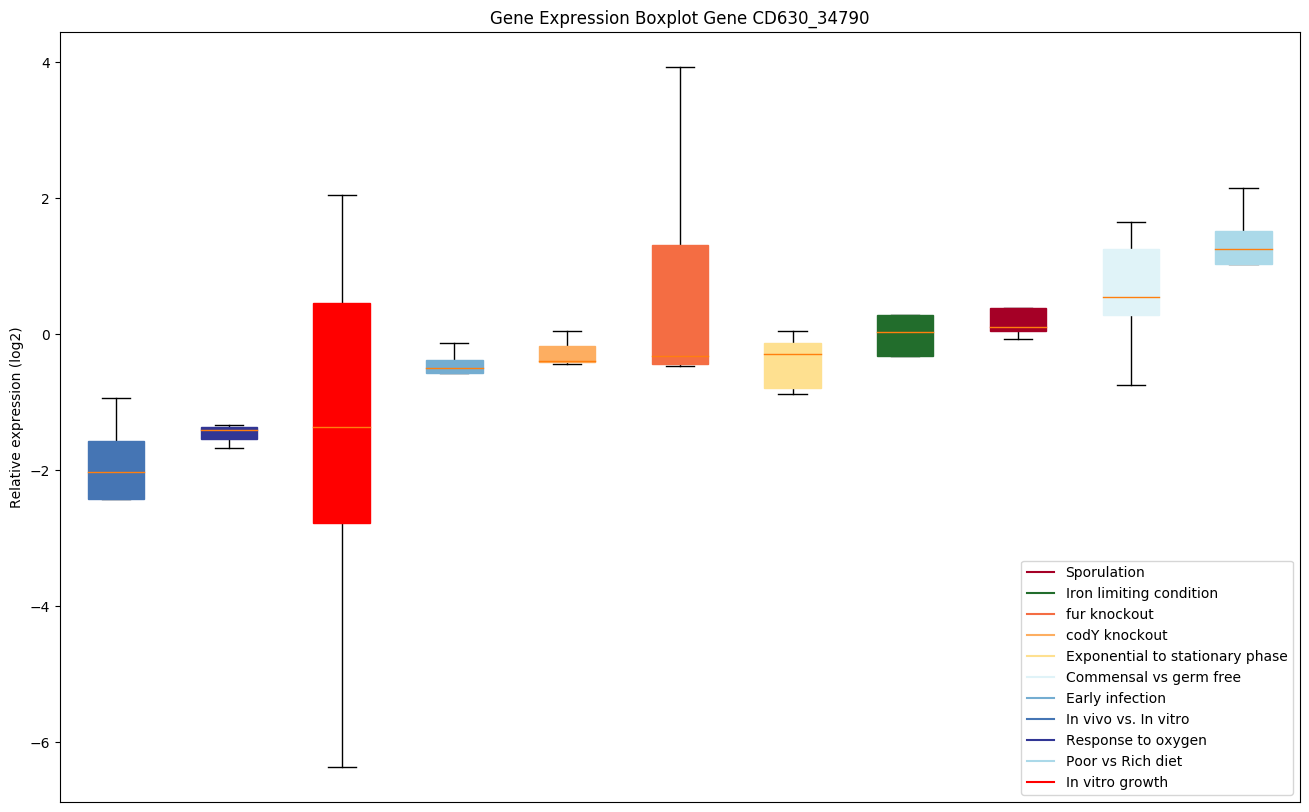 |
|||
| CD630_03100 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_34820 | Putative RNA-binding protein | Required for the formation of a threonylcarbamoyl group on adenosine at position 37 (t(6)A37) in tRNAs that read codons beginning with adenine. | Yes |
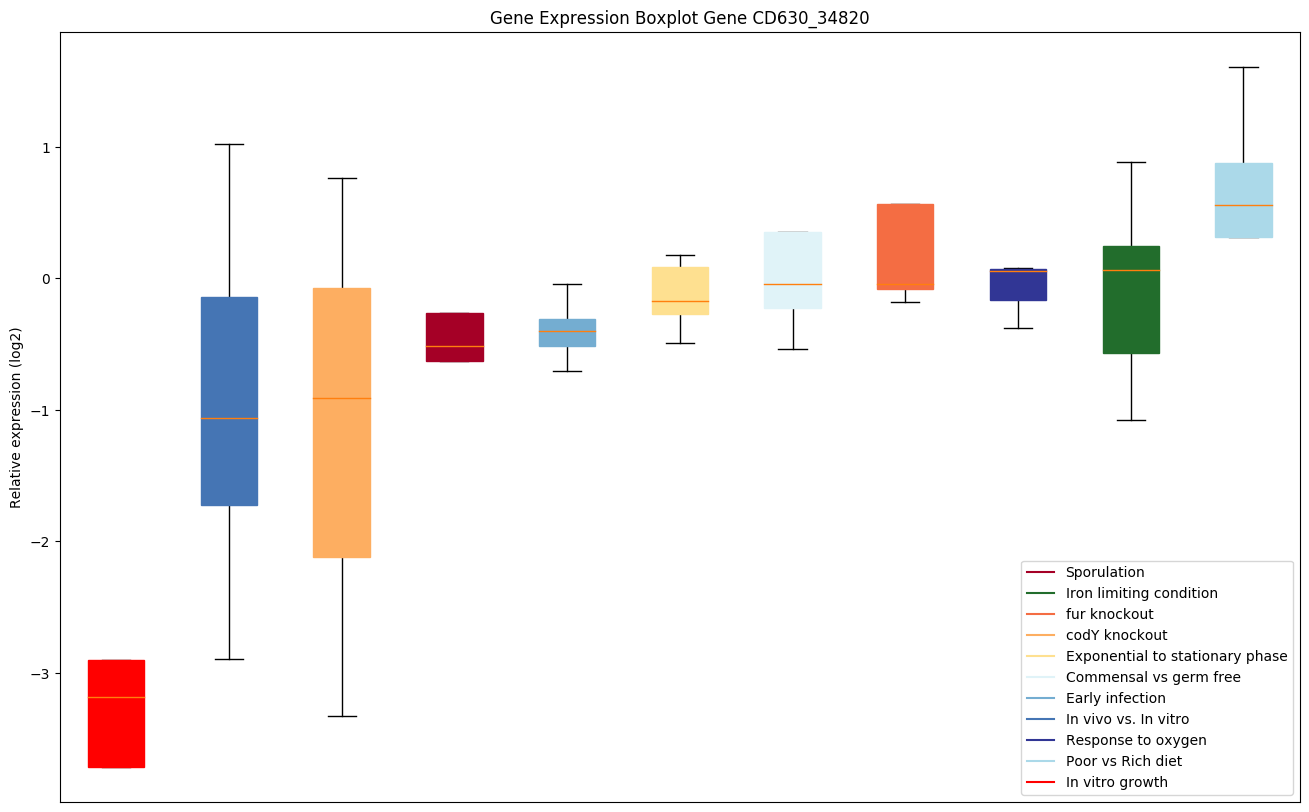 |
|||
| CD630_34861 | rpmE | 50S ribosomal protein L31 | Binds the 23S rRNA. | Yes |
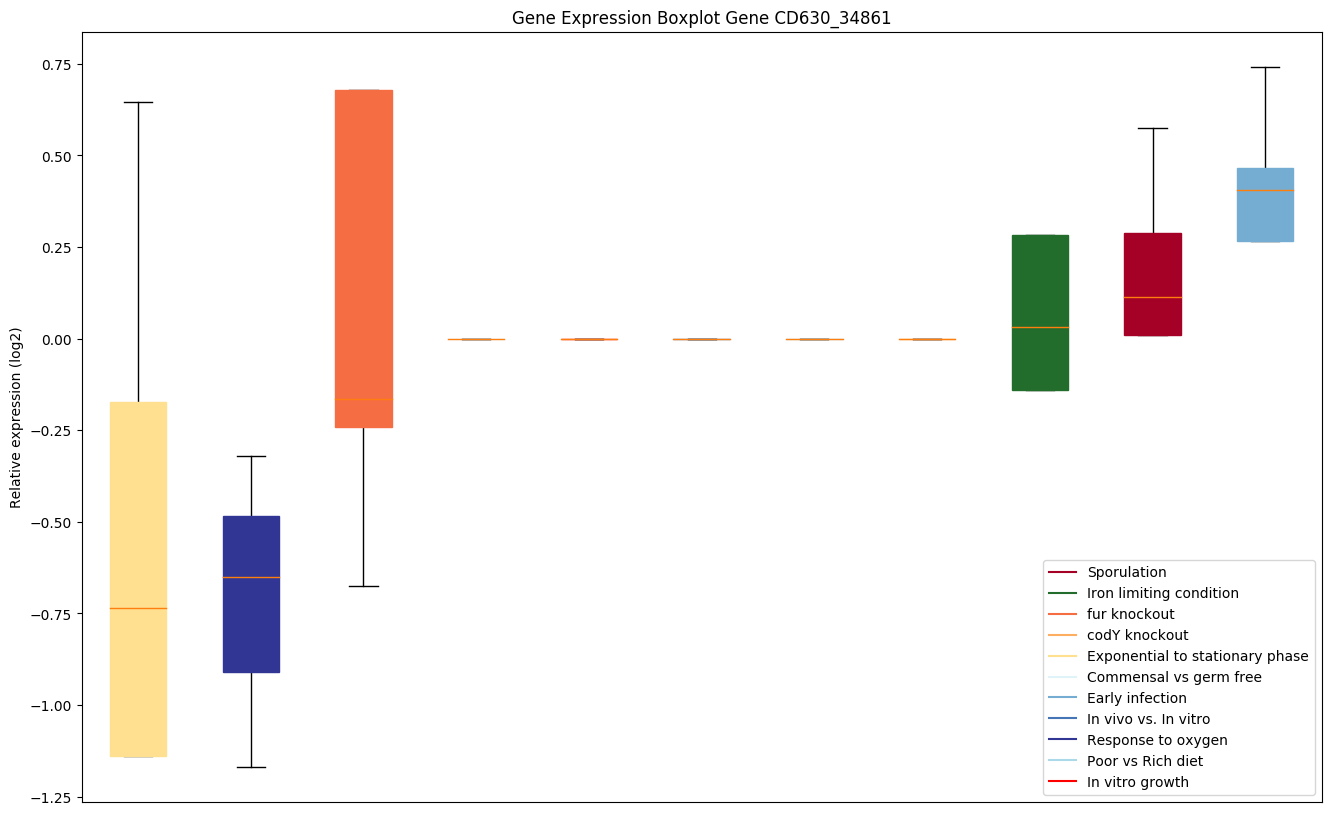 |
||
| CD630_34860 | Putative membrane protein |
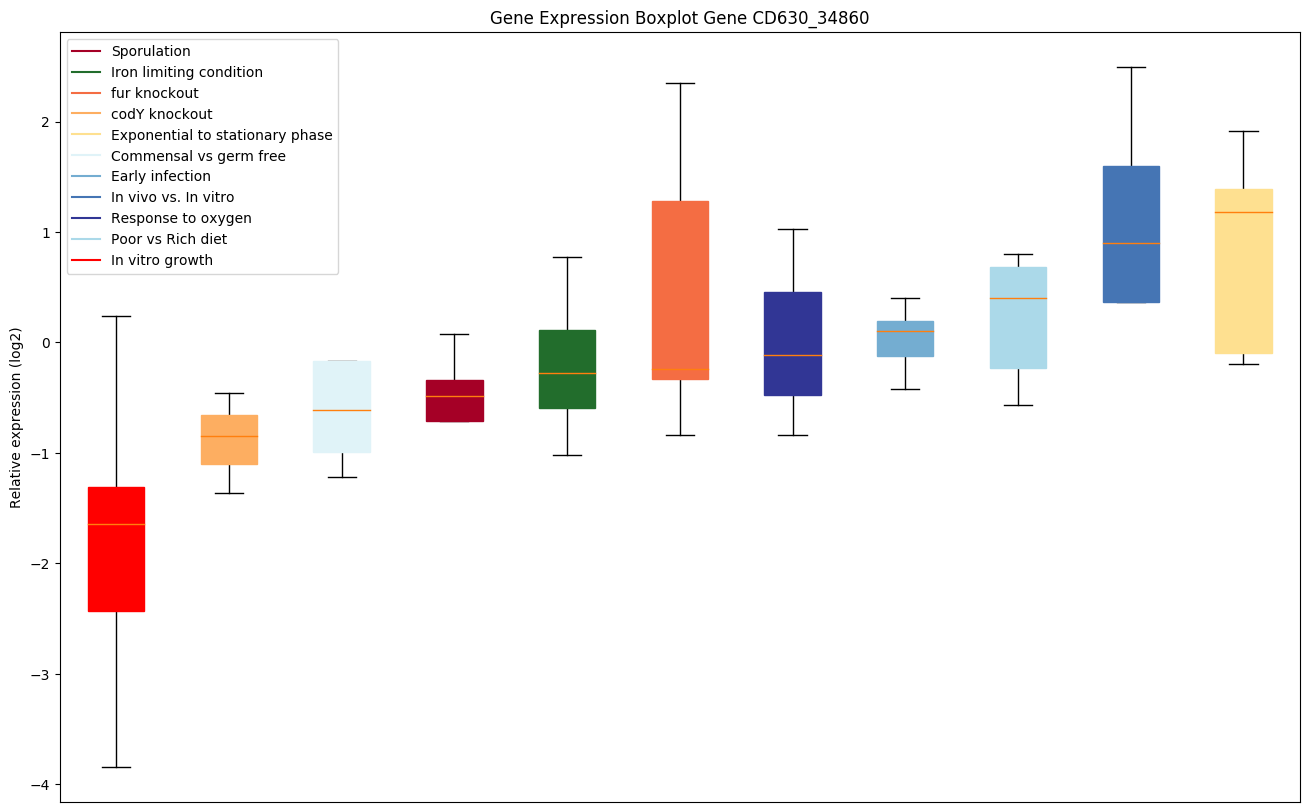 |
|||||
| CD630_00270 | radA | DNA repair protein | DNA-dependent ATPase involved in processing of recombination intermediates, plays a role in repairing DNA breaks. Stimulates the branch migration of RecA-mediated strand transfer reactions, allowing the 3' invading strand to extend heteroduplex DNA faster. Binds ssDNA in the presence of ADP but not other nucleotides, has ATPase activity that is stimulated by ssDNA and various branched DNA structures, but inhibited by SSB. Does not have RecA's homology-searching function. |
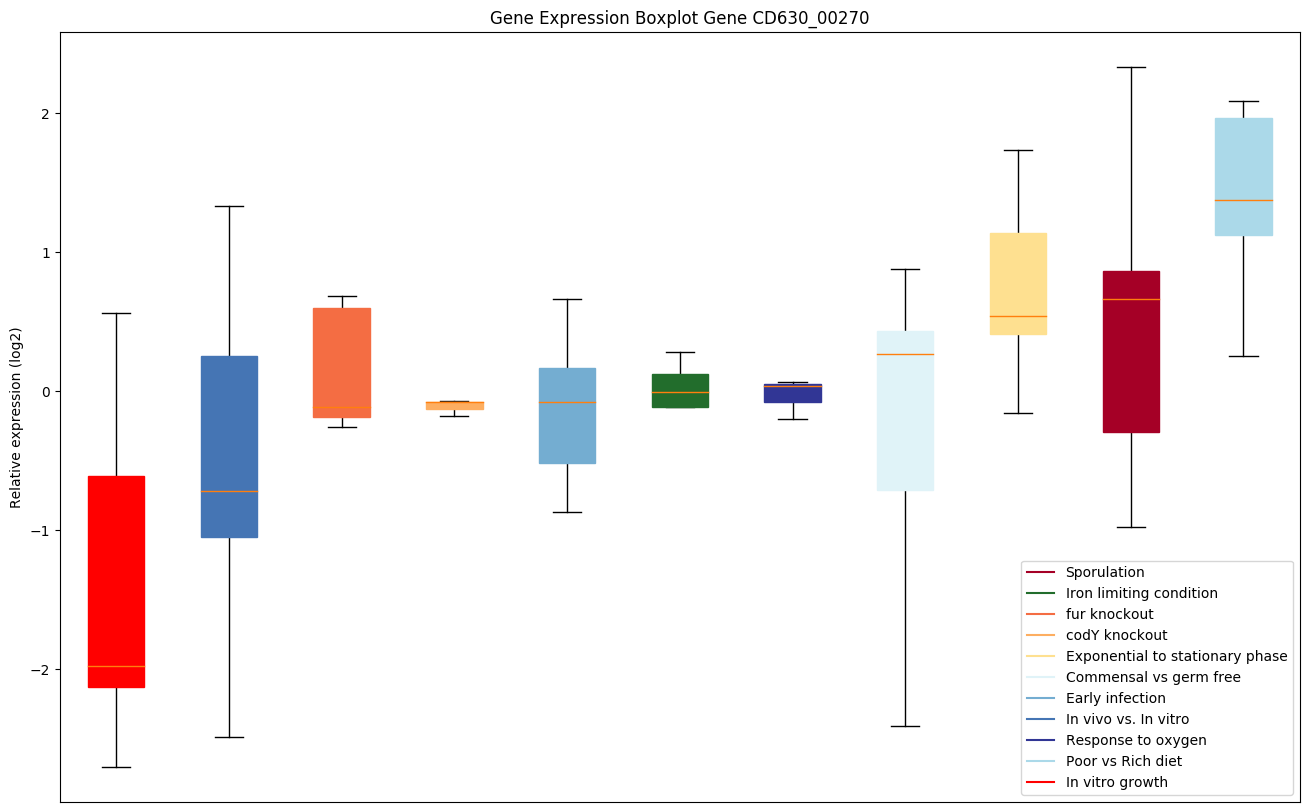 |
|||
| CD630_22700 | fruK | Fructose 1-phosphate kinase |
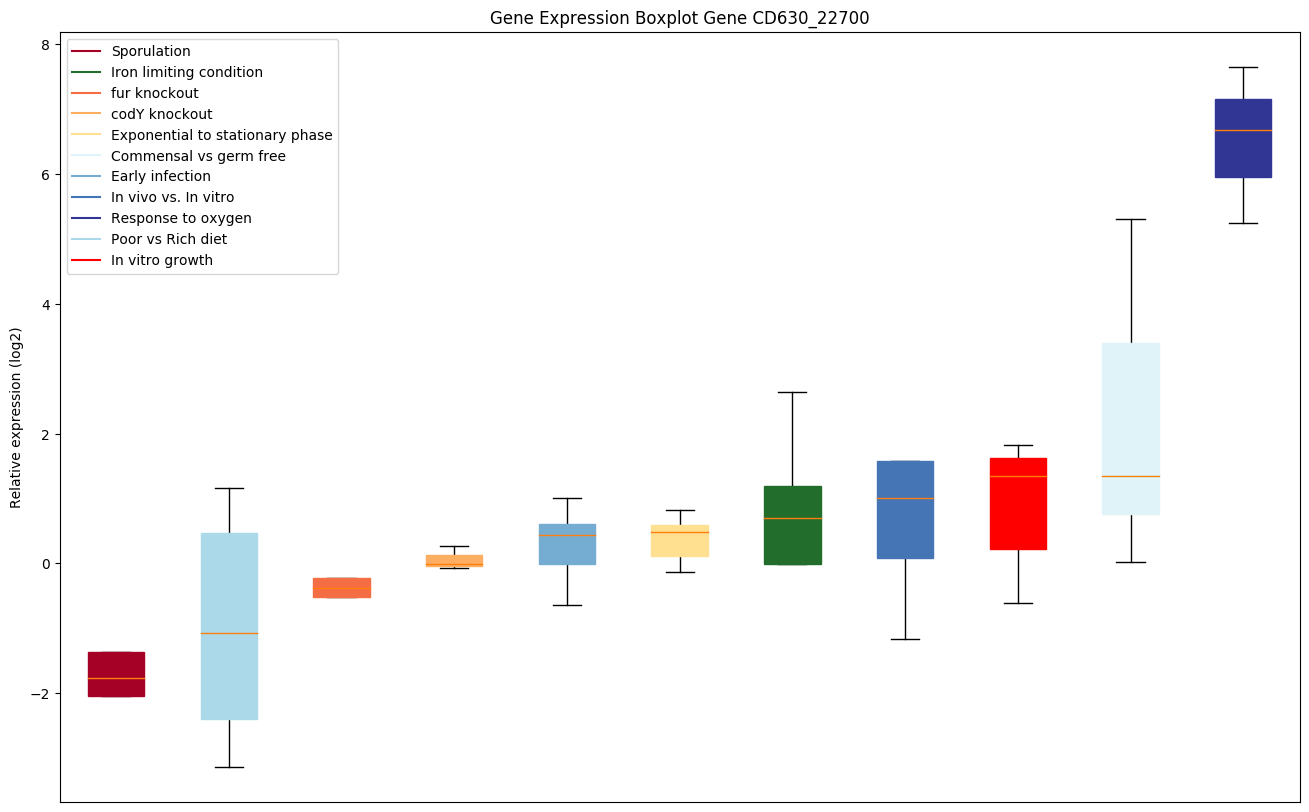 |
||||
| CD630_22690 | fruABC | PTS system, fructose-specific IIABC component |
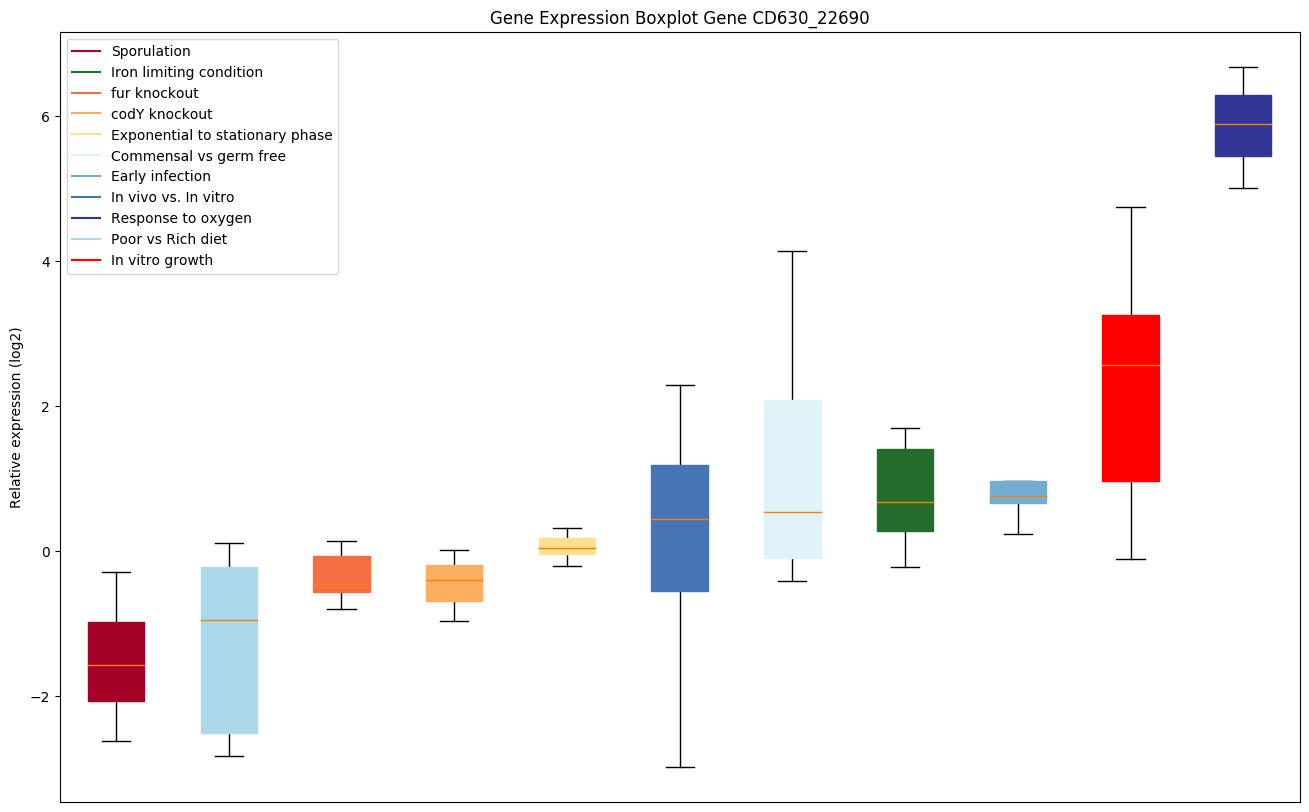 |
||||
| CD630_05430 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
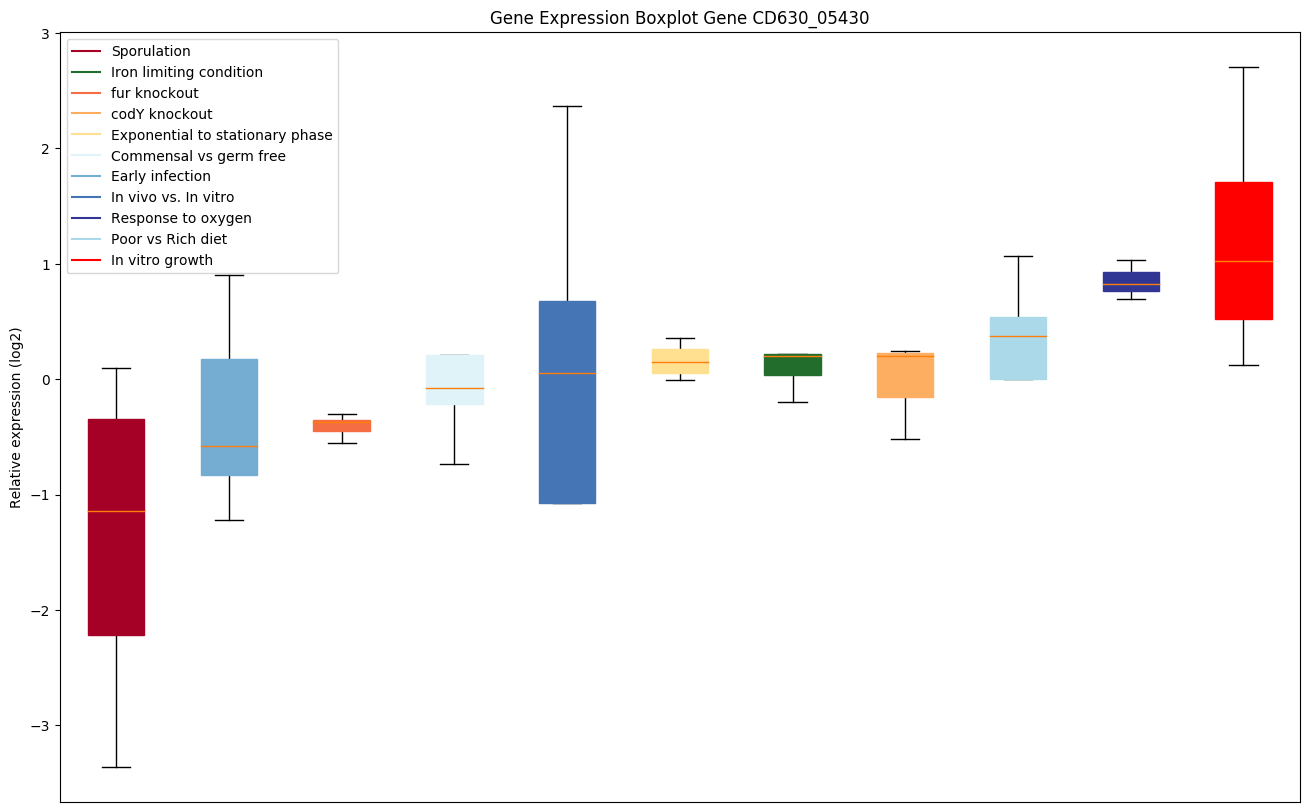 |
|||||
| CD630_00280 | disA | DNA integrity scanning protein disA | Participates in a DNA-damage check-point that is active prior to asymmetric division when DNA is damaged. DisA forms globular foci that rapidly scan along the chromosomes during sporulation, searching for lesions. When a lesion is present, DisA pauses at the lesion site. This triggers a cellular response that culminates in a temporary block in sporulation initiation. |
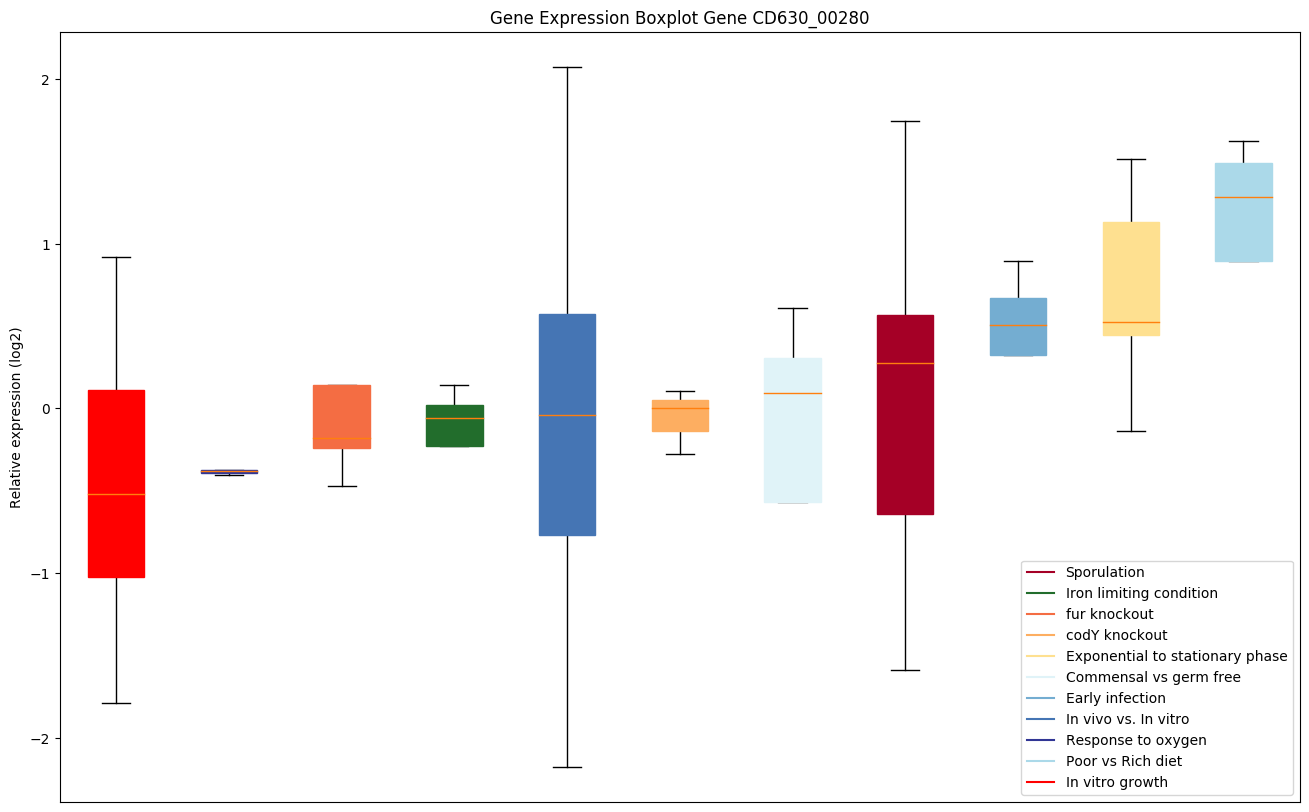 |