Module 130
Summary
| Residual | Gene Count | Condition Count | 1st Q Condition Block * | 5th Q Condition Block * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.57 | 28 | 61 | In vitro growth | NA |
Bicluster expression profile
Expression of genes in subset of conditions included in bicluster on left side of red dashed line and out of bicluster on right of red dashed line. Each condition is represented as a boxplot, ordered by their median expression for the bicluster genes (smallest to largest) and colored according to condition blocks.
|
|
de novo identified motifs are listed below
Candidate transcriptional regulators for each module were determined with a linear regression based approach (Inferelator) and by evaluating the statistical significance of the overlap (Hypergeometric) between modules and putative TF and alternative sigma factor regulons (CcpA, CodY, Fur, PrdR, SigB, SigD, SigE, SigF, SigG, SigH, SigK, Spo0A) compiled from available literature.
For filtering high confidence influences, we used hypergeometric test adjusted p-value <=0.05 and minimum four genes in the overlap between the module and the TF regulon. The same thresholds were used for evaluating the functional enrichment.
1. Betas: correspond to the average coefficients of the Bayesian regressions between module expression and TF expression profiles. The values indicate the magnitude and direction (activation or repression for positive or negative values, respectively) of each TF-module interaction.
2. Confidence scores: indicate the likelihood of the TF-module interactions.
| TF | Module | Confidence Score | Beta |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Transcriptional regulator, beta-lactamsrepressor |
130 | 0.26 | 0.1369 |
|
Putative cyclic nucleotides-binding protein |
130 | 0.29 | 0.1742 |
|
Two-component response regulator |
130 | 0.18 | 0.1079 |
|
Putative dinitrogenase iron-molybdenum cofactor |
130 | 0.15 | 0.1344 |
|
Transcriptional regulator, ArsR family |
130 | 0.52 | 0.3321 |
The module is significantly enriched with genes associated to the indicated functional terms
The enrichment was determined with hypergeometric test using the genome functional annotation compiled by Girinathan et al (2020).
| Module | Pathway | Overlap | pvalue | Adjusted pvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 130 | DNA Replication | 5 | 0.000003 | 0.001399 |
Genes that are included in this module
* "Gene essentiality is based on TnSeq Data from: Dembek M, Barquist L, Boinett CJ, et al. High-throughput analysis of gene essentiality and sporulation in Clostridium difficile. mBio. 2015;6(2):e02383. Published 2015 Feb 24.doi:10.1128/mBio.02383-14".
| Title | Short Name | Product | Function | Essentiality * | in vivo Essentiality | Rich broth Essentiality | Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
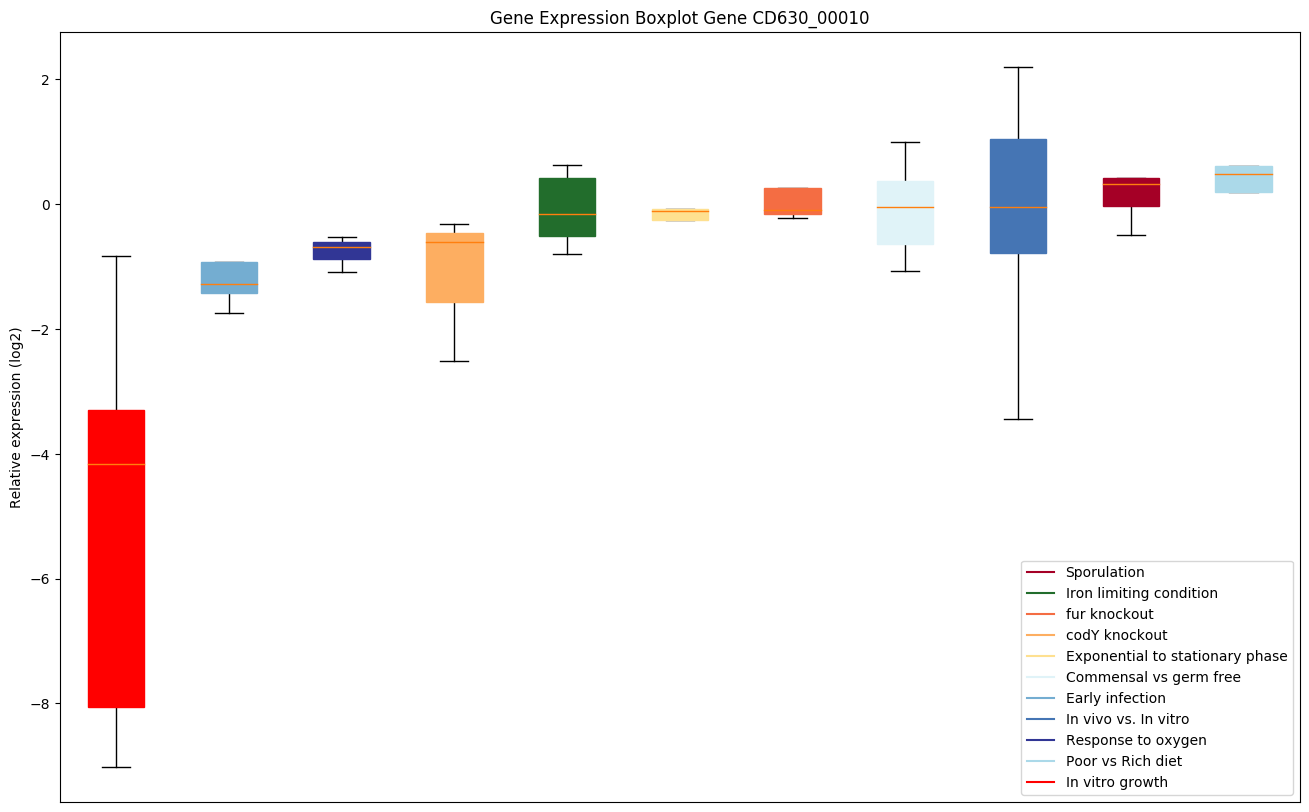
| CD630_00010 | dnaA | Chromosomal replication initiator protein | Plays an important role in the initiation and regulation of chromosomal replication. Binds to the origin of replication; it binds specifically double-stranded DNA at a 9 bp consensus (dnaA box): 5'-TTATC[CA]A[CA]A-3'. DnaA binds to ATP and to acidic phospholipids. |
 |
|||
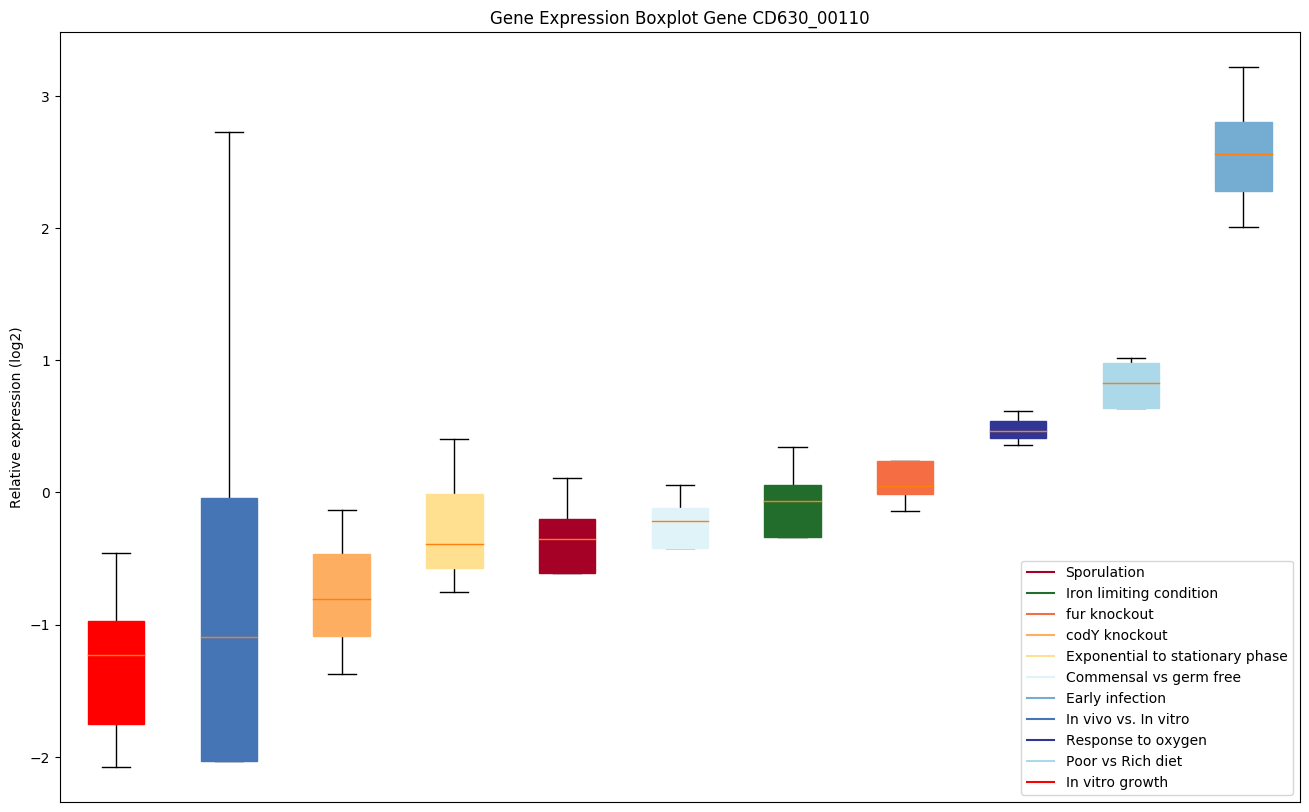
| CD630_00110 | sigB | RNA polymerase sigma-B factor |
 |
||||
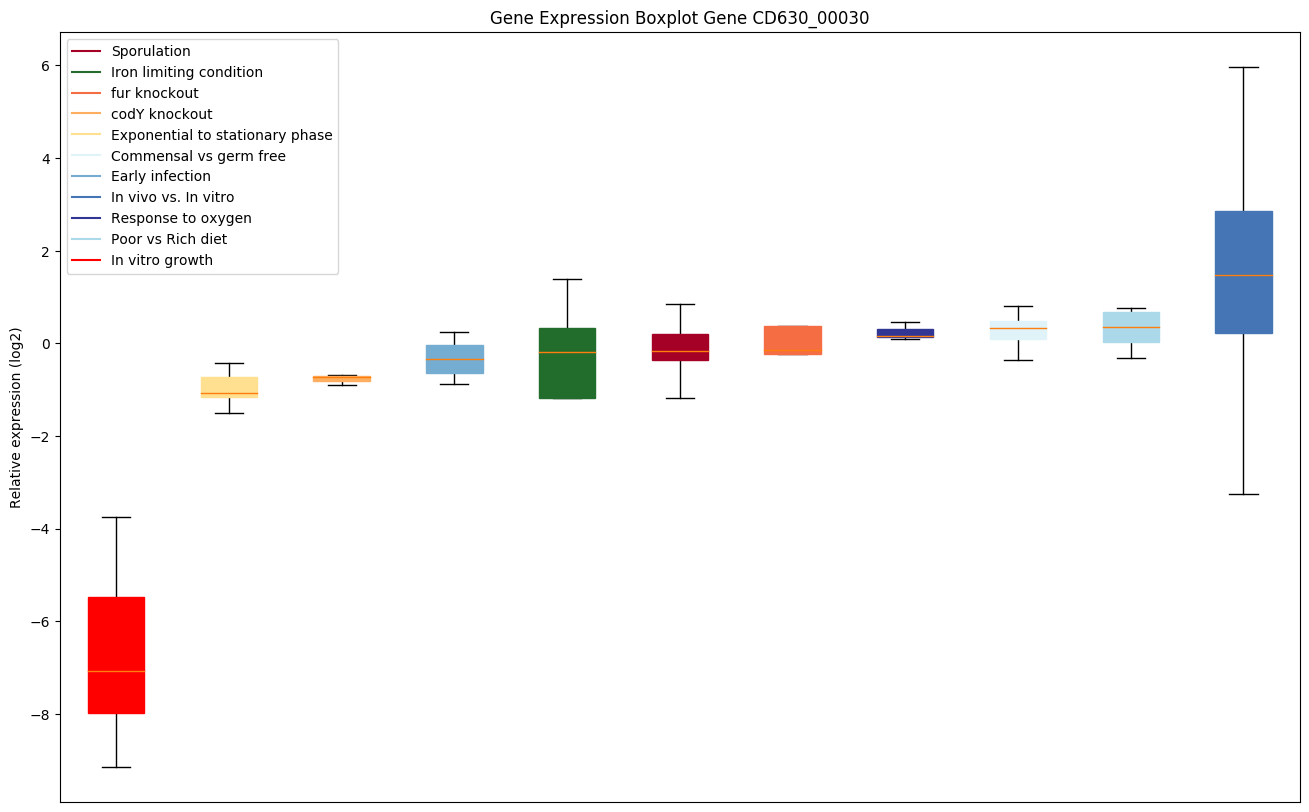
| CD630_00030 | Putative RNA-binding mediating protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_00070 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
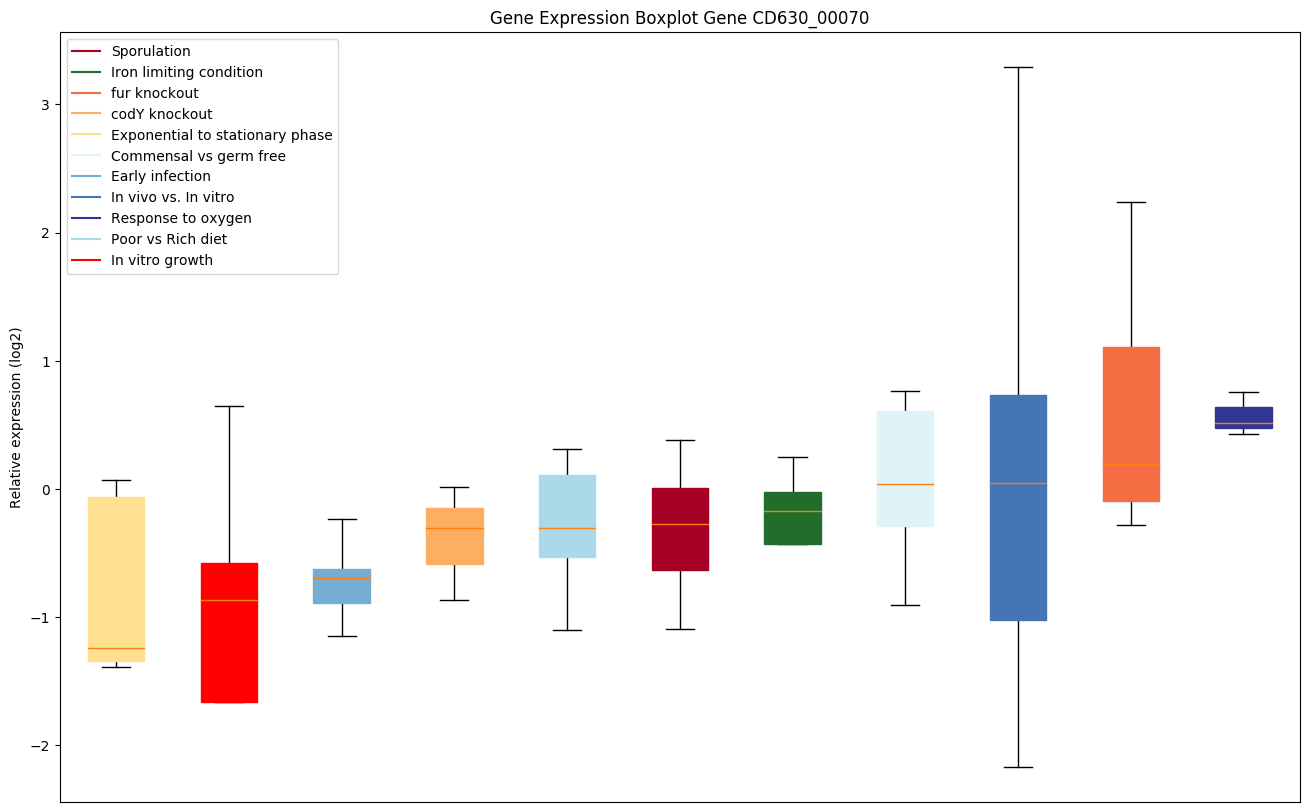 |
|||||
| CD630_00050 | gyrB | DNA gyrase subunit B | A type II topoisomerase that negatively supercoils closed circular double-stranded (ds) DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to modulate DNA topology and maintain chromosomes in an underwound state. Negative supercoiling favors strand separation, and DNA replication, transcription, recombination and repair, all of which involve strand separation. Also able to catalyze the interconversion of other topological isomers of dsDNA rings, including catenanes and knotted rings. Type II topoisomerases break and join 2 DNA strands simultaneously in an ATP-dependent manner. |
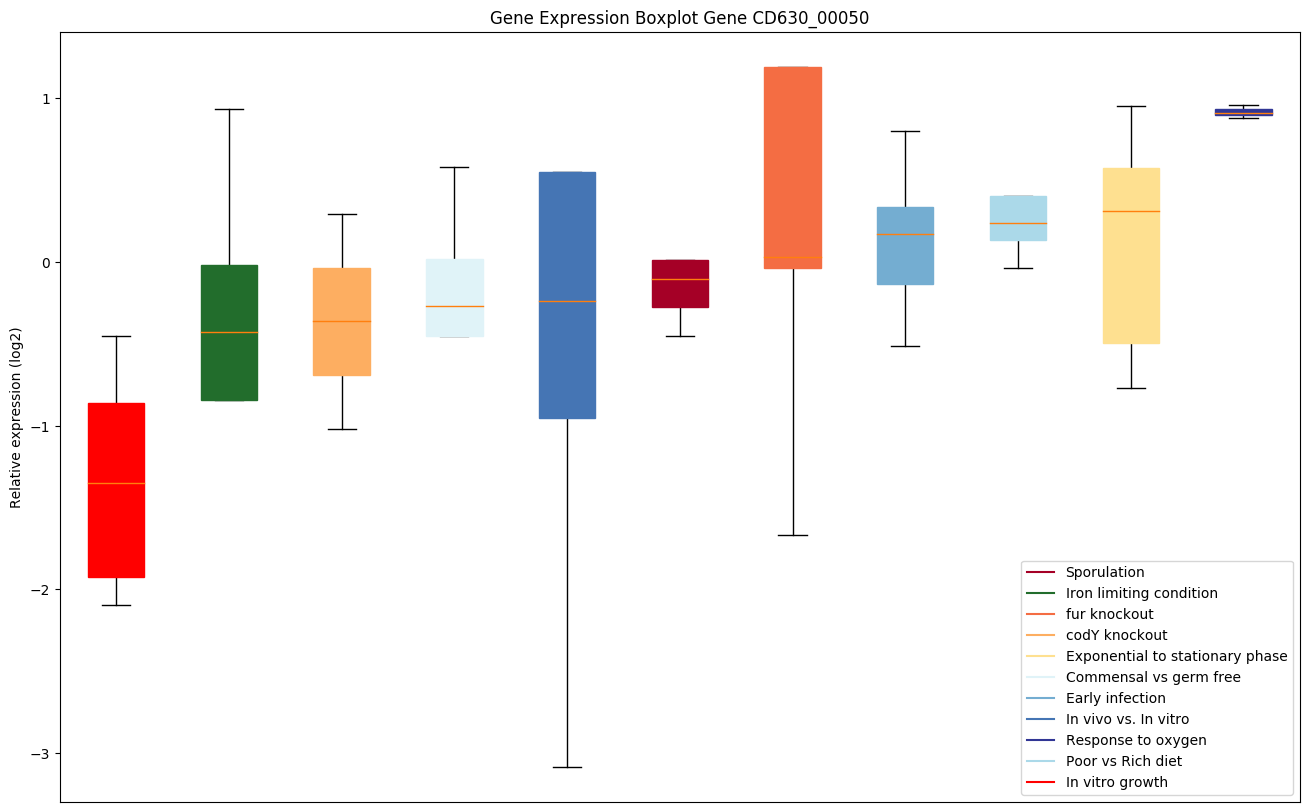 |
|||
| CD630_17460 | gltC | Sodium/glutamate symporter | Catalyzes the sodium-dependent transport of glutamate. |
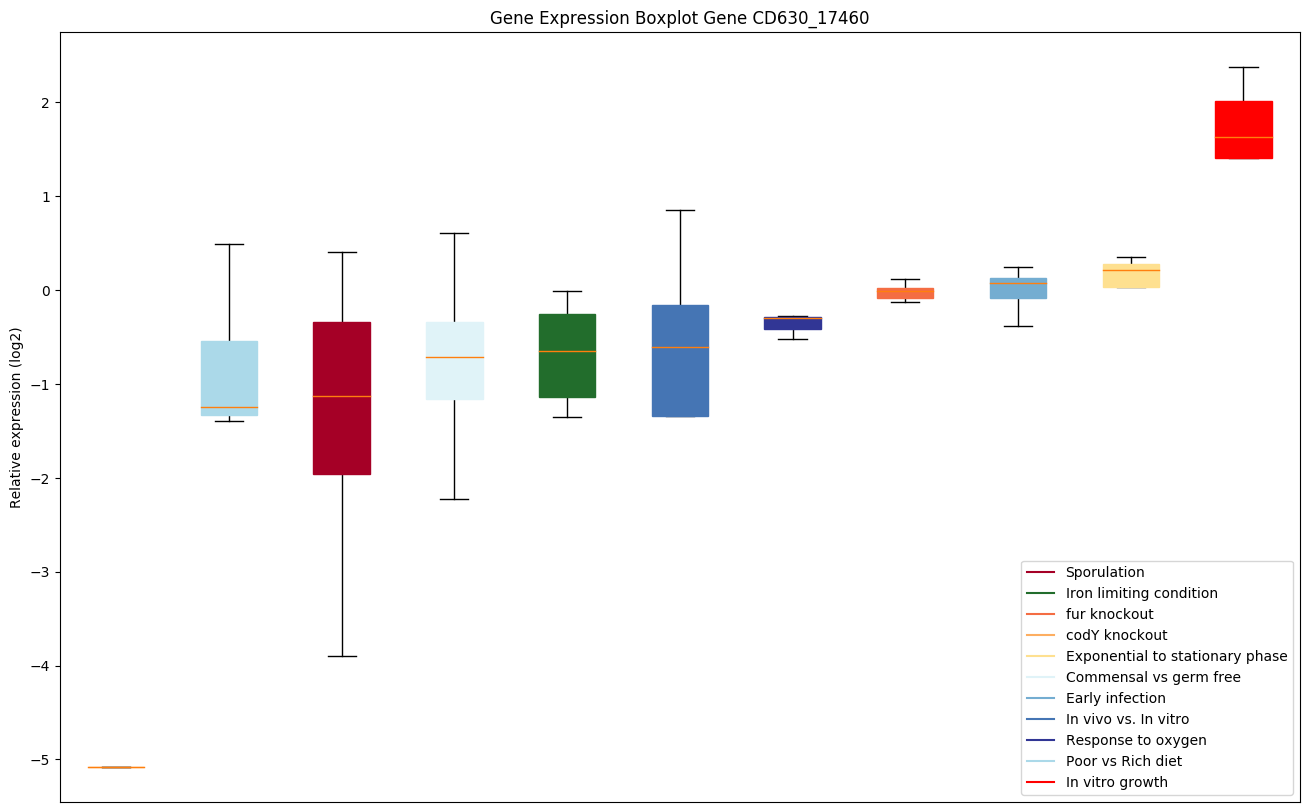 |
|||
| CD630_00090 | rsbV | Anti-anti-sigma factor |
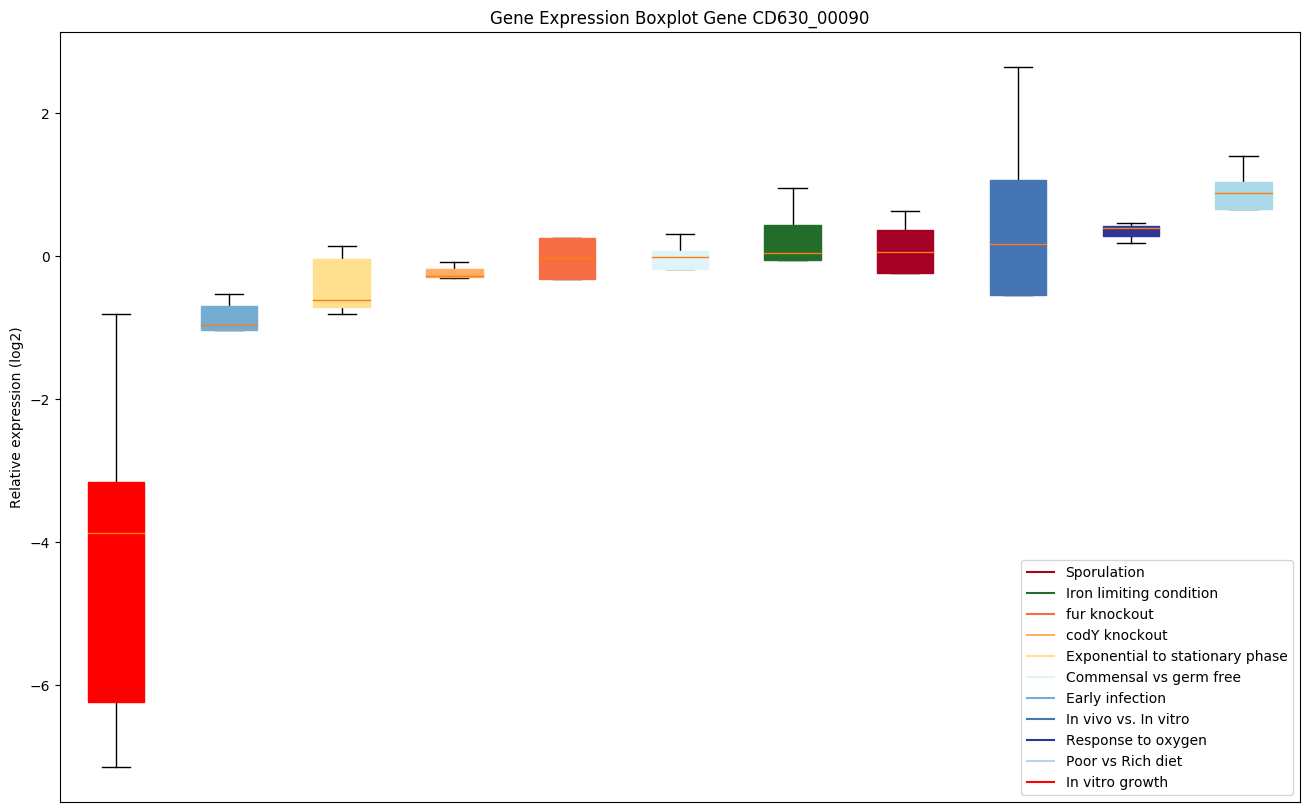 |
||||
| CD630_24910 | pmi | Mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (Phosphomannoseisomerase) (PMI) (Phosphohexomutase) |
 |
||||
| CD630_21070 | Xanthine/uracil/thiamine/ascorbate permeasefamily protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_16900 | trxA | Thioredoxin |
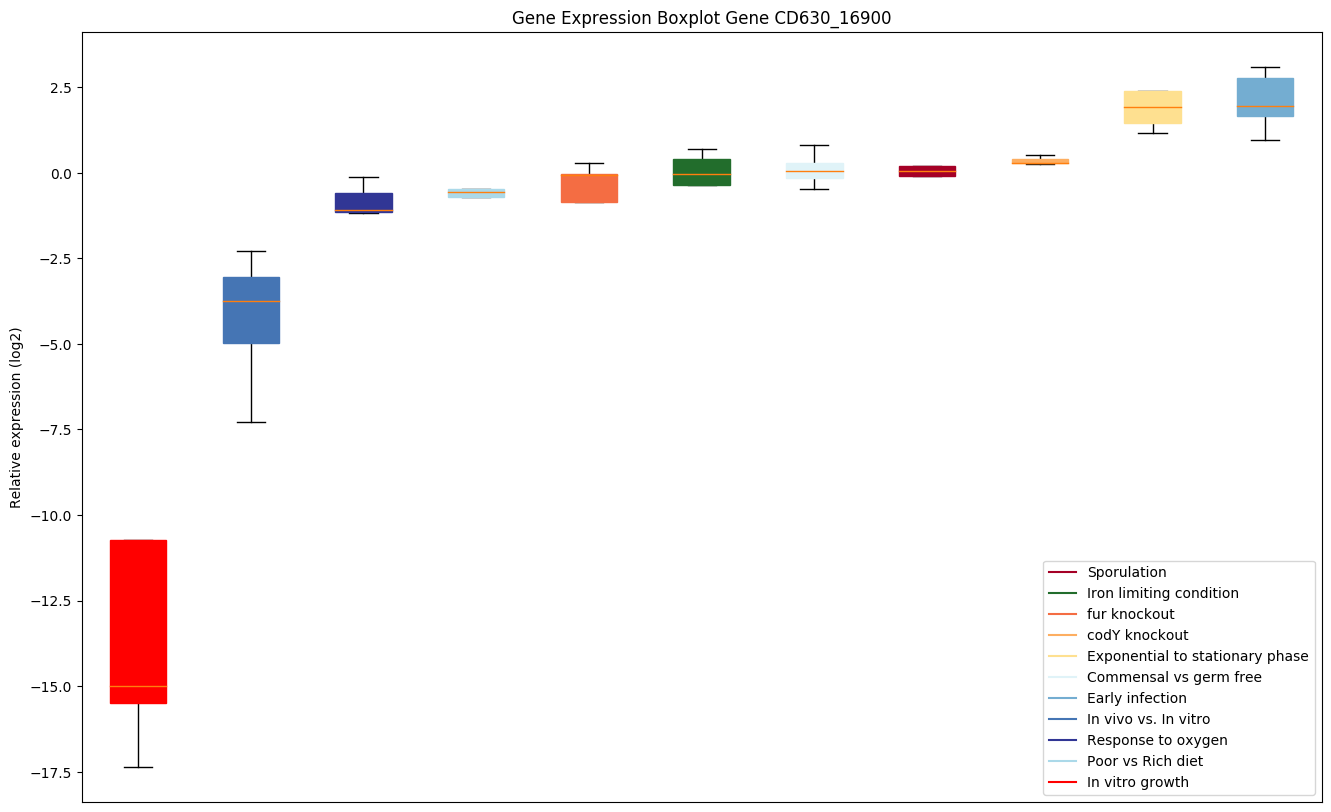 |
||||
| CD630_24820 | Putative lipoprotein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_18000 | terD | Tellurium resistance protein |
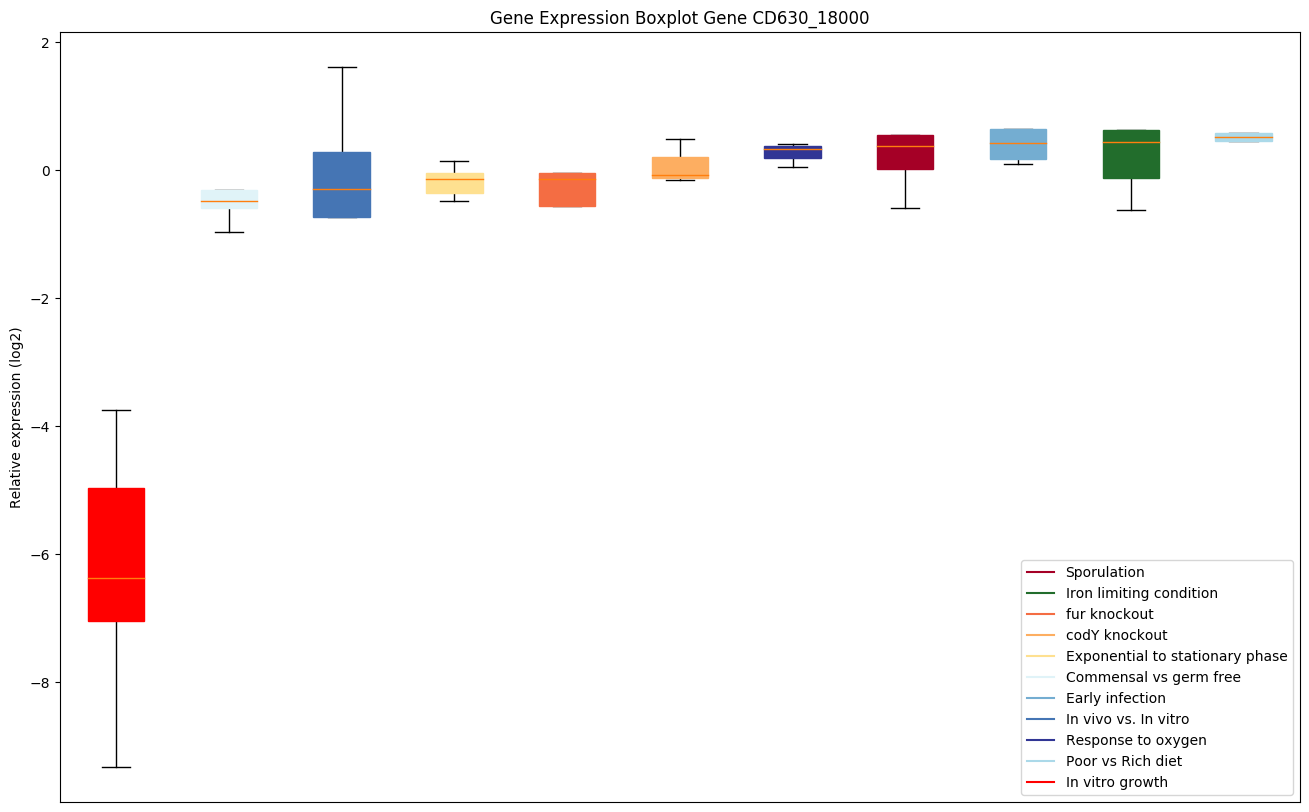 |
||||
| CD630_26160 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
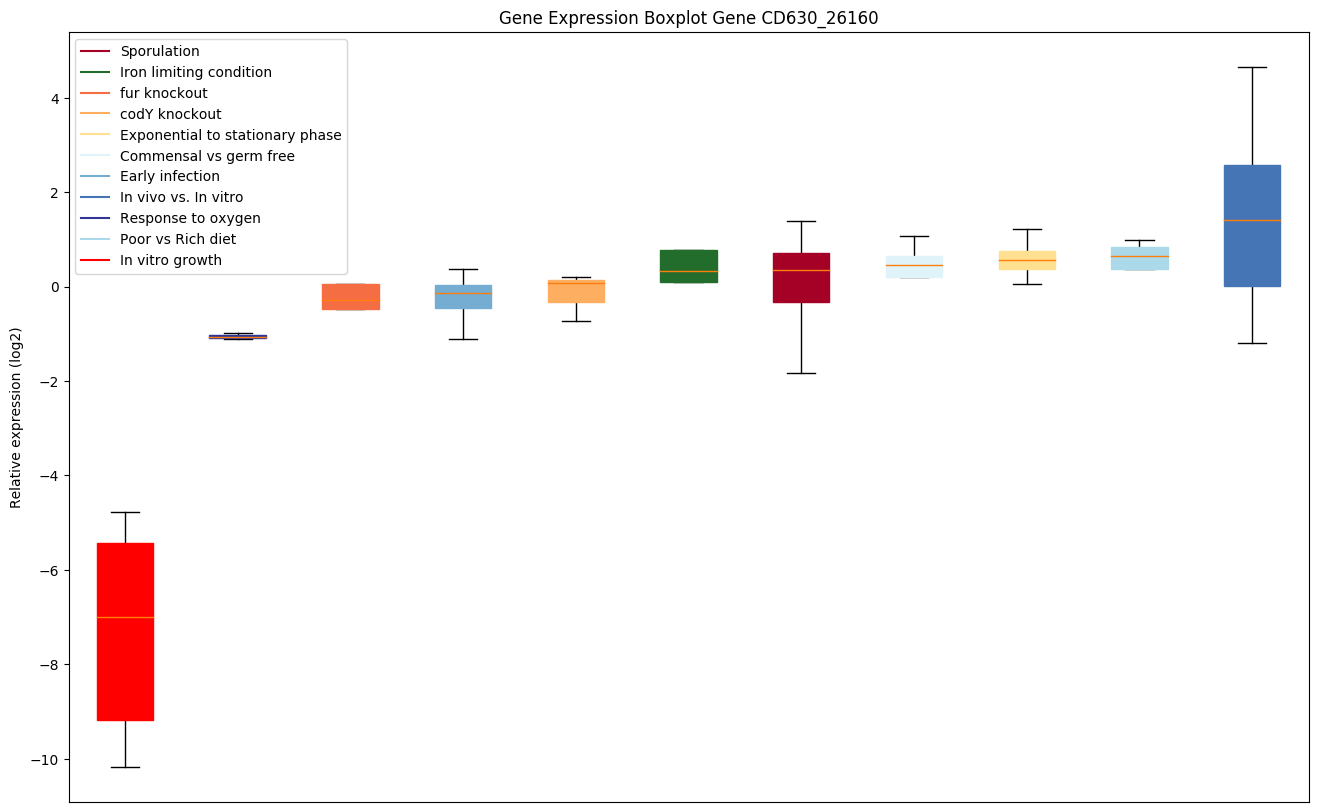 |
|||||
| CD630_00040 | recF | DNA replication and repair protein RecF | The RecF protein is involved in DNA metabolism; it is required for DNA replication and normal SOS inducibility. RecF binds preferentially to single-stranded, linear DNA. It also seems to bind ATP. |
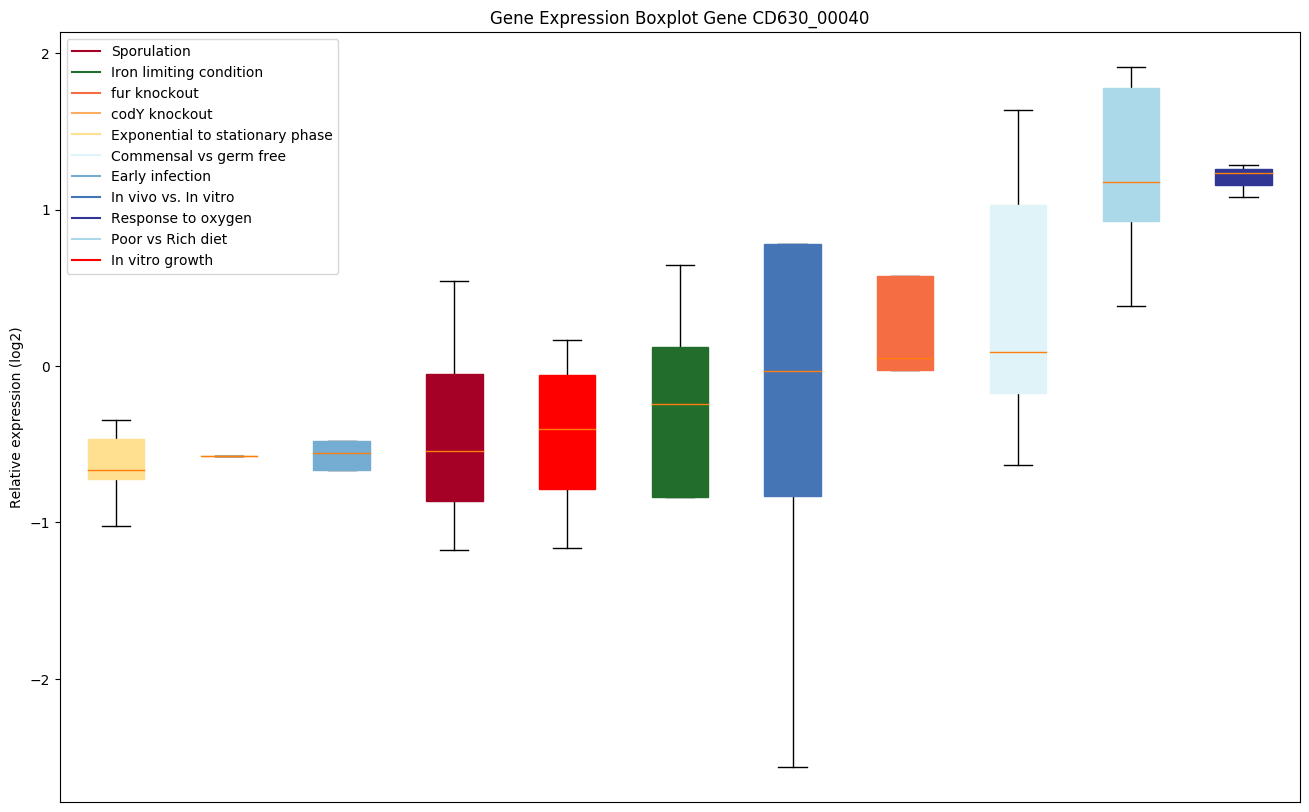 |
|||
| CD630_24830 | Putative lipoprotein | Flavin transferase that catalyzes the transfer of the FMN moiety of FAD and its covalent binding to the hydroxyl group of a threonine residue in a target flavoprotein. |
 |
||||
| CD630_00020 | dnaN | DNA polymerase III subunit beta | Confers DNA tethering and processivity to DNA polymerases and other proteins. Acts as a clamp, forming a ring around DNA (a reaction catalyzed by the clamp-loading complex) which diffuses in an ATP-independent manner freely and bidirectionally along dsDNA. Initially characterized for its ability to contact the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase III (Pol III), a complex, multichain enzyme responsible for most of the replicative synthesis in bacteria; Pol III exhibits 3'-5' exonuclease proofreading activity. The beta chain is required for initiation of replication as well as for processivity of DNA replication. |
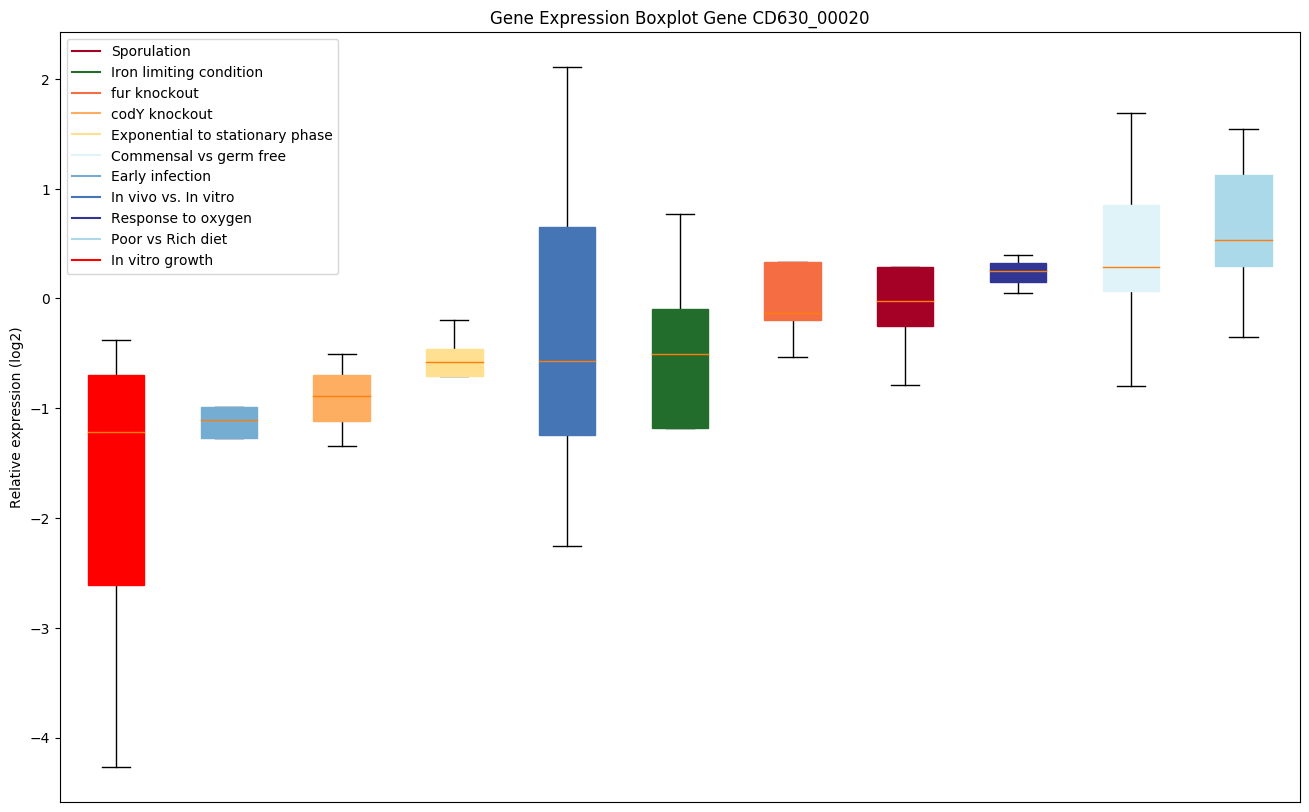 |
|||
| CD630_32290 | dapB2 | Dihydrodipicolinate reductase 2 (DHPR 2) | Catalyzes the conversion of 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate (HTPA) to tetrahydrodipicolinate. |
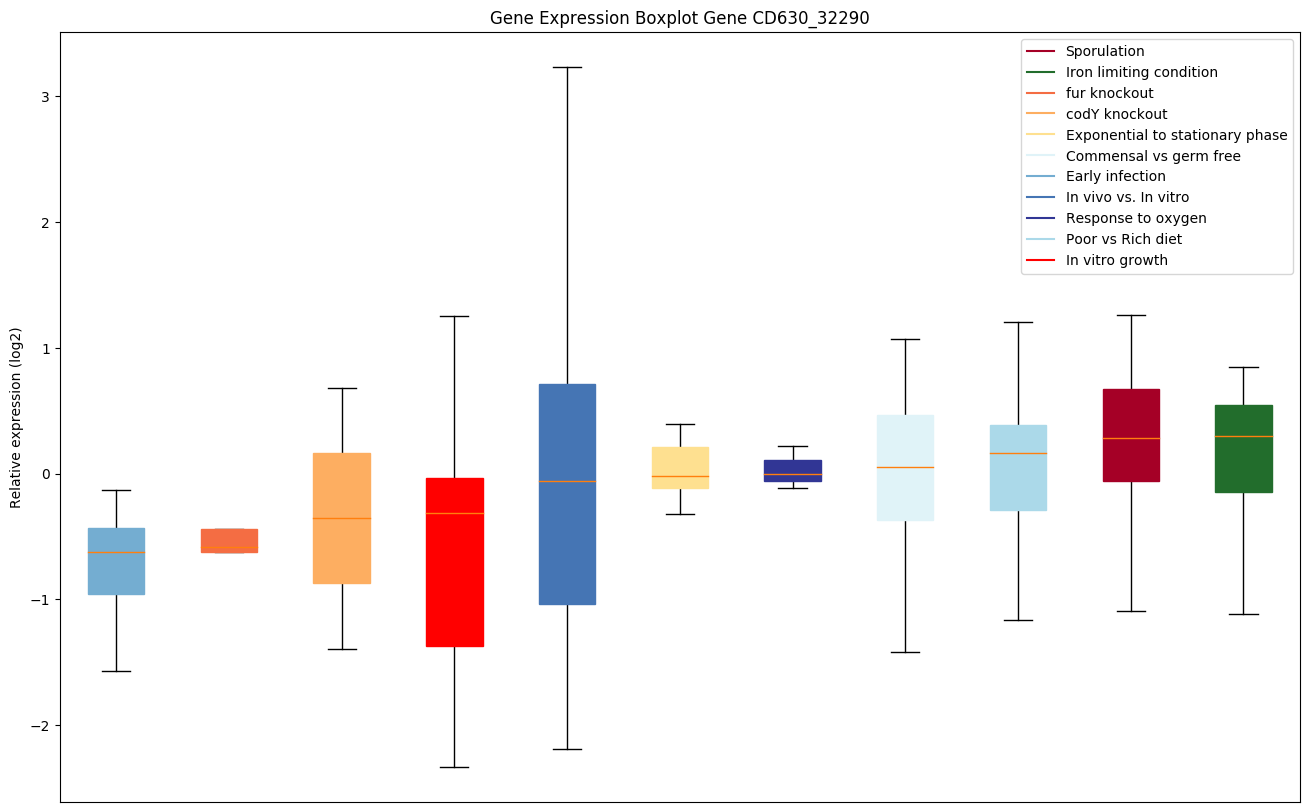 |
|||
| CD630_00060 | gyrA | DNA gyrase subunit A | A type II topoisomerase that negatively supercoils closed circular double-stranded (ds) DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to modulate DNA topology and maintain chromosomes in an underwound state. Negative supercoiling favors strand separation, and DNA replication, transcription, recombination and repair, all of which involve strand separation. Also able to catalyze the interconversion of other topological isomers of dsDNA rings, including catenanes and knotted rings. Type II topoisomerases break and join 2 DNA strands simultaneously in an ATP-dependent manner. |
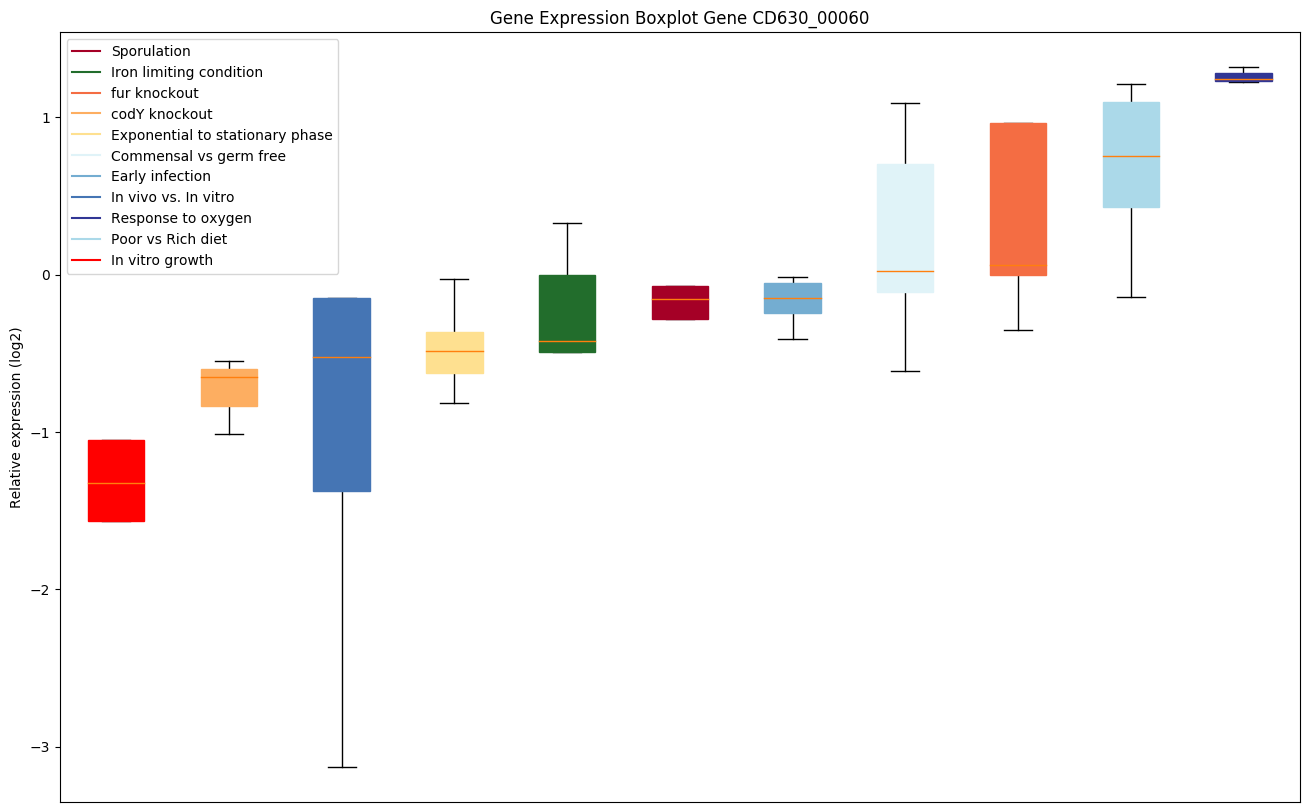 |
|||
| CD630_04030 | fba | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase | Yes |
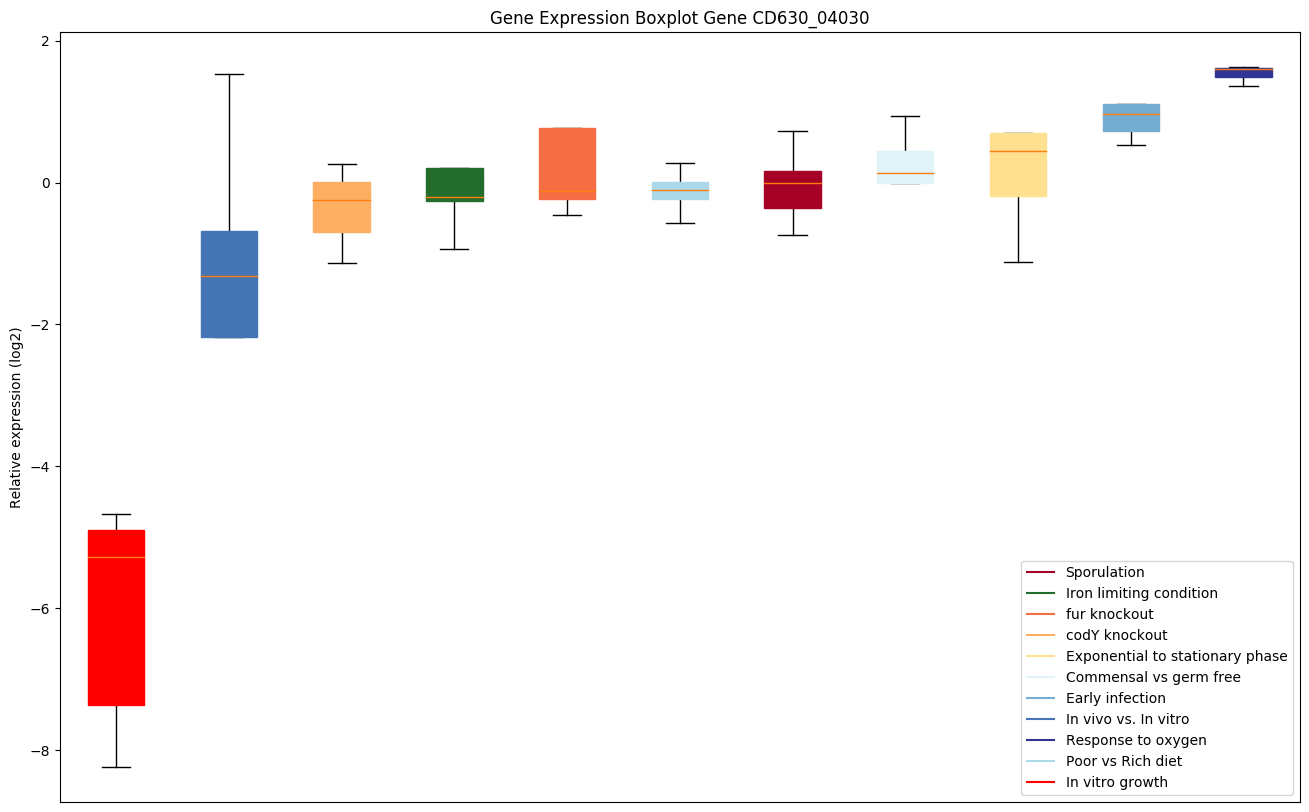 |
|||
| CD630_24900 | Putative peptidase, M20A family |
 |
|||||
| CD630_17451 | feoA | Ferrous iron transport protein |
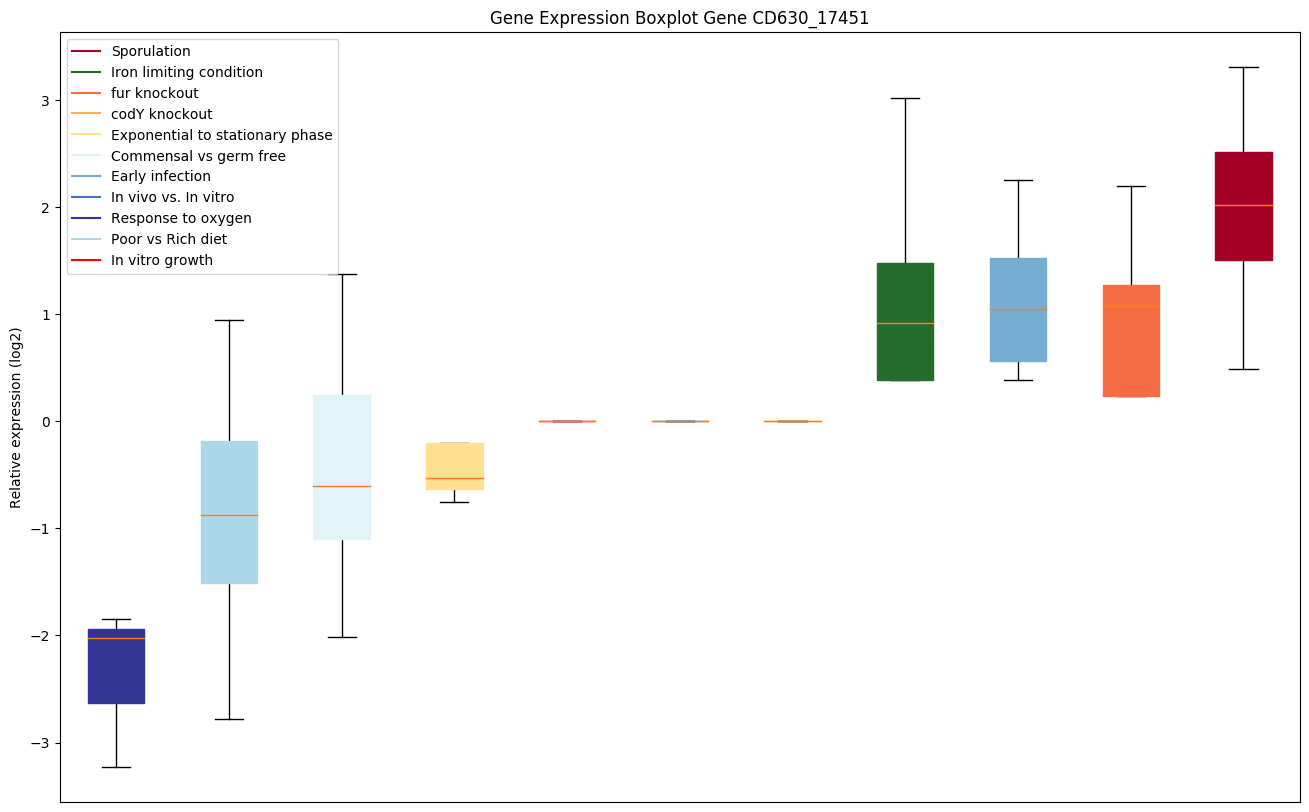 |
||||
| CD630_01070 | aspC | Aspartate aminotransferase |
 |
||||
| CD630_24411 | PhoH-like protein |
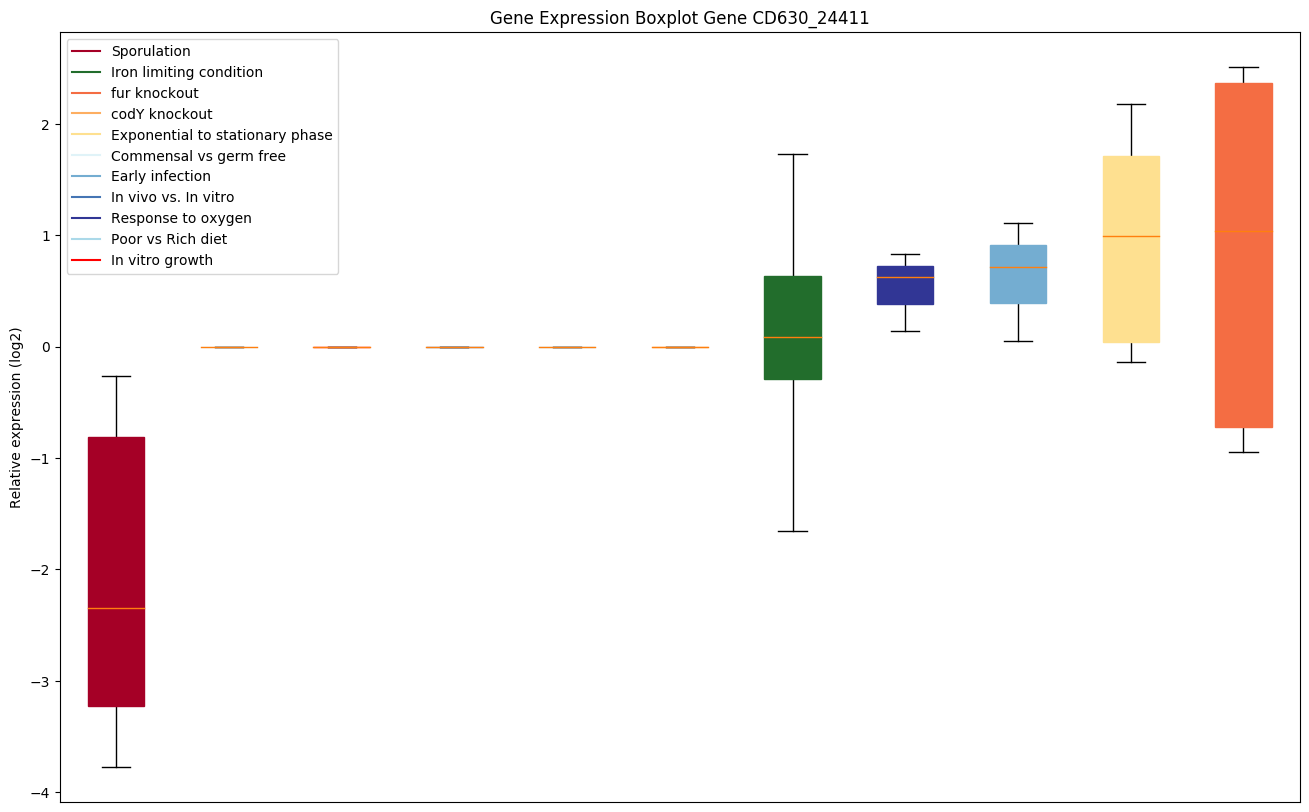 |
|||||
| CD630_28290 | Putative membrane protein |
 |
|||||
| CD630_24810 | ung | Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) | Excises uracil residues from the DNA which can arise as a result of misincorporation of dUMP residues by DNA polymerase or due to deamination of cytosine. |
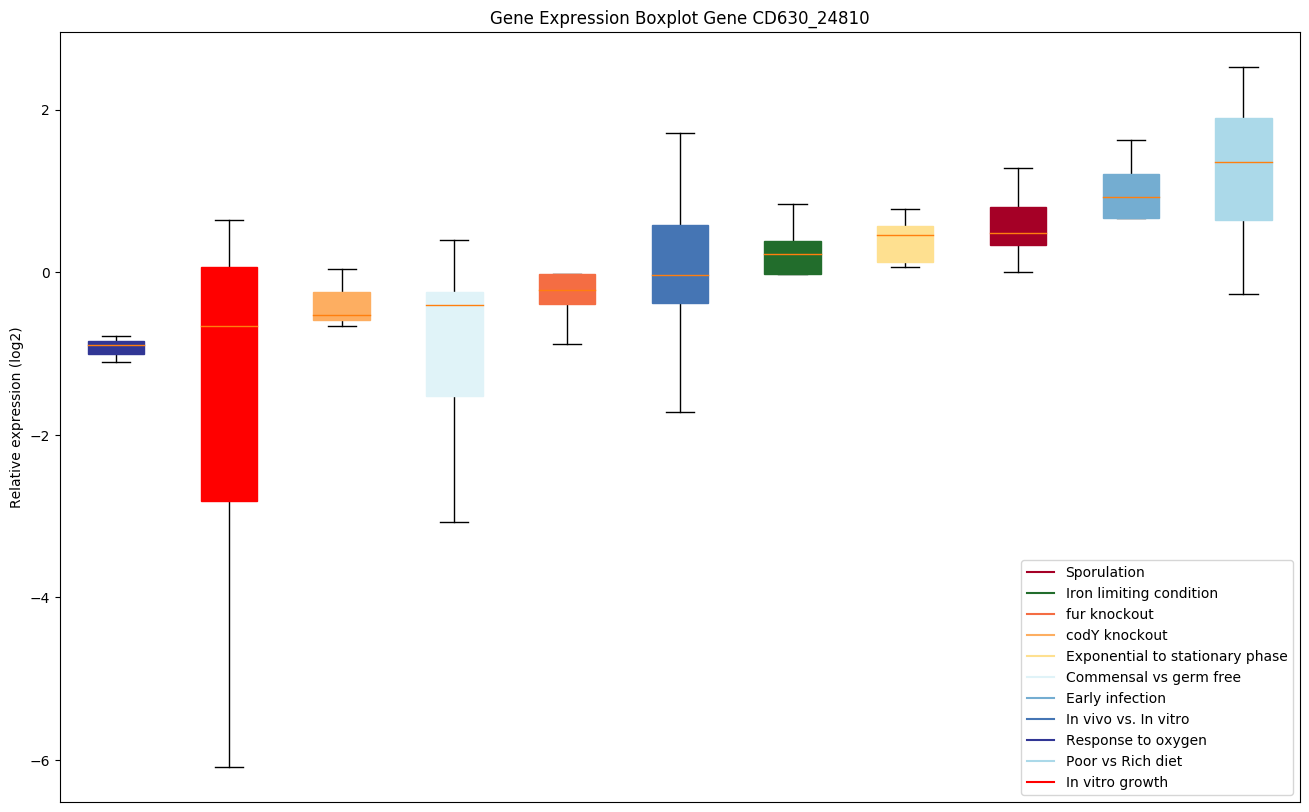 |
|||
| CD630_20590 | glnS | Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase | Yes |
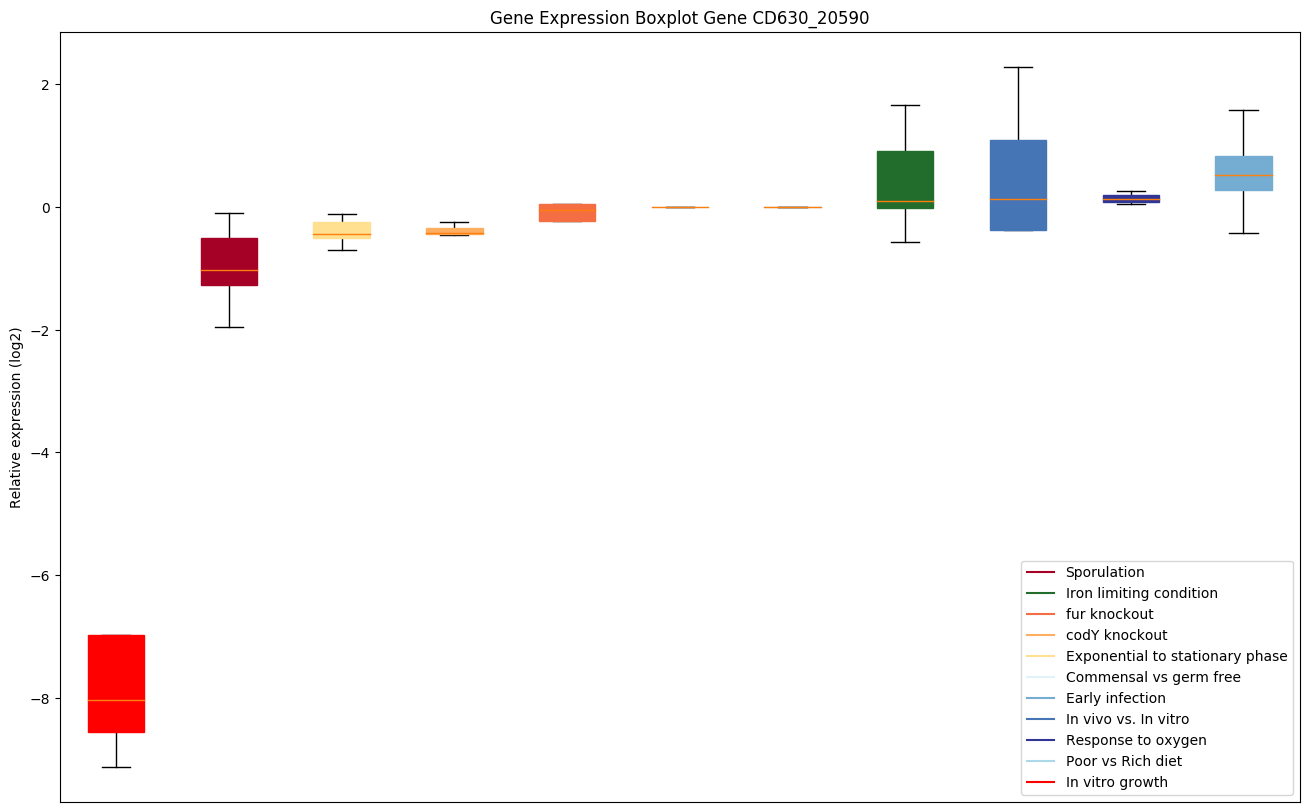 |
|||
| CD630_13390 | aspB | Aspartate aminotransferase (AspAT) (TransaminaseA) |
 |
||||
| CD630_16910 | trxB | Putative thioredoxin-disulfide reductase |
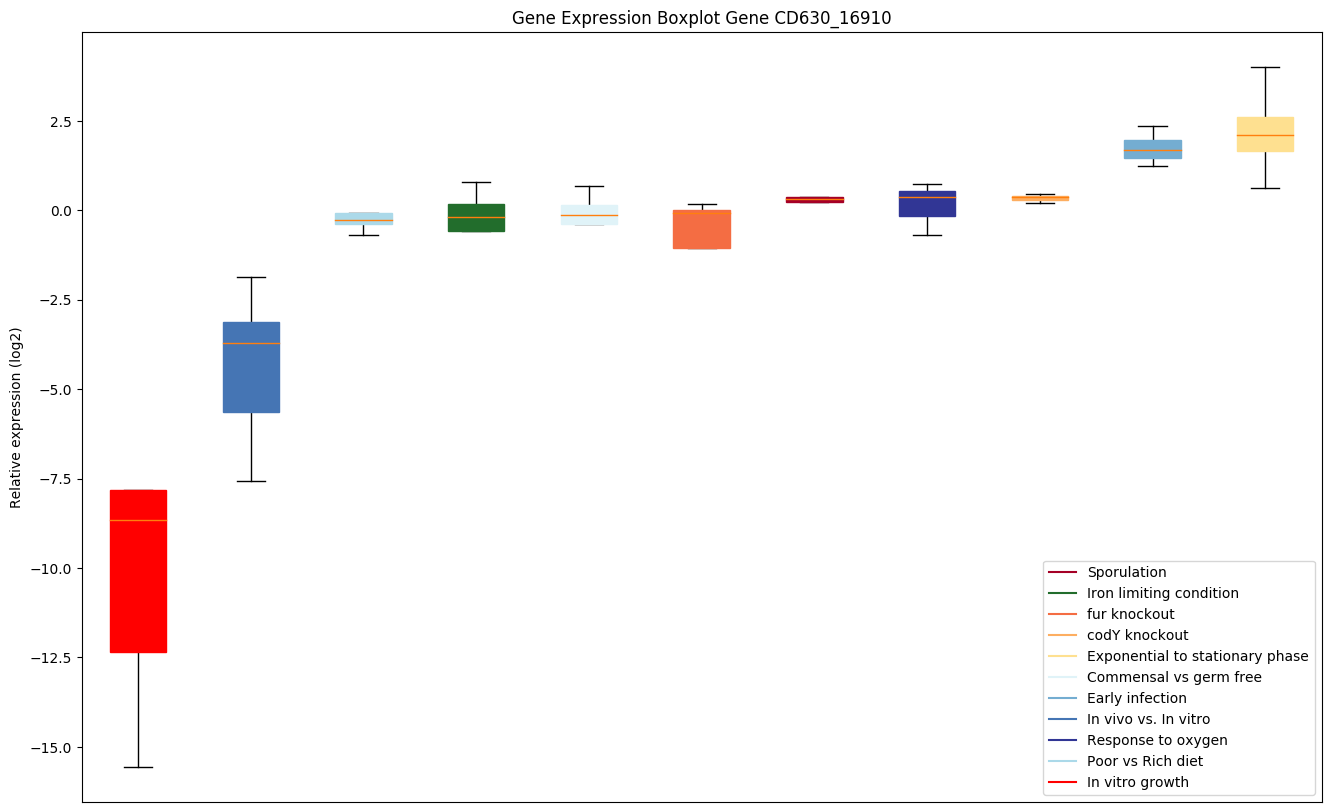 |